Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test PDF 1
Test PDF 1
Uploaded by
dhruvthedon2Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test PDF 1
Test PDF 1
Uploaded by
dhruvthedon2Copyright:
Available Formats
1
01
CELL BIOLOGY
CELL THEORY
st
1 Dead cell Robert Hook.
st
1 Live cell Leeuwenhoek.
Schleiden- German Botanist- All Plant are composed of different kinds of cells which form
tissues.
Schwann- British Zoologist- All animal cells have outer layer- plasma membrane. Presence of cell wall is a unique character of plant cells.
Together they formed cell theory- didnt explain new cell formation.
Rudolf Virchow- Cell Lineage theory- Omnis cellula e cellula. New cells formed from
preexisting cells.
Main arena for celluar activities- Cytoplasm.
Shape of cells varies with the function they perform. Human RBC- 7.0 um Diameter.
PROKARYOTIC CELL
Please refer plant diversity
EUKARYOTIC CELL
Extensive compertmantalisation of cytoplasm
Organise nucleas and nuclear membrane
1. CELL WALL (ONLY IN PLANTS)
Non living rigid structure discovered by Robert Hook
Plants- cellulose, Hemicellulose, pectins and proteins
Algae- cellulose, galactans , mannans and CaCO3
Primary- Capable of growth, Diminishes
Secondary- rigid, Absent in meristem
Tertiary- only in tracheids of gymnosperm
Middle lamella- Ca & Mg pectate (Ca More)
Mauka Mile (Mau = More , Ka = Ca ,Mile = Middle Lamella)
Plasmodesmata- connects two cells cytoplasm
2. CELL MEMBRANE
Thin, delicate, Elastic, selectively permeable, living boundary. Studied in Human RBC
Fluid mosaic model- singer and Nicolson.
Proteins (Hydrophillic) arranged in phospholipid bilayer (Hydrophobic tail & Hydrophillic
head)
For stability:- Eukaryotes Cholesterol
Prokaryotes - Hopanoides
RBC- 52% Protein 40% lipid and rest carbohydrate
Proteins- lateral movement
Lipids- Flip Flop Movement
Glycolipid and glycoprotein present on outer surface (not symmetrical)
He who sweats more in peace, bleeds less in war
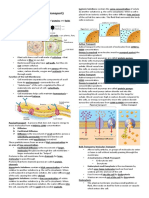
ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body, lysosome and vacuole.
1. Endoplasmic Reticulum :- Tiny tubular str ucture.
Cisternae, Vesicles, and tubules
Divides cytoplasm into luminal and extra luminal compartment
RER
SER
1. 80s Ribosomes
1. 70s Ribosomes
2. Protein Synthesis and
2. Synthesis of lipid and
Secretion
glycogen
2. Golgi Body:- Obser ved as densly stained reticular appar atus
Pleomorphic structure made of parallel flat disc shaped cisternae ( Remember not cristae. Cristae in mitochondria )
Near the nucleas- convex/ cis/ forming face
Far from nucleas- concave/ trans/ maturing face
Packaging materials and modifying them Eg. Formation of glycoprotein and glycolipid.
Formation of lysosome and acrosome of sperm
Varied number (Remember not fixed ) of cisternae are present in golgi complex
Cis and trans face are entirely different but inter connected
Golgi body remains in close association with E.R.
3. Lysosomes :- Membr ane Bound Vesicular Str ucture
Filled with Hydrolytic enzymes which function in acidic medium
Polymorphic in structure
Cholesterol, cortisone etc. are membrane stabilizers while progesterone, estrogen are labilizers.
4. Vacoules: Absent in animal cells and meristematic plant cells. Product not use full for plant are stored in
it
In plants vacuole occupy 90% of volume of the cell
Contratile vacuole- amoeba- excretion
Food vacuole- protists
Tonoplast- transport of ions against concentration gradient
MITOCHONDRIA
Not visible until specifically stained by Janus Green B.
Shape Sausage/ Cylinderical, Double mebraned.
Inner membrane divides space into two :- 1. Matrix 2. Inner membrane space
Cell within Cell or Power house of the cell.
Inner Membrane studded with F1-F0 particles which form ATP.
Matrix has 70s ribosomes, circular DNA,RNA & enzymes for krebs cycle
Divide by fission
Number varies depending on physiological activity
Two membrane have their own specific enzymes.
PLASTIDS
All plant cells and euglenoids. They are large and easily seen under microscope.
Chromoplasts :- Fat soluble pigments Carotenoids and Xanthophyll
Chloroplast :- Chlorophyll and carotenoids Trap light.
Leucoploast :- Non Green plant cells. Varied shape and size.
Amyloplast store Amylase (Carbohydrate)
Aleuroplast store protein and Elaioplast store Fat. Ellu- Fat boy Stores fat
Chloroplast are lens shaped, oval, spherical, discoid or ribbon like.
They are double membraned. Inner membrane less permeable-Encloses stroma.
RIBOSOME
Observed by George Palade. Called Engine of the cell.
Granular structure found in all cells except mammalian RBC
Composed of RNA and protein
1.80s
2. 70s
S:- Sedimentation rate 40% rRNA,60% Protein
60% rRNA,40% Protein
Mg is essential for binding of subunits.
