Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diazepam
Uploaded by
Gwyn Rosales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views3 pagesDiazepam
Uploaded by
Gwyn RosalesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
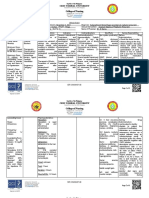
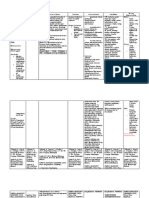
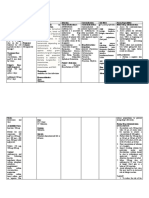
Generic Name: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacodynamics General Indication: - Acute angle- CNS: Anterograde Before Drug
Diazepam Benzodiazepine or Mechanism of To relieve closure glaucoma amnesia, anxiety, Administration
Action: anxiety - hypersensitivity to ataxia, confusion, - Do not dilute or mix
Trade/Brand Name: Therapeutic Class: May potentiate effects To treat diazepam or its depression, dizziness, with any other drug.
Diastat, Diazemuls, Anticonvulsant, of gamma symptoms of components drowsiness, fatigue, Otherwise, it may
Valium anxiolytic, sedative- aminobutyric acid acute alcohol - untreated open- headache, insomnia, become unstable and
hypnotic, skeletal (GABA) and other withdrawal angle glaucoma lethargy, light- increase the risk of
Minimum dose: muscle relaxant Inhibitory To provide headedness, serious adverse
5 mg q3-4h PRN neurotransmitters by muscle relaxation paradoxical reactions.
Pregnancy Category: binding to specific and sedation reactions, psychiatric
Maximum dose: D benzodiazepine To treat seizures effects, sedation, During Drug
10 mg q3-4h PRN receptors in limbic and To treat status sleepiness, slurred Administration
cortical areas of CNS. epilepticus and speech, suicidal - Give direct IV by
Patient’s Dose: GABA inhibits severe recurrent ideation, tremor, injecting drug slowly,
5 mg IVTT STAT excitatory stimulation, seizures vertigo taking at least 1 min
which helps control To treat tetanus for each 5 mg (1 mL).
Route: emotional behavior. CV: Hypotension, - Monitor I&O ratio,
Intravenous Limbic system Patient’s Indication: palpitations, including urinary and
contains For relief of patient’s tachycardia bowel elimination.
Frequency: a dense area of vertigo -Ensure safety of the
STAT benzodiazepine EENT: Blurred vision, patient.
receptors, which may diplopia, dry mouth,
Availability: explain drug’s increased salivation After Drug
Tablet antianxiety effects. Administration
Oral Solution GI: Anorexia, - Observe patient
Solution for injection Pharmacokinetics: constipation, diarrhea, closely and monitor
Rectal gel Absorption: Readily elevated liver vital signs when
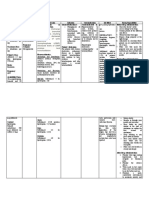
from GI tract; erratic enzymes, jaundice, diazepam is given
Content: IM absorption. nausea, vomiting parenterally;
hypotension, muscular
Onset: 1–5 min IV. GU: Libido changes, weakness, tachycardia,
urinary incontinence, and respiratory
Peak: 15 min– urine retention depression may occur.
1 h IV -Supervise ambulation.
HEME: Neutropenia Adverse reactions such
Distribution: as drowsiness and
Crosses blood–brain MS: dysarthria, muscle ataxia are more likely
barrier weakness to occur.
Diazepam, anhydrous - Monitor lab tests:
lactose, corn starch, Metabolism: In liver to RESP: Respiratory Periodic CBC.
pregelatinized starch active metabolites. depression
and calcium stearate
Elimination: Primarily SKIN: Dermatitis
in urine. Half-Life: 20–
50 h. Other: Physical and
psychological
dependence
References:
Vallerand, A., Sanoski, C., & Deglin, J. (2017). Drug Guide for Nurses. 15th Ed. FA Davis Company: Philadelphia
Schull, P. D. (2013). McGraw-Hill nurses drug handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical.
