Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: Shock
Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: Shock
Uploaded by
Jaycee Mallari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
diazepam
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: Shock
Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: Shock
Uploaded by
Jaycee MallariCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
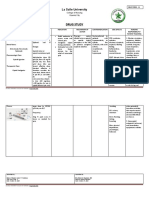
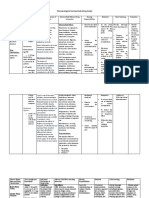
Drug Name Dosage & Route Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility
Body as a Whole: Throat
DIAZEPAM Status Psychotherapeutic agent Drug of choice for status Injectable form: Shock, Assessment & Drug Effects
and chest pain. CNS:
(dye-az'e-pam) Epilepticus related to chlordiazepoxide; epilepticus. Management of coma, acute alcohol
Drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia,
Adult: IV/IM 5–10 mg, reportedly superior in anxiety disorders, for short- intoxication, depressed vital
confusion, paradoxic rage, • Monitor for adverse reactions.
Apo-Diazepam, Diastat, repeat if needed at 10– antianxiety and term relief of anxiety signs, obstetrical patients,
dizziness, vertigo, amnesia, Most are dose related. Physician will
Diazemuls , E-Pam , 15 min intervals up to anticonvulsant activity, with symptoms, to allay anxiety infants <30 d of age. Tablet
vivid dreams, headache, rely on accurate observation and
Meval , Novodipam , 30 mg, then repeat if somewhat shorter duration of and tension prior to surgery, form: Infants <6 mo of age,
slurred speech, tremor; EEG reports of patient response to the
Valium, Valrelease, Vivol needed q2–4h action. Like cardioversion and endoscopic acute narrow-angle glaucoma,
changes, tardive dyskinesia. drug to determine lowest effective
Child: IV/IM <5 y, chlordiazepoxide, it appears procedures, as an amnesic, untreated open-angle
CV: Hypotension, maintenance dose.
Classifications: CENTRAL 0.2–0.5 mg slowly q2– to act at both limbic and and treatment for restless glaucoma; during or within
tachycardia, edema,
NERVOUS SYSTEM 5min up to 5 mg; >5 y, subcortical levels of CNS. legs. Also used to alleviate
cardiovascular collapse.
14 d of MAO inhibitor • Monitor for therapeutic
AGENT; 1 mg slowly q2–5min acute withdrawal symptoms therapy. Safe use during effectiveness. Maximum effect may
Special Senses: Blurred
BENZODIAZEPINE up to 10 mg, repeat if of alcoholism, voiding pregnancy (category D) and require 1–2 wk; patient tolerance to
vision, diplopia, nystagmus.
ANTICONVULSANT; needed q2–4 h problems in older adults, and lactation is not established. therapeutic effects may develop
GI: Xerostomia, nausea,
ANXIOLYTIC adjunctively for relief of after 4 wk of treatment.
constipation, hepatic
Anxiety, Muscle skeletal muscle spasm
Spasm, associated with cerebral
dysfunction. Urogenital: • Observe necessary preventive
Incontinence, urinary precautions for suicidal tendencies
Convulsions, palsy, paraplegia, athetosis,
retention, gynecomastia that may be present in anxiety states
Alcohol stiff-man syndrome, tetanus.
(prolonged use), menstrual accompanied by depression.
Withdrawal irregularities, ovulation • Observe patient closely and
Adult: PO 2–10 mg failure. Respiratory:
b.i.d. to q.i.d. or 15–30 monitor vital signs when diazepam
Hiccups, coughing, is given parenterally; hypotension,
mg/d sustained laryngospasm. Other: Pain,
release IV/IM 2–10 muscular weakness, tachycardia, and
venous thrombosis, phlebitis respiratory depression may occur.
mg, repeat if needed in at injection site.
3–4 h • Lab tests: Periodic CBC and liver
Geriatric: PO 1–2 mg function tests during prolonged
1–2 times/d (max: 10 therapy.
mg/d)
• Supervise ambulation. Adverse
Child: PO >6 mo, 1–
reactions such as drowsiness and
2.5 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d.
ataxia are more likely to occur in
older adults and debilitated or those
receiving larger doses. Dosage
adjustment may be necessary.
• Monitor I&O ratio, including
urinary and bowel elimination.
You might also like
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RoutepiasolNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Week 7 Course TaskDocument13 pagesWeek 7 Course TaskRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- LevodopaDocument3 pagesLevodopaderic50% (2)
- DS DR RodasDocument7 pagesDS DR RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AntipsychoticDocument9 pagesDrug Study AntipsychoticAMAL ALI HASSANNo ratings yet
- Injections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolDocument3 pagesInjections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolthesarayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: La Salle UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: La Salle UniversityJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamShane Shaira G PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormatCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Pharma Lab. Activity 2Document55 pagesPharma Lab. Activity 2Majestic RavenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Module 4Document6 pagesDrug Study Module 4Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- ValiumDocument1 pageValiumJess MatiasNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument37 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsJoanne Bernadette AguilarNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug Studyjoaqiun100% (1)
- 7 Midazozalam Drug StudyDocument3 pages7 Midazozalam Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamSherwin LauronNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Drug StudyDocument35 pagesNCM 112 - Drug StudyZoe WsetNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla MedsudrugstudyDocument11 pagesForcadilla MedsudrugstudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepamRochelle DiezmoNo ratings yet
- Dosage: 50 MG Order: PRN q6h Route: IV (Case Scenario Based)Document3 pagesDosage: 50 MG Order: PRN q6h Route: IV (Case Scenario Based)Edward Luis EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mcp1Document2 pagesDrugs Mcp1Ahrjey DUey PanganNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DonepezilDocument2 pagesDonepezilAmberNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Drug StudyDocument11 pagesMedsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument1 pageHaloperidol PDFAda AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DiazepamCerie Anne Olay40% (5)
- 4 SeizuresDocument11 pages4 SeizuresApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia DSDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia DSCatungal RophineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DRDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DRNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Activity 2 Drug Study LinaoDocument21 pagesActivity 2 Drug Study LinaoNursing ClassNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Dosage/ Indication Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effect/ Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Name Classification Dosage/ Indication Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effect/ Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- ERDrug Study DimayugaDocument25 pagesERDrug Study DimayugaSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Phenobarbital SodiumDocument1 pagePhenobarbital SodiumKevin Gonzales100% (1)
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- FluoxetineDocument2 pagesFluoxetineSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla - Drug Study orDocument31 pagesForcadilla - Drug Study orKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepamBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Drugs For Anxiety and InsomniaDocument10 pagesDrugs For Anxiety and InsomniaApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DiazepamDocument2 pagesDrug Study DiazepamBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Flupentixol Drug StudyDocument7 pagesFlupentixol Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Yanga - NCP, Drug Study, FdarDocument7 pagesYanga - NCP, Drug Study, Fdar3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Print Drug StudDocument12 pagesPrint Drug StudGabriel HinolanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyDocument12 pagesForcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Perphenazine Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPerphenazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepam1adie1907No ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicDocument2 pagesValproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Risperidone (Aspidon OS)Document8 pagesRisperidone (Aspidon OS)Khristle DavidNo ratings yet
- Beating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesFrom EverandBeating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NCP CholeDocument2 pagesNCP CholeinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument37 pagesThesisinfectionman100% (1)
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument2 pagesHerpes ZosterinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- CS NCPDocument2 pagesCS NCPinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- CVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In FormDocument22 pagesCVLSPMS Splash Screen: CVLSPMS Log-In ForminfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RouteinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument1 pageCardiac DysrhythmiainfectionmanNo ratings yet