Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejercicios Ciclo Rankine
Uploaded by
carlos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThis document describes two examples of a Rankine cycle power system.
The first example is an ideal Rankine cycle with saturated steam as the working fluid. It enters the turbine at 8.0 MPa and exits the condenser at 0.008 MPa, with a net power output of 100 MW.
The second example modifies the first by including isentropic efficiencies of 85% for the turbine and pump. It determines the same parameters as the first example and discusses the effects of irreversibilities within the turbine and pump on the vapor cycle.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes two examples of a Rankine cycle power system.
The first example is an ideal Rankine cycle with saturated steam as the working fluid. It enters the turbine at 8.0 MPa and exits the condenser at 0.008 MPa, with a net power output of 100 MW.
The second example modifies the first by including isentropic efficiencies of 85% for the turbine and pump. It determines the same parameters as the first example and discusses the effects of irreversibilities within the turbine and pump on the vapor cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageEjercicios Ciclo Rankine
Uploaded by
carlosThis document describes two examples of a Rankine cycle power system.
The first example is an ideal Rankine cycle with saturated steam as the working fluid. It enters the turbine at 8.0 MPa and exits the condenser at 0.008 MPa, with a net power output of 100 MW.
The second example modifies the first by including isentropic efficiencies of 85% for the turbine and pump. It determines the same parameters as the first example and discusses the effects of irreversibilities within the turbine and pump on the vapor cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Termotecnia
Prof. Dr. Hctor Valds M.
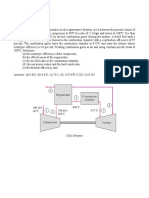
Analysing Vapour Power SystemsRankine Cycle
E X A M P L E 8 . 1 Ideal Rankine Cycle
1. Ideal Rankine Cycle
Steam is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapour enters the
turbine at 8.0 MPa and saturated liquid exits the condenser at a pressure of 0.008 MPa.
The net power output of the cycle is 100 MW. Determine for the cycle:
(a) the thermal efficiency,
(b) the back work ratio,
(c) the mass flow rate of the steam, in kg/h,
(d) the rate of heat transfer, Qin, into the working fluid as it passes through the boiler, in
MW,
(e) the rate of heat transfer, Qout, from the condensing steam as it passes through the
condenser, in MW,
(f) the mass flow rate of the condenser cooling water, in kg/h, if cooling water enters the
condenser at 15C and exits at 35 C.
2. Rankine Cycle with Irreversibilities
Reconsider the vapour power cycle of Exercise 1, but include in the analysis that the
turbine and the pump each have an isentropic efficiency of 85%. Determine for the
modified cycle
(a) the thermal efficiency,
(b) the mass flow rate of steam, in kg/h, for a net power output of 100 MW,
(c) the rate of heat transfer, Qin, into the working fluid as it passes through the boiler, in
MW,
(d) the rate of heat transfer, Qout, from the condensing steam as it passes through the
condenser, in MW,
(e) the mass flow rate of the condenser cooling water, in kg/h, if cooling water enters
the condenser at 15C and exits as 35C. Discuss the effects on the vapour cycle of
irreversibilities within the turbine and pump.
You might also like
- Problems Set 1Document2 pagesProblems Set 1suby0% (1)
- ME267 Assignment01Document1 pageME267 Assignment01InsaneNo ratings yet
- Water Is The Working Fluid in An Ideal Rankine CycleDocument1 pageWater Is The Working Fluid in An Ideal Rankine CycleMochammad Gama AdriansyahNo ratings yet
- ET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedDocument3 pagesET II Assignment 2 - ModifiedbaliamajhiNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument80 pagesProblemario MFCBassaldua AlfreedNo ratings yet
- Problemario MFCDocument31 pagesProblemario MFCPonce MrlnNo ratings yet
- Tugas Turbin Uap: of Problem 2 Above Is Modified To Include ReheatDocument2 pagesTugas Turbin Uap: of Problem 2 Above Is Modified To Include ReheatRudy ArthaNo ratings yet
- Net Power Output of The Cycle Is 110 MW. DetermineDocument3 pagesNet Power Output of The Cycle Is 110 MW. DetermineDhias VidathyaNo ratings yet
- Taller EficienciasDocument2 pagesTaller EficienciasJohan Maldonado100% (1)
- Tutorium steamPowerPlantDocument4 pagesTutorium steamPowerPlantQue LanNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 2Document1 pageLearning Task 2zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFDocument1 page1.2 Actual Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFsuby100% (1)
- Aços Carbono Construção CivilDocument5 pagesAços Carbono Construção CivilIrvin WilliamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument3 pagesTutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesShariff Mohamad Fairuz0% (1)
- Rankine CycleDocument3 pagesRankine Cyclefor gameunliNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument27 pagesVapor Power Cycleshrithik khannaNo ratings yet
- PPE AssignmentDocument3 pagesPPE AssignmentAshish Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Steamturbine Problem1Document10 pagesSteamturbine Problem1dasun dananjayaNo ratings yet
- Assign#4 Vapor CycleDocument3 pagesAssign#4 Vapor Cyclemihreteab ghebregzabherNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9Document20 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9ZelNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document3 pagesModule 1സാരംഗ്എസ്കുമാർNo ratings yet
