Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Loading Handout
Loading Handout
Uploaded by
M Refaat FathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Loading Handout
Loading Handout
Uploaded by
M Refaat FathCopyright:
Available Formats
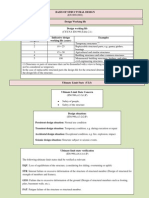
Combination Factors
Loading
Introduction to EN 1990
Covers the Basis of Structural Design
Use with the other Eurocodes
Gives safety factors needed for ULS and
SLS verifications
partial factors (see Table 1)
combination factors (See Table 2)
ULS Checks
Action
0 1
Imposed loads in buildings,
Category A : domestic/residential
areas
0.7 0.5
Category B : office areas
0.7 0.5
Category C : congregation areas 0.7 0.7
Category D : shopping areas
0.7 0.7
Category E : storage areas
1.0 0.9
Category F : traffic area, < 30kN 0.7 0.7
Category G : traffic area, 30 160 0.7 0.5
kN
0.7 0
Category H : roofs
Snow (sites up to 1000m)
0.5 0.2
Wind
0.5 0.2
Table 2: Extract from Table NA.A1.1
EQU: static equilibrium
Combinations of Actions
STR: strength/buckling etc
Can use either:
GEO: Failure of excessive deformation of
ground
Equation 6.10
Less favourable of 6.10a and 6.10b
Method: Get the factors from Tables 1 and 2
FAT: fatigue failure
and substitute them into the equation you are
using, check for a range of different loading
combinations and take the least favourable
Actions
result.
Permanent actions , G (Dead loads)
Equation 6.10
Variable actions , Q (Live loads)
G,jGk,j + PP + Q,1Qk,1 + Q,i0,iQk,i
Qk
0Qk Combination value
1Qk Frequent value
2Qk Quasi-permanent value
Characteristic value ( = 1.0)
Equation 6.10a
Partial Factors
G,jGk,j + PP + Q,10,iQk,1 + Q,i0,iQk,i
Unfavourable
Favourable
1.35
1.0
Q
1.5
0
Table 1: Partial Factor values from the UK NA
Equation 6.10b
jG,jGk,j + PP + Q,1Qk,1 + Q,i0,iQk,i
j is 0.925 (From NA 2.2.3.2)
2
0.3
0.3
0.6
0.6
0.8
0.6
0.3
0
0
0
You might also like
- Eurocode Example Load CombinationsDocument15 pagesEurocode Example Load CombinationsRobert Ellul100% (3)
- Lecture 1 Basics - Oct 12 - EndDocument97 pagesLecture 1 Basics - Oct 12 - EndrjtcostaNo ratings yet
- 2.3.4 Design Values of Actions: BS EN 1990: A1.2.2 & NaDocument3 pages2.3.4 Design Values of Actions: BS EN 1990: A1.2.2 & NaSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- SISO-MIMO Design ExamplesDocument14 pagesSISO-MIMO Design ExamplesLuisGerardoPrietoNo ratings yet
- Eurocodes - Background and Applications: Eurocode Example: Actions On A Six Storey BuildingDocument15 pagesEurocodes - Background and Applications: Eurocode Example: Actions On A Six Storey Buildingkumaresvaran.mNo ratings yet
- WIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataDocument3 pagesWIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataJester AbucayNo ratings yet
- 3 3.. C Co Om MB Biin Na Attiio On Ns S o Off A Ac Cttiio On Ns SDocument1 page3 3.. C Co Om MB Biin Na Attiio On Ns S o Off A Ac Cttiio On Ns Snuwan01No ratings yet
- EC0 CalcsDocument3 pagesEC0 CalcsAko BogdaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Calculation of CabanaDocument36 pagesStructural Design Calculation of CabanasaravqwertyNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Base ASCE 7-05 For Operation WarehouseDocument18 pagesWind Load Base ASCE 7-05 For Operation WarehouseEl riza annaml0% (1)
- Pci Mtech 2019Document6 pagesPci Mtech 2019Saif AliNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Deck Example To EurocodesDocument5 pagesReinforced Concrete Deck Example To EurocodesjonNo ratings yet
- General Wind ASCE702WDocument2 pagesGeneral Wind ASCE702WJohann Alexander Caballero BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Basis of Structural Design (En1990 2002) Loadings Snow WindDocument15 pagesBasis of Structural Design (En1990 2002) Loadings Snow Windkiss_59856786100% (1)
- Annex CHDocument22 pagesAnnex CHMario1234No ratings yet
- Delft: Matlab and Simulink For Modeling and ControlDocument12 pagesDelft: Matlab and Simulink For Modeling and Controlawan_krNo ratings yet
- En 1990 Basis of Structural Design - Annex B Reliability Differentiation Annex C Reliability TheoryDocument31 pagesEn 1990 Basis of Structural Design - Annex B Reliability Differentiation Annex C Reliability TheoryHarikrishnan P0% (1)
- How To Test For Cointegration Using The Johansen ProcedureDocument12 pagesHow To Test For Cointegration Using The Johansen ProcedureDaniel WyczolkowskiNo ratings yet
- Ecu Adi FerencDocument17 pagesEcu Adi FerencROYNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document12 pagesCH 6aprilswapnilNo ratings yet
- Etabs ModelingDocument39 pagesEtabs ModelingHemal Mistry100% (10)
- WIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Main Wind-Force Resisting SystemDocument1 pageWIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Main Wind-Force Resisting SystemMario FeghaliNo ratings yet
- EN 1990 " Eurocode: Basis of Structural DesignDocument49 pagesEN 1990 " Eurocode: Basis of Structural DesigndoschhNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Introduction To EC2Document48 pagesLecture-Introduction To EC2denyfate100% (1)