CYTOSKELETON
Network of filamentous proteinaceous structure.
Microtubule- Tubulin protein
Microfilament Actin protein.
1.Cillia and Flagella- Covered with Plasma Membrane. Core Axoneme
Arrangement 9 Doublets + 2 Singlets
CILLIA
FLAGELLA
1.Small
1. Longer
2.Movement of either cell
2. Only cell movement
or surrounding fluid
Prokaryotic bacteria also posses flagella but they are structurally different from eukaryotic
flagella.
2.Centrosome and Centriole- Car twheel str ucture
Centrosome means Two centrioles placed perpendicular with amorphous pericentriolar material around
Nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin. Central part Proteinaceous hub
Form Basal Body of cilia and flagella.
MICRO BODIES
Single Membrane bound vesicles present in both plant and animal cells.
Sphaerosome :- Plant cells. Lipid storae and synthesis
Peroxisomes :- Photorespiration and breakdown of H2O2
Glyoxisomes :- Only in plants Convert fat to starch
NUCLEAS
Discovered By Robert Brown
Absent in mature phloem sieve tube element and mature RBC
Material of nucleas stained by Basic dyes Chromatin by Flemming
1.Nuclear Membrane :- Two unit membr ane space between them is peri nuclear space.
Outer membrane Bears Ribosomes
Nuclear pore present Way of transport
2. Nucleoplasm:- Contains nucleolus and chromatin.
3. Nucleolus :- Not membr ane bound rRNA synthesis
Larger and more numerous nucleoli are present in cells carrying protein synthesis. Human
cells :- 5 Nucleoli
4. Chromatin :- DNA + RNA + Histone + Non Histone.
Human 2m long 46 Chromosomes
EUCHROMATIN
HETEROCHROMATIN
Thin light stained
Thick dark stained
Less Histone
More Histone
5. Chromosome :-
On the basis of centromere:1 Meta centric
2 Sub metacentric
3 Acrocentric
4 Telocentric
Sometimes few chromosome have non staining secondary constriction. This gives the appearance of satellite.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Module General Biology 1 Week 1 FinalDocument40 pagesModule General Biology 1 Week 1 FinalI Love You 3000100% (9)
- UDDD1104 Cell Biology Lab Manual 2013Document44 pagesUDDD1104 Cell Biology Lab Manual 2013Winserng 永森No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Title: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Title: Cell Structure and FunctionRea A. Bilan100% (7)
- Exercise - I: V E M LDocument38 pagesExercise - I: V E M LDivyansh MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Spaced Learning Session 1 Life ProcessesDocument37 pagesSpaced Learning Session 1 Life Processesapi-210088695No ratings yet
- Cell Note - BDB FiitjeeDocument5 pagesCell Note - BDB FiitjeeSankar MandalNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell: - Powerpoint Presentation of Group 1Document20 pagesPlant and Animal Cell: - Powerpoint Presentation of Group 1Hanz Nujapa BalistoyNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- Cells Exploration ActivitiesDocument16 pagesCells Exploration ActivitiesMorticia VizactyhNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of Plant Cell 1Document18 pagesUltra Structure of Plant Cell 1Kumaran JothiramNo ratings yet
- Biology IXDocument89 pagesBiology IXKanchan SawantNo ratings yet
- Science Notes: Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesScience Notes: Plant and Animal CellRosalinda LappayNo ratings yet
- Cells Test Study GuideDocument3 pagesCells Test Study GuideKatie StephensNo ratings yet
- 0970 s18 QP 11 CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument16 pages0970 s18 QP 11 CIE IGCSE BiologySri GanesNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cells PowerpointDocument24 pages02 - Cells PowerpointMisbah FatimaNo ratings yet
- Review On The Significance of Chlorine For Crop Yield and QualityDocument41 pagesReview On The Significance of Chlorine For Crop Yield and QualityAbel VargasNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Document6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Jyoti AmbwaniNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Edexcel (9-1) Student Book Answers PDF Cell (Biology) FertilisationDocument1 pageBIOLOGY Edexcel (9-1) Student Book Answers PDF Cell (Biology) Fertilisationjasmine.elabedNo ratings yet
- Biology Igcse Chapter 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesBiology Igcse Chapter 2 Summarytaliaamjad771No ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNo ratings yet
- Ubd Unit - Grade 7: Brief Summary of Unit (Including Curricular Context and Unit Goals)Document12 pagesUbd Unit - Grade 7: Brief Summary of Unit (Including Curricular Context and Unit Goals)Erwin Y. CabaronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDFAngelene PelayoNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes Unit 5 ActiveDocument2 pagesCornell Notes Unit 5 Activeapi-3300708430% (1)
- STM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesSTM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerAllessandra AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartCyril Mae MagallanesNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE BIOLOGY ZASE WordDocument382 pagesSIMPLE BIOLOGY ZASE WordConnary Kunda50% (2)
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Angel MerilloNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismsErica GarciaNo ratings yet
- BSB 113 Biology of Cells-notes-August 2018Document47 pagesBSB 113 Biology of Cells-notes-August 2018Thabo ChuchuNo ratings yet
- National 5 Biology TextbookDocument217 pagesNational 5 Biology Textbooks9dijdjiNo ratings yet