JONES & BARTLETT LEARNING. (2018). Nurses Drug Handbook. SUDBURY.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension Managementbhavana100% (1)
- Newborn Care ProceduresDocument5 pagesNewborn Care Proceduresallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- Cretenism Case StudyDocument8 pagesCretenism Case StudyMonica Marie MoralesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument2 pagesDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Antibiotics - ViosDocument8 pagesAssignment On Antibiotics - ViosIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- AdrenalineDocument2 pagesAdrenalinerazvan032006100% (1)
- ChemotherapyDocument11 pagesChemotherapyRekha G.No ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsDocument22 pagesNursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsG a i l R i c h w e l lNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Generic Name TizanidineDocument3 pagesGeneric Name TizanidinemadamcloudnineNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Diet HandoutDocument2 pagesCardiac Diet Handoutapi-537434972No ratings yet
- Esophageal DiverticulaDocument13 pagesEsophageal DiverticulaShekaira B. SimsimNo ratings yet
- Disulfiram Therapy: An Aid for Alcohol DependenceDocument15 pagesDisulfiram Therapy: An Aid for Alcohol Dependencevarsha thakur100% (1)
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Public Health Nursing in SchoolsDocument45 pagesPublic Health Nursing in SchoolsdaveNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY TablesDocument9 pagesCASE STUDY TablesMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- NCP M7Document3 pagesNCP M7rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Ampicillin Drug Study GuideDocument3 pagesAmpicillin Drug Study GuideAlyssa Mae DumularNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkier khierNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila Development Screening TestDocument3 pagesMetro Manila Development Screening TestMae PonceNo ratings yet
- RibavirinDocument2 pagesRibavirinAnonymous 6u2S47fbxnNo ratings yet
- HYOSCINE HBr, CEFTAZIDIME, PARACETAMOL, GENTAMYCIN nursing responsibilitiesDocument6 pagesHYOSCINE HBr, CEFTAZIDIME, PARACETAMOL, GENTAMYCIN nursing responsibilitiesDonna ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Premenstrual Dysphoric DisorderDocument11 pagesPremenstrual Dysphoric Disorderapi-3764215No ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Chapter 23: Inserting A Rectal SuppositoryDocument1 pageProcedure Checklist Chapter 23: Inserting A Rectal Suppositorymacs_smacNo ratings yet
- NCP and DrugsDocument7 pagesNCP and DrugsRach AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Bibliography on Urban Waste ManagementDocument45 pagesBibliography on Urban Waste ManagementRavikar ShyamNo ratings yet
- Lithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsDocument2 pagesLithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsgavinbuzzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJessica MakalintalNo ratings yet
- Kidney CancerDocument31 pagesKidney CancerEfren Elico VenguaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification: Antacid & Antihistamine Student ReportDocument2 pagesDrug Classification: Antacid & Antihistamine Student ReportKish AmoreNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaBinita Shakya100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAlisse Sales De-PazNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia Care Plan/OthersDocument11 pagesOsteomalacia Care Plan/OthersJill Jackson, RNNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsCatherine Martinez AvilaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument12 pagesOxygenationCherry Lou Guanzing100% (1)
- What Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistDocument12 pagesWhat Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistLidiaAMonroyRNo ratings yet
- Share DRUGSTUDYDocument4 pagesShare DRUGSTUDYTyronne JingcoNo ratings yet
- NCP EsrdDocument2 pagesNCP EsrdAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentQueenie Silva100% (1)
- A Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageA Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanJulius Caesar ColladoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- Manaois - Drug STUDY (Lorazepam)Document2 pagesManaois - Drug STUDY (Lorazepam)Dan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Mayur BV BPH 3 Semester PSPHDocument29 pagesHypertension: Mayur BV BPH 3 Semester PSPHBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- On Dan Set RonDocument1 pageOn Dan Set Ronzepoli_zepoly6232No ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument10 pagesNCP Risk For Infectionson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- (Generic Name) ® Drotaverine 40mgDocument2 pages(Generic Name) ® Drotaverine 40mgSangar Sardar100% (1)
- Fludrocortisone (Florinef)Document17 pagesFludrocortisone (Florinef)passer byNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument32 pagesThalassemiaBinal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyzenNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument3 pagesMethergineJohn AlanoNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide drug guideDocument2 pagesHyoscine-N-Butylbromide drug guideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- MeperidineDocument3 pagesMeperidineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Combivent Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesCombivent Nursing ResponsibilitiesGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- NimodipineDocument5 pagesNimodipineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- PhenobarbitalDocument6 pagesPhenobarbitalGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for CotrimoxazoleDocument5 pagesNursing responsibilities for CotrimoxazoleGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- IronDocument3 pagesIronGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- IntralipidDocument3 pagesIntralipidGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- LevetiracetamDocument4 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismDocument4 pagesCebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument3 pagesDexamethasoneGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument5 pagesGliclazideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Tetanus ToxoidDocument3 pagesTetanus ToxoidGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- DiphenhydramineDocument3 pagesDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CeftriaDocument5 pagesCeftriaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CiticolineDocument3 pagesCiticolineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument4 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ColistinDocument2 pagesColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument2 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- (Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveDocument4 pages(Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- General Indications: Body As A Whole: Allergy,: Therapeutic EffectDocument3 pagesGeneral Indications: Body As A Whole: Allergy,: Therapeutic EffectGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CapecitabineDocument2 pagesCapecitabineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Sulfate Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesAmikacin Sulfate Nursing ResponsibilitiesGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Amlodipine Reduces Systolic, Diastolic, and Mean Arterial Blood Pressure. It Also Decreases Pain Due To AnginaDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Reduces Systolic, Diastolic, and Mean Arterial Blood Pressure. It Also Decreases Pain Due To AnginaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CefoxitinDocument3 pagesCefoxitinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Antitussives & MucolyticsDocument50 pagesAntitussives & MucolyticsSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Advil - PLUS - FA - For - Download - ENGLISHDocument2 pagesAdvil - PLUS - FA - For - Download - ENGLISHShuvroNo ratings yet
- Acceptable Latin Terms and Abbreviations: Units (Approved Abbreviation Unit)Document2 pagesAcceptable Latin Terms and Abbreviations: Units (Approved Abbreviation Unit)Jamaica LimejuiceNo ratings yet
- Seizures/Epilepsy: Case PersentationDocument14 pagesSeizures/Epilepsy: Case PersentationAbdulmalik AliNo ratings yet
- Price List September 2022Document61 pagesPrice List September 2022Ade IrawanNo ratings yet
- PentojectDocument2 pagesPentojectandreisandorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Study GuideDocument121 pagesPharmacology Study GuideZoza QueenNo ratings yet
- Dopunska Lista Lijekova - Po Dijelovima - Web - Stupa Na Snagu - 23 - 06 - 2022Document256 pagesDopunska Lista Lijekova - Po Dijelovima - Web - Stupa Na Snagu - 23 - 06 - 2022Alma FazlićNo ratings yet
- DiethylcarbamazineDocument1 pageDiethylcarbamazineashithabenny896No ratings yet
- MENDOZA, Francis Luigi C. - DRUG STUDY Hyoscine N ButylbromideDocument2 pagesMENDOZA, Francis Luigi C. - DRUG STUDY Hyoscine N Butylbromidebaka esh toNo ratings yet
- NCLEX PharmacologyDocument51 pagesNCLEX PharmacologyJan Mitchelle100% (2)
- Sir Mendoza Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSir Mendoza Drug StudykyleNo ratings yet
- 3.one Compartment Open ModelDocument15 pages3.one Compartment Open ModelSAM KNo ratings yet
- OBAT YANG MENDEKATI EXPIRE DATE 2021Document2 pagesOBAT YANG MENDEKATI EXPIRE DATE 2021vicki yugasworoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Valproate SodiumDocument4 pagesDrug Study Valproate SodiumLouie Danielle SegarraNo ratings yet
- PPM Arvreferencepricing Table enDocument3 pagesPPM Arvreferencepricing Table enayawe888888No ratings yet
- Exel So Desember 2021 10 Januari 2022Document279 pagesExel So Desember 2021 10 Januari 2022Ani Nur RohmaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-ChlorpromazineDocument1 pageDrug Study-ChlorpromazineMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Antiretroviral DrugsDocument60 pagesAntiretroviral DrugsDeribe BekeleNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High Alert Dan Lasa PKM Sendang AgungDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat High Alert Dan Lasa PKM Sendang AgungDian PutraNo ratings yet
- Copaxone - Ms Drug StudyDocument1 pageCopaxone - Ms Drug StudygraceNo ratings yet
- ProductsDocument106 pagesProductsbochieng404No ratings yet
- CANAMED 01 03 2022oficialDocument936 pagesCANAMED 01 03 2022oficialStefan IonutNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology overview and key conceptsDocument16 pagesPharmacology overview and key conceptscuolyNo ratings yet
- Trazodone prescription details for Angela ReifDocument1 pageTrazodone prescription details for Angela ReifAnderson Manuel Marquez NuñezNo ratings yet
- Dispensing 1: Unit 3: The Prescription and Medication OrderDocument4 pagesDispensing 1: Unit 3: The Prescription and Medication OrderAllana TapadoNo ratings yet
- Pricelist CVG Split Generik & Man Untuk DokterDocument21 pagesPricelist CVG Split Generik & Man Untuk DokterMonica SandraNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin TazobactamDocument1 pagePiperacillin TazobactamRakesh DudiNo ratings yet
- WWW Globalrph Com Narcotic HTMDocument5 pagesWWW Globalrph Com Narcotic HTMroooNo ratings yet