- Processcontrol Topic13 PidtuningDocument15 pagesProcesscontrol Topic13 Pidtuningmuthukumartharani100% (1)
- DescriptionDocument2 pagesDescriptionHasan ÇalışkanNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Wind Loads On Structures According To ASCE 7 - 2005 Wind Load Calculation ProceduresDocument8 pagesCalculation of Wind Loads On Structures According To ASCE 7 - 2005 Wind Load Calculation ProcedureslsatchithananthanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument3 pagesThesisFahad ZakariyaNo ratings yet
- Elec Eng 4Cl4:: Control System DesignDocument20 pagesElec Eng 4Cl4:: Control System DesignMorteza SepehranNo ratings yet
- "Asce710W" - Asce 7-10 Code Wind Analysis ProgramDocument57 pages"Asce710W" - Asce 7-10 Code Wind Analysis ProgramSamrith YoangNo ratings yet
- Asce710w - Code Wind Analysis ProgramDocument57 pagesAsce710w - Code Wind Analysis ProgramAhmadiBinAhmadNo ratings yet
- ASCE710W v2.4Document23 pagesASCE710W v2.4Jaafar DahlanNo ratings yet
- Calculation CCR (RC)Document123 pagesCalculation CCR (RC)bonnicoNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 - Combination of Loads, Partial Safety FactorsDocument5 pagesAppendix 2 - Combination of Loads, Partial Safety FactorsMois DanielNo ratings yet
- Transactions of The VŠB - Technical University of OstravaDocument6 pagesTransactions of The VŠB - Technical University of OstravaAli Al-BashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7, Problem 3: S Mpa KDocument14 pagesChapter 7, Problem 3: S Mpa KFatih AŞCINo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control PREV PAPERDocument9 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control PREV PAPERNisha TNNo ratings yet
- RC BEAM, Eurocode 2 With French National AnnexDocument8 pagesRC BEAM, Eurocode 2 With French National AnnexjonrasNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson MethodDocument33 pagesNewton Raphson MethodAnnan_Faridi_517No ratings yet
- Facoltà Di Ingegneria: Università Degli Studi Di PadovaDocument16 pagesFacoltà Di Ingegneria: Università Degli Studi Di PadovaConstanzo MarulloNo ratings yet
- EXAM 2 Fall 2009 PDFDocument4 pagesEXAM 2 Fall 2009 PDFIsmael KhalilNo ratings yet
- Exam Pas IwebDocument26 pagesExam Pas IwebcoolvatNo ratings yet
- Wind Load ASCE-05Document1 pageWind Load ASCE-05Aya MontesNo ratings yet
- PR 2303Document4 pagesPR 2303Karthik Srinivas0% (1)
- Workshop 4b Nonlin BucklingDocument30 pagesWorkshop 4b Nonlin BucklingRon RaeNo ratings yet
- Tower SizingDocument6 pagesTower SizingNagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Organic Matrix Composites: Effect of Thermo-oxidative AgeingFrom EverandMechanical Behavior of Organic Matrix Composites: Effect of Thermo-oxidative AgeingNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- High Productivity With ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES. Steelmaking PlantsDocument16 pagesHigh Productivity With ELECTRIC ARC FURNACES. Steelmaking PlantsflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Hydro-Viscous Soft Start of Belt Conveyor: MENG Qing-Rui, HOU You-FuDocument7 pagesMechanism of Hydro-Viscous Soft Start of Belt Conveyor: MENG Qing-Rui, HOU You-FuflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Rope-Towed Trolley or Machinery TrolleyDocument11 pagesRope-Towed Trolley or Machinery Trolleyflasnicug100% (1)
- ABB - ACS800 Learning Guide - Drive Dimensioning For CranesDocument65 pagesABB - ACS800 Learning Guide - Drive Dimensioning For CranesflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Candidate ManualDocument63 pagesCandidate ManualflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Machinery Trolley CranesDocument11 pagesMachinery Trolley CranesflasnicugNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic Wheel-Rail Contact Stresses For Wagon On Various TracksDocument7 pagesThe Dynamic Wheel-Rail Contact Stresses For Wagon On Various TracksflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Inspection Examination of Tower CranesDocument111 pagesMaintenance Inspection Examination of Tower CranesflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Failures in Industry - Case Studies: Ž. Domazet and T. PiršicDocument6 pagesFatigue Failures in Industry - Case Studies: Ž. Domazet and T. PiršicflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Jib Cranes DemagDocument30 pagesJib Cranes Demagflasnicug100% (1)
- DEMI 2011 ProceedingsDocument1,046 pagesDEMI 2011 ProceedingsflasnicugNo ratings yet
- T05570 01 CangDocument10 pagesT05570 01 CangflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Remaining Life Prognostication For The Metal Construction of Bridge CranesDocument8 pagesRemaining Life Prognostication For The Metal Construction of Bridge CranesflasnicugNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Inspection Examination of Tower CranesDocument111 pagesMaintenance Inspection Examination of Tower CranesflasnicugNo ratings yet