Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Monopolistic Competition
Uploaded by
Thomas PhillipsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Monopolistic Competition
Uploaded by
Thomas PhillipsCopyright:
Available Formats
Monopolistic competition
Monopolistic completion is a form of market in which there are a set of particular criteria. It could be
said to be in-between monopoly and perfect competition. The criteria include:
The industry is made up of a fairly large number of firms.
The firms are small, relative in size to the industry. This means that the actions of a single
firm are unlikely to have a significant effect on the overall industry and its competitors. Each
firm is able to act independently.
The firms all produce slightly differentiated products. This means that it is possible for a
consumer to distinguish between different firms products.
There are no barriers to entry or exit from the industry. Allowing firms to enter of leave as
the industry freely.
The difference from perfect competition is that there is product differentiation. Differentiation is
seen when a good is seen/perceived to be different from another product of the same function. This
can include: brand, colour, appearance, packaging, design, service, skill level etc. An example of a
monopolistic competitive industry is hairdressing. There is free entry and it is at least possible that
people know enough about their hairdressing options so that the "sufficient knowledge" condition is
fulfilled. But the products of different hairdressers are not perfect substitutes. At the very least, their
services are differentiated by location. A hairdresser in the Centre of London is not a perfect
substitute for a hairdresser in a alleyway in Crawley, although they may be good substitutes from the
point of view of a customer who lives in the suburbs but works in city centre. Hairdressers' services
may be differentiated in other ways as well.
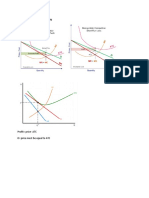
The adjacent graph shows the
demand for a firm in monopolistic
competition. The firm faces a
downward sloping demand curve
with a marginal revenue curve that
is below it and produces so that it
is maximising profits where
MC=MR. This means that the firm
shown in the diagram will produce
an output of Q and sell that output
at the price of P.
There are also long and short run
monopolistic competition. In short run it is possible to sustain short-run profit or loss situations. In
the long-run however, all firms will end up making normal profits.
You might also like
- Market Structures: Imperfect Or: Monopolistic CompetitionDocument29 pagesMarket Structures: Imperfect Or: Monopolistic CompetitionHendrix NailNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 14th Edition Mcconnell Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 14th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manualanagogegirdler.kycgr100% (23)
- IB Econ Chap 09 Monop CompDocument5 pagesIB Econ Chap 09 Monop CompMilan v.de MeebergNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic and Oligopoly: © 2006 Thomson/South-WesternDocument34 pagesMonopolistic and Oligopoly: © 2006 Thomson/South-WesternSurya PanwarNo ratings yet
- Market Structures and Price-Output DeterminationDocument40 pagesMarket Structures and Price-Output DeterminationHartin StylesNo ratings yet
- Economics Principles Problems and Policies Mcconnell 20th Edition Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesEconomics Principles Problems and Policies Mcconnell 20th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (39)
- Competition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeDocument4 pagesCompetition: Monopolistic Fairly LargeNagaraj BeeduNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ix 1Document8 pagesPertemuan Ix 1Rumiati 72No ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition: ReferenceDocument5 pagesMonopolistic Competition: ReferenceSabu VincentNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument4 pagesMonopolistic CompetitionAzharNo ratings yet
- Economics Principles and Policy 13Th Edition Baumol Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument23 pagesEconomics Principles and Policy 13Th Edition Baumol Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsarah.parker268100% (10)
- Lecture 4 Business EconomicsDocument15 pagesLecture 4 Business EconomicsTayyaba JawedNo ratings yet
- Monopolies, Monopsonies and Dominant FirmsDocument47 pagesMonopolies, Monopsonies and Dominant FirmsHendrix NailNo ratings yet
- Altaf Eco AssignmentDocument12 pagesAltaf Eco Assignmentmoiz8_6No ratings yet
- OligopolyDocument16 pagesOligopolyMd. Amran HossainNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Macroeconomics Principles and Policy 12th Edition DownloadDocument3 pagesSolution Manual For Macroeconomics Principles and Policy 12th Edition DownloadGaryLeemtno100% (40)
- Economics Principles and Policy 13th Edition Baumol Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesEconomics Principles and Policy 13th Edition Baumol Solutions Manualedwardleonw10100% (31)
- Oli LR Compares To PC LRDocument1 pageOli LR Compares To PC LRHeoHamHốNo ratings yet
- Period But Failed To Outperform The Market After The Book's Publication. Why?Document2 pagesPeriod But Failed To Outperform The Market After The Book's Publication. Why?Melody BautistaNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument17 pagesMonopolistic CompetitionAlok ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 SeminarDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Seminarnominnomiko0709No ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 15Th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 15Th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmatthewavilawpkrnztjxs100% (11)
- Microeconomics Canadian 15th Edition Mcconnell Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 15th Edition Mcconnell Solutions Manualclubhandbranwq8100% (25)
- Price and Output Determination Under Imperfect CompetitionDocument19 pagesPrice and Output Determination Under Imperfect CompetitionAshish PareekNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition and Product DifferentiationDocument18 pagesMonopolistic Competition and Product DifferentiationSurya PanwarNo ratings yet
- Eco 111 Principles of Economics - 014352Document6 pagesEco 111 Principles of Economics - 014352ebubeeke846No ratings yet
- Imperfect Comp. - Monopolistic CompetitionDocument12 pagesImperfect Comp. - Monopolistic CompetitionPPE-T-3757 Hrushikesh TetwarNo ratings yet
- Market Structure Original Unit 3Document32 pagesMarket Structure Original Unit 3Priya SonuNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition: Market PowerDocument13 pagesPerfect Competition: Market Powerdenny_sitorusNo ratings yet
- 8 - Monopolistic CompetitionDocument22 pages8 - Monopolistic CompetitionShashwat JhaNo ratings yet
- Brue3e Chap07 FinalDocument14 pagesBrue3e Chap07 Finalnadiahnur07No ratings yet
- Revision NotesDocument6 pagesRevision NotesJyot NarangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplyDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplyRitesh RajNo ratings yet
- Chap011 RevDocument12 pagesChap011 RevBlackbubbleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Seminar AnswerDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Seminar AnswerMisheel MinannNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Unit 9Document18 pagesManagerial Economics: Unit 9Mary Grace V. PeñalbaNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS CH11 SolutionsDocument33 pagesMICROECONOMICS CH11 Solutions傅庠燁No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics (M.com IVth Sem.) - L6 15-4Document13 pagesManagerial Economics (M.com IVth Sem.) - L6 15-4Phatehkrishna AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition and OligopolyDocument17 pagesMonopolistic Competition and OligopolyshradhaNo ratings yet
- Eric Stevanus 2201756600 LA28Document2 pagesEric Stevanus 2201756600 LA28eric stevanusNo ratings yet
- Parkin 13ge Econ IMDocument12 pagesParkin 13ge Econ IMDina SamirNo ratings yet
- The Firm and Market StructuresDocument36 pagesThe Firm and Market StructuresPrince AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Price & Output Determination: by Radhika Faculty Member J.H.Bhalodia Women's CollegeDocument42 pagesUnit - 3 Price & Output Determination: by Radhika Faculty Member J.H.Bhalodia Women's CollegerajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 6 1Document8 pagesActivity No. 6 1Carlos Lois SebastianNo ratings yet
- 3.4. Market StructuresDocument24 pages3.4. Market StructuresDecision SitoboliNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 13Document23 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 13202110782No ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Introduction To Markets and Pricing Policies: Size of The MarketDocument10 pagesUNIT-4 Introduction To Markets and Pricing Policies: Size of The Marketarzun666No ratings yet
- Ch11solution ManualDocument24 pagesCh11solution ManualStoneCold Alex Mochan100% (3)
- Price Determination Under Imperfect Competition (Explain With Diagram)Document23 pagesPrice Determination Under Imperfect Competition (Explain With Diagram)HebaNo ratings yet
- Monopoly Equilibrium UploadedDocument10 pagesMonopoly Equilibrium Uploadedasal661No ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompettionDocument5 pagesMonopolistic Compettionvidushi bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionDocument13 pagesLecture 3.2 - Perfect CompetitionLakmal SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.2Document26 pagesChapter 5.2Sandesh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Nataliemoore MonopoliesDocument1 pageNataliemoore Monopoliessnehilhaldar1998No ratings yet
- Oligopolycharacteristics 090925201939 Phpapp01Document16 pagesOligopolycharacteristics 090925201939 Phpapp01gunu_f1No ratings yet
- Draw Before Presentation: Profit price-ATC 0 Price Must Be Equal To ATCDocument4 pagesDraw Before Presentation: Profit price-ATC 0 Price Must Be Equal To ATCRegine Mae MandapNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Price & Output Determination: by Radhika Faculty Member J.H.Bhalodia Women's CollegeDocument42 pagesUnit - 3 Price & Output Determination: by Radhika Faculty Member J.H.Bhalodia Women's CollegeDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Price Leadership PDFDocument7 pagesPrice Leadership PDFKartikey SinghNo ratings yet
- Perfectly Competitive Market: Perfect CompetitionDocument8 pagesPerfectly Competitive Market: Perfect CompetitionLuna KimNo ratings yet
- Assessment Paper and Instructions To CandidatesDocument3 pagesAssessment Paper and Instructions To CandidatesJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- AlwarDocument94 pagesAlwarSaurabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- IMPL Standalone Financial FTY 2020-21Document41 pagesIMPL Standalone Financial FTY 2020-21Movies BazarNo ratings yet
- RWJ Chapter 5 NPV and Other Investment RulesDocument55 pagesRWJ Chapter 5 NPV and Other Investment RulesMinh Châu Tạ ThịNo ratings yet
- Design Patterns Presentation - Observer Pattern: Winter 2017Document2 pagesDesign Patterns Presentation - Observer Pattern: Winter 2017Willy WonkaNo ratings yet
- OM&TQM Week1 ModuleDocument10 pagesOM&TQM Week1 ModuleKanton FernandezNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall (RW) Bar Detail: Bar Arrangement at Onfill Face of Wall Bar Arrangement at Exposed Face of WallDocument1 pageRetaining Wall (RW) Bar Detail: Bar Arrangement at Onfill Face of Wall Bar Arrangement at Exposed Face of WallRaljun MaturanNo ratings yet
- ChallanFormDocument1 pageChallanFormrmzmuhammedNo ratings yet
- Big Blue v11pdf PDFDocument2,380 pagesBig Blue v11pdf PDFAlfonsus W.M.No ratings yet
- NightmarketDocument30 pagesNightmarketMaria Cecilia Y. AbellaNo ratings yet
- MS 500T04A ENU TrainerHandbookDocument128 pagesMS 500T04A ENU TrainerHandbookSalin SubranNo ratings yet
- Sod-Analyze Using MS ExcelDocument9 pagesSod-Analyze Using MS ExcelJeethender KummarikuntaNo ratings yet
- Transfer Policy 2023Document8 pagesTransfer Policy 2023pankaj singhalNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg Cement India LTD Vs Commissioner of Cenq140293COM838303Document9 pagesHeidelberg Cement India LTD Vs Commissioner of Cenq140293COM838303Rıtesha DasNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Montessori V de La Salle BrothersDocument2 pagesDe La Salle Montessori V de La Salle BrothersAleli BucuNo ratings yet
- FM 1 MergedDocument90 pagesFM 1 MergedMadhur AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Objectives of IAS 27Document4 pagesObjectives of IAS 27Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- ISO Management System For UN Sustainable Development Goals 1663397135Document70 pagesISO Management System For UN Sustainable Development Goals 1663397135richardNo ratings yet
- Air Cargo Tracking and NewsDocument3 pagesAir Cargo Tracking and NewsMarcello Aires RomãoNo ratings yet
- IADC Presentation LMADocument11 pagesIADC Presentation LMADragos NeaguNo ratings yet
- Surity FormDocument5 pagesSurity FormRaaM E RNo ratings yet
- Offer of Kiln TyreDocument3 pagesOffer of Kiln TyreNapoleon DasNo ratings yet
- Acct 111 Financial Accounting NotesDocument61 pagesAcct 111 Financial Accounting NotesSharon Rose GalopeNo ratings yet
- Form For Cargo Information For Solid Bulk Cargoes: E.g., Class & UN No. or "MHB"Document2 pagesForm For Cargo Information For Solid Bulk Cargoes: E.g., Class & UN No. or "MHB"Jayme LemNo ratings yet
- Brand Study & Marketing Plan Preparation: AdidasDocument41 pagesBrand Study & Marketing Plan Preparation: AdidasSachin Attri100% (1)
- Placementdata OthersDocument48 pagesPlacementdata OthersmegaspiceNo ratings yet
- Turnover of Unit and Move in GuidelinesDocument2 pagesTurnover of Unit and Move in GuidelinesRemer JalbunaNo ratings yet
- Clara Lorenza SaraswatiDocument192 pagesClara Lorenza SaraswatiSeptian Jefry Cahyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Plant Management TafskillsDocument4 pagesPlant Management TafskillsTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- Employee Engagement: The BusinessDocument3 pagesEmployee Engagement: The BusinessyowNo ratings yet