Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem22 18
Problem22 18
Uploaded by
IENCSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem22 18
Problem22 18
Uploaded by
IENCSCopyright:
Available Formats
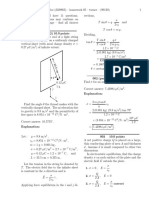
22.18: Draw a cylindrical Gaussian surface with the line of charge as its axis.
The
cylinder has radius 0.400 m and is 0.0200 m long. The electric field is then 840 N/C at
every point on the cylindrical surface and directed perpendicular to the surface. Thus
∫ E ⋅ d s = ( E )( Acylinder) = ( E )(2πrL)
= (840 N/C) (2 π ) (0.400 m) (0.0200 m) = 42.2 N ⋅ m 2 /C
The field is parallel to the end caps of the cylinder, so for them ∫ E ⋅ d s =0 . From
Gauss’s law:
C2 N ⋅ m2
q = ε0 ΦE = (8.854 × 10 −12 ) ( 42 .2 )
N ⋅ m2 C
= 3.74 × 10 −10 C
You might also like
- University Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFDocument1 pageUniversity Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFMohammed Rashwan32% (19)
- Chen SolutionsDocument10 pagesChen Solutionssujayan2005100% (5)
- The Health Physics Solution Manual (246-280)Document35 pagesThe Health Physics Solution Manual (246-280)omarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Cou LombDocument50 pagesCou LombJm RezanoNo ratings yet
- Homework 05-Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesHomework 05-Solutions PDFld393563No ratings yet
- Mongo Shell Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMongo Shell Cheat SheetJamie Smith100% (1)
- Data AnalyticsDocument54 pagesData Analyticsbivi wangNo ratings yet
- 23 - 26 - solutions 물리Document9 pages23 - 26 - solutions 물리전삼기No ratings yet
- =5.0 cm =q =q =q =75 μ C: W q a a a q a q aDocument7 pages=5.0 cm =q =q =q =75 μ C: W q a a a q a q akevin.sanghyunNo ratings yet
- Y0405 2 md1Document6 pagