Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bony Thorax and Chest Wall Anatomy
Uploaded by
andiedeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bony Thorax and Chest Wall Anatomy
Uploaded by
andiedeeCopyright:
Available Formats
8/5/2012
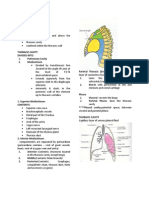
BONY THORAX
Contains organs of
respiration, circulation &
digestion
Anterior wall (Short):
Sternum
1st 10 pairs of ribs
Costal cartilages
Lateral wall
ribs
Posterior wall
12 thoracic vertebrae and
the ribs
8/5/2012
BONY THORAX
Superior Aperture (inlet):
Boundaries:
Body of 1st thoracic
vertebra
1st ribs
1st cartilages
Upper border of the
manubrium
Sibsons fascia:
Diaphragm of the inlet
From transverse process
of 7th cervical vert. to the
1st rib
Protects cervical dome of
the pleura
Covered by the scalene
muscles
Inferior Aperture
(outlet):
Boundaries:
12th thoracic vert.
Lowest ribs (7th 12th)
Xiphisternal joint
Respiratory diaphragm
8/5/2012
BONY THORAX
Ribs (Costae):
1.
True ribs
(vertebrosternal ribs)
1st 7 pairs of ribs
2.
False ribs
a.
Vertebrochondral
8th 10th ribs
b.
Vertebral ribs
11th 12th ribs
The 7th & 8th ribs are
the longest
BONY THORAX
Ribs (Costae):
1.
Typical ribs:
3rd to 9th ribs
has head, neck, tubercle
and shaft
Head has 2 facets
connects to two adjacent
vert.
Tubercle connects to the
transverse process
Has rounded shaft
superiorly and sharp edge
inferiorly has costal
groove
8/5/2012
BONY THORAX
Ribs (Costae):
2.
Atypical ribs:
1st, 2nd, 10th, 11th & 12th
ribs
a. 1st rib: (superlative)
Highest, broadest,
strongest, flattest,
shortest & most
curved)
angle coincides w/ its
tubercle
articulates w/ one
vertebra
Has LISFRANC
tubercle attachment of
scalenus anterior
BONY THORAX
Ribs (Costae):
2.
Atypical ribs:
b. 2nd rib:
tubercle is lateral
to its angel
Has attachment to
post. scalene
8/5/2012
BONY THORAX
Ribs (Costae):
2.
Atypical ribs:
a. 10th ribs
One facet in its
head
uncertain rib it
may be floating
rib or attached
w/ the 9th rib w/
a cartilage
b. 11th rib:
single facet in its
head
have no neck nor
tubercle
costal groove not
distinct
c. 12th rib:
one facet in its head
has no tubercle, angle
and costal groove
BONY THORAX
Costal Cartilage:
1st 7 cartilages
articulate w/ the
sternum
8th, 9th and 10th
costal cartilages
joins to form:
Subcostal margins:
formed by cartilages of
7th-10th
8/5/2012
BONY THORAX
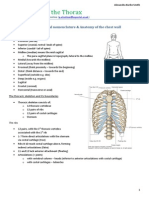
Sternum (Breast Bone)
Manubrium
broadest
most massive
3 notches
1.
2 clavicular notch
2. Suprasternal (jugular
notch)
Body
Made up of 4 sternebrae
Xiphoid (ensiform)
process
smallest
Sternal Angle (angle of Louis
or Ludwig)
Where the 2nd rib is
attached
Longitudinal Lines
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Midsternal line
Lateral sternal line
Mammary line
Parasternal line
Anterior axillary line
Posterior axillary line
Midaxillary line
Scapular line
Paravertebral line
Spinal line
8/5/2012
INTERCOSTAL SPACES
Muscles:
1.
External intercostal
Anterior intercostal
membrane
2.
Internal intercostal
Posterior intercostal
membrane
3.
Transverse thoracis
a. Sternocostalis
b. Innermost intercostal
c.
Subcostal
INTERCOSTAL SPACES
Sternocostalis
(transverse thoracis
/ triangularis sterni):
The most constant
Fails to cross the 1st
two intercostal
spaces
The internal thoracic
vessels descend in
front of it
the pleura is
immediately behind it
8/5/2012
INTERCOSTAL SPACES
Innermost Intercostal:
incomplete and variable
passes from ribs to ribs
it is separated from the
internal intercostal muscle by
the intercostal nerve and
vessels
Subcostal muscle:
INTERCOSTAL SPACES
Intercostal Spaces:
11 intercostal spaces
Upper 9 spaces are closed
3rd intercostal space is the
widest
It is wider on inspiration
Subcostal Groove:
Is located deep surface of the
ribs sharp lower border.
VAN (from above downward)
8/5/2012
BLOOD VESSELS
Arteries:
1.
Posterior intercostal
arteries:
a. Upper 2 branches of the
highest intercostal arteries are
branches of the costocervical
trunk of subclavian artery
b. Lower 9 branches of the
thoracic artery
Each has anterior and posterior
branches
BLOOD VESSELS
Arteries:
2.
Anterior Intercostal
Arteries:
Arise from internal
mammary arteries (upper 6)
Arise from musculophrenic
artery (lower 5)
3.
Subcostal artery:
Since there is no 12th
intercostal space.
8/5/2012
BLOOD VESSELS
Arteries:
4.
Internal Mammary Artery:
Branch of subclavian artery
Divides:
a. Superior epigastric
artery
b. Musculophrenic artery
Intercostal Nerves
12 pairs (11intercostal
and 1 subcostal nerves)
Typical ICN supplies
muscular and skin
except:
1. 1st ICN forms the brachial
plexus
2. 2nd ICN crosses the axilla
supplies the posteromedial
aspect of the arm as
intercostobrachial nerve
2nd-6th ICN thoracic
courses, while 7th-11th ICN
travels partly thoracic and
abdominal
10
8/5/2012
Intercostal Nerves
Intercostal and Subcostal
nerves
Supplies:
1. External, internal & innermost
intercostal muscles
2. Subcostal & Transversus
3.
4.
5.
6.
thoracis
Levator costarum
External, internal &
transverse abdominis
Rectus abdominis
Pyramidalis
BREAST (MAMMARY
GLAND)
ANATOMY:
Boundaries (foramen
of Langer)
Arterial blood supply
Lymphatic drainage
11
8/5/2012
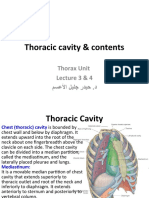
DIAPHRAGM
Origin:
1. Sternal (xiphoid process)
2. Costal (lower 6 costal
cartilages)
3. Crura (right & left)
4. Ligaments: (lumbocostal
arches)
a. Lateral arcuate
(Quadratus lumborum)
b. Medial arcuate (psoas
muscle)
Insertion:
Central tendon
DIAPHRAGM
Nerve Innervation:
Phrenic nerve
(C3,C4,C5)
Arterial Supply:
1. Pericardiophrenic
artery (Superior
phrenic artery)
2. Inferior phrenic
artery
3. Musculophrenic
artery
4. Intercostal arteries
12
8/5/2012
DIAPHRAGM
Foramina:
1. Aortic hiatus: (T12)
a.
b.
c.
2.
Aorta
Thoracic duct
Azygos vein
Esophageal hiatus:
(T10)
a.
b.
3.
R & L vagus nerve
Esophageal branches of left
gastric artery
Inferior vena cava
Hiatus: (T8)
a.
b.
c.
IVC
Right phrenic nerve
Lymphatic vessel
THANK YOU
13
You might also like
- Orientation of Thoracic Wall.Document54 pagesOrientation of Thoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall.Document48 pagesThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- ThoraxDocument29 pagesThoraxapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Thoracic CavityDocument6 pagesThoracic CavityRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Autumn 2006 Q4 Write Short Notes On Three of The FollowingDocument4 pagesAutumn 2006 Q4 Write Short Notes On Three of The Following3cinr3bNo ratings yet
- The Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryDocument7 pagesThe Thoracic Cage: University Ovidius" of Constanta Faculty of DentistryAndreeaNo ratings yet
- ABS-Anatomy of The ThoraxDocument52 pagesABS-Anatomy of The ThoraxAtti Tamas100% (1)
- M, Thorax, Lectures IDocument30 pagesM, Thorax, Lectures IJessica PachecoNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument211 pagesAnatomyIshimwe TheotimeNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021Document7 pagesHuman Anatomy Assignment 1. DR Onanuga-2021AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThoraxDocument43 pagesAnatomy of ThoraxNunmoy HnialumNo ratings yet
- THORACIC ANATOMYDocument7 pagesTHORACIC ANATOMYDaggy AngcaoNo ratings yet
- Thorax - Anatomy.Document26 pagesThorax - Anatomy.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- ثوراكس نظري كاملDocument112 pagesثوراكس نظري كاملyousif.algarahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3Document33 pagesAnatomy 3bikedet268No ratings yet
- Anatomy Personal NoteDocument7 pagesAnatomy Personal NoteShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانDocument9 pagesالمحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- 72 HR ReviewerDocument8 pages72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RCR1 RespiratoryDocument7 pagesAnatomy RCR1 RespiratoryeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Thorax MooreDocument8 pagesThorax MooreivanajanealexisNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cage Thoracic InletDocument40 pagesThoracic Cage Thoracic InletERIAS TENYWANo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesRespiratory SystemMusadiq Khan DurraniNo ratings yet
- Explaining the anatomy of the human thoraxDocument3 pagesExplaining the anatomy of the human thoraxSukma WulandariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Document24 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Thoracic CageDocument46 pagesThoracic CageEmtnan MuntiNo ratings yet
- 1.thoracic Wall and CavityDocument34 pages1.thoracic Wall and Cavityokoti.omutanyi22No ratings yet
- The Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsDocument2 pagesThe Chest: Chest Wall, Pulmonary, and Cardiovascular Systems The BreastsAn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall and MediastinumDocument10 pagesThoracic Wall and MediastinumLorenz SmallNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall ShortDocument11 pagesThoracic Wall ShortkiranNo ratings yet
- Thoracic WallDocument87 pagesThoracic WallAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter On ThoraxDocument16 pagesChapter On Thoraxson00No ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Document23 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 4, Thoracic Wall (2) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument38 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RespiratoryDocument68 pagesAnatomy RespiratorydofezdsNo ratings yet
- 2.Intercostal-SpaceDocument35 pages2.Intercostal-SpaceDua NjeemNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pectoral Gridle 2014Document15 pagesAnterior Pectoral Gridle 2014kakashi1992No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Lecture on Peripheral Circulation and StructuresDocument45 pagesHuman Anatomy Lecture on Peripheral Circulation and StructuresPhilip GituriNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall 2 Muscles Arteries Veins Nerves E-Learning Lec 2Document25 pagesThoracic Wall 2 Muscles Arteries Veins Nerves E-Learning Lec 2Hla AlwaisyNo ratings yet
- Thoracic cavity & contents: Thorax Unit Lecture 3 & 4 مسعلأا ليلج رديح .دDocument18 pagesThoracic cavity & contents: Thorax Unit Lecture 3 & 4 مسعلأا ليلج رديح .دMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory TractDocument79 pagesThe Respiratory TractbayennNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument30 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyamieNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDocument40 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Ch.19 Thorax and LungsDocument14 pagesCh.19 Thorax and LungsJose R. MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Oral Region:: It Includes The Oral Cavity, Teeth, Gingivae, Tongue, Palate, and Region of Palatine TonsilDocument19 pagesThe Oral Region:: It Includes The Oral Cavity, Teeth, Gingivae, Tongue, Palate, and Region of Palatine TonsilOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Document44 pagesAnatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Syahmi IeskandarNo ratings yet
- 1) Layers Around Lung: ST NDDocument9 pages1) Layers Around Lung: ST NDAzzam AliNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDocument9 pagesDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of RespirationDocument44 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respirationleenadevi90No ratings yet
- Lungs and PleuraDocument7 pagesLungs and PleuraArvin ArliandoNo ratings yet
- Thorax Part 1Document56 pagesThorax Part 1idrimuha333No ratings yet
- L1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmDocument8 pagesL1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmAurora TamNo ratings yet
- Lect 3Document8 pagesLect 3علي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Thoracic Cavity and LungsDocument46 pagesAnatomy of the Thoracic Cavity and LungsAhmadNo ratings yet
- Handout-Respiratory-System-2022-2023Document3 pagesHandout-Respiratory-System-2022-2023reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Know The Human BodyDocument12 pagesKnow The Human BodyhaleemmohdNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall 01Document22 pagesThoracic Wall 01Dr. Saber Ar RaffiNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeFrom EverandThoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeNo ratings yet
- Testicular LumpDocument3 pagesTesticular LumpandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Physics LightDocument3 pagesPhysics LightandiedeeNo ratings yet
- CDX After 1 Year MasayaDocument102 pagesCDX After 1 Year MasayaandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Ent SyllabusDocument1 pageEnt SyllabusandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Tips For The Physicians Licenszcdcxure Examination1Document7 pagesTips For The Physicians Licenszcdcxure Examination1filchibuff100% (2)
- Surg Path Peer EvalDocument1 pageSurg Path Peer EvalandiedeeNo ratings yet
- CPC Mar 15, 2018Document3 pagesCPC Mar 15, 2018andiedeeNo ratings yet
- Reg Table 5 CompleteDocument8 pagesReg Table 5 CompleteandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Transmutation Table For Grade ScoresDocument25 pagesTransmutation Table For Grade ScoresArchie Miranda75% (4)
- SUMMARIZED Family Relationships - Parent Child - Home MGTDocument2 pagesSUMMARIZED Family Relationships - Parent Child - Home MGTandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Medical student exam scheduleDocument1 pageMedical student exam scheduleandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Arm and Back - TabulatedDocument5 pagesArm and Back - TabulatedandiedeeNo ratings yet
- P L M Student HandbookDocument42 pagesP L M Student HandbookandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Bone Soft Tissue Case Jan 2018Document1 pageBone Soft Tissue Case Jan 2018andiedeeNo ratings yet
- CB 1 CheatsDocument5 pagesCB 1 CheatsandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Medical MnemonicsDocument158 pagesMedical MnemonicsBeryl de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Antero-Lateral LegDocument3 pagesAntero-Lateral LegandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Practicum GuidelinesDocument8 pagesPracticum GuidelinesandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Room Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaDocument111 pagesRoom Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaTinoRepaso0% (1)
- Review Schedule: Date DAY Topic LecturerDocument1 pageReview Schedule: Date DAY Topic LecturerandiedeeNo ratings yet
- MARCH 2016: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageMARCH 2016: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Review Schedule: Date DAY Topic LecturerDocument1 pageReview Schedule: Date DAY Topic LecturerandiedeeNo ratings yet
- CB 1 CheatsDocument5 pagesCB 1 CheatsandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Lumbo-sacral plexus and lower extremity nervesDocument1 pageLumbo-sacral plexus and lower extremity nervesandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Room Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaDocument111 pagesRoom Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaTinoRepaso0% (1)
- Room Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaDocument111 pagesRoom Assignments BLEPP2015 ManilaTinoRepaso0% (1)
- FEU Official LetterheadDocument1 pageFEU Official Letterheadandiedee100% (1)
- Practicum GuidelinesDocument8 pagesPracticum GuidelinesandiedeeNo ratings yet
- CB 1 CheatsDocument5 pagesCB 1 CheatsandiedeeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Month 41 of Booty by Bret!: This Month Is A & PlanDocument15 pagesWelcome To Month 41 of Booty by Bret!: This Month Is A & Planolle3870No ratings yet
- Functional Fitness Testing PDFDocument3 pagesFunctional Fitness Testing PDFPhooi Yee LauNo ratings yet
- Muscles and MovementDocument4 pagesMuscles and MovementmcgarrigleNo ratings yet
- Upper Trapezius MuscleDocument6 pagesUpper Trapezius MusclejpNo ratings yet
- Lower Body ExercisesDocument2 pagesLower Body ExercisesaczirokNo ratings yet
- Ariile BrodmannDocument1 pageAriile BrodmannIrina NorocNo ratings yet
- Katz Sandor enDocument49 pagesKatz Sandor enAlexNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory Endurance ExplainedDocument38 pagesCardiorespiratory Endurance ExplainedHilarion Vidal OlimpoNo ratings yet
- Trauma Is Really Strange PDFDocument36 pagesTrauma Is Really Strange PDFTEOFILO PALSIMON JR.100% (6)
- Giles - A3.doc ReviwerDocument27 pagesGiles - A3.doc ReviwerCatrina Tan100% (2)
- Yoga For A New YouDocument498 pagesYoga For A New YouOlivera Milovanovic90% (10)
- Neuro ArtDocument13 pagesNeuro ArtSam JamNo ratings yet
- BDS (CS)Document207 pagesBDS (CS)Aman RajputNo ratings yet
- Management of Facial AsymmetryDocument28 pagesManagement of Facial AsymmetrykrazeedoctorNo ratings yet
- Air Squat - CrossFit Training GuideDocument5 pagesAir Squat - CrossFit Training GuideKarim HaridiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1st Edition Reisel Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1st Edition Reisel Solutions ManualEdwardBishopacsy100% (32)
- Bank Soal AMSA Youth ProjectDocument24 pagesBank Soal AMSA Youth ProjectTuti Awwaliah27No ratings yet
- PhysioEx Lab Report on Renal Response to Blood PressureDocument4 pagesPhysioEx Lab Report on Renal Response to Blood PressureNicole de LeonNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument38 pagesHeartanuzNo ratings yet
- Body Beast Lean Workout SheetsDocument11 pagesBody Beast Lean Workout SheetsSanthosh Inigoe0% (1)
- The Anatomy of the Face and NeckDocument74 pagesThe Anatomy of the Face and Neckhazell_aseronNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Histology of The Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament Complex of The ShoulderDocument8 pagesThe Anatomy and Histology of The Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament Complex of The ShoulderDoomNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cns ExaminationDocument33 pagesNeonatal Cns ExaminationShishir KumarNo ratings yet
- Roy Benitez MALE - 5-DAY HOME DB WORKOUTDocument7 pagesRoy Benitez MALE - 5-DAY HOME DB WORKOUTVictorNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Pain and Motor Control 2011 HodgesDocument9 pagesPain and Motor Control 2011 HodgesPedro SilvaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury Rehab GoalsDocument17 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Rehab GoalsRaghu Nadh100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Wrist and Hand ComplexDocument8 pagesBiomechanics of Wrist and Hand ComplexKIARA VENICE DELGADO100% (1)
- Sectiuni CreierDocument20 pagesSectiuni CreierAndreeaAbuziloaeNo ratings yet
- Workout Program For Cadet Rough DraftDocument2 pagesWorkout Program For Cadet Rough DraftGeorgefrankNo ratings yet