- Chap7 1Document10 pagesChap7 1Cm EtcmNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Important QuestionsMaha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2 - Quiz 1Document1 pageThermo 2 - Quiz 1Danielson CulanibanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Document11 pagesTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803No ratings yet
- Problems Carnot and RankineDocument12 pagesProblems Carnot and RankineHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Regenerative Rankine Cycle: Answers: (A) 1016.5 KJ/KG (B) 37.8 %Document1 pageModule 3 - Regenerative Rankine Cycle: Answers: (A) 1016.5 KJ/KG (B) 37.8 %subyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Regenerative Rankine Cycle PDFDocument1 page3.1 Regenerative Rankine Cycle PDFsubyNo ratings yet
- ME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFDocument5 pagesME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFVikasKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Thermo I Set of Questions 2022Document6 pagesThermo I Set of Questions 2022Paa Kwesi ArhinfulNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions: (A) The Exit Velocity, in M/sDocument2 pagesTwo Mark Questions: (A) The Exit Velocity, in M/sRajvir Preet GillNo ratings yet
- Problem-Set 2Document20 pagesProblem-Set 2ERROLL ZANDRE NACAYA ANOBARNo ratings yet
- 01-Sheet 01Document9 pages01-Sheet 01samir mohamedNo ratings yet
- End Prob. CengelDocument5 pagesEnd Prob. CengelErvz MissionNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Reheat Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFDocument1 page2.1 Reheat Rankine Cycle Problems Set PDFsubyNo ratings yet
- Questions Topic-Vapour Power Cycle Subject-Applied ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesQuestions Topic-Vapour Power Cycle Subject-Applied ThermodynamicsXerox WorldNo ratings yet
- Thermo of MechDocument2 pagesThermo of MecheyobNo ratings yet
- 20130511233558467Document3 pages20130511233558467ahmadskhanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engg Assignment-1Document2 pagesPower Plant Engg Assignment-1keyredin selmanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 - Quiz #2 (Set A) : 1 1-k 1 K 2 1-k 2 KDocument2 pagesThermodynamics 2 - Quiz #2 (Set A) : 1 1-k 1 K 2 1-k 2 KCabagnot Piolo JuliusNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11Document2 pagesVapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11MaykaMidreliDeandraLigutomNo ratings yet
- Tarea de CiclosDocument6 pagesTarea de CiclosSebastiánGarcía100% (1)
- ME 201 AssignmentDocument3 pagesME 201 Assignmentmz_haqNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument36 pagesVapor Power CyclesKusmakarNo ratings yet
- MPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesDocument3 pagesMPD 2012 - Sheet 3 - Binary and Combined CyclesPeter Raouf100% (1)
- Assignment 1 - 151906 - Conventional Power EngineeringDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - 151906 - Conventional Power EngineeringSai BalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicR SuyaoNo ratings yet
- Assingment 2Document2 pagesAssingment 2habtish100% (1)
- Assig1-Due On Feb 1,2018Document3 pagesAssig1-Due On Feb 1,2018Graeme KendallNo ratings yet
- 11Document12 pages11Mario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Ch04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESDocument9 pagesCh04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESTSEGAAB NIGUSSENo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasNo ratings yet
- Exercise of Thermodynamics - Sept292016Document4 pagesExercise of Thermodynamics - Sept292016bro0% (1)
- Test #2Document3 pagesTest #2Dar QuetzalNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TermodinamikaDocument24 pagesContoh Soal TermodinamikaDea FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleDocument24 pagesAssignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleMatthias100% (1)
- Lectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PDocument2 pagesLectut MIN 106 PDF MI 106 Tutorial VIII - BcPSc3PPritam PaulNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 MS2230 Sem II 18-19 PDFDocument1 pageTugas 2 MS2230 Sem II 18-19 PDFHanif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1Anagha ChimankarNo ratings yet
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy: Physics, Engineering, Environmental Impacts, Economics and PlanningFrom EverandRenewable Energy: Physics, Engineering, Environmental Impacts, Economics and PlanningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsFrom EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- Building Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingFrom EverandBuilding Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EFrom EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ERating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- Oil: An Overview of the Petroleum IndustryFrom EverandOil: An Overview of the Petroleum IndustryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Renewable Energy Finance: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandRenewable Energy Finance: Theory and PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureFrom EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (48)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Oil companies and the energy transitionFrom EverandOil companies and the energy transitionNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringFrom EverandThe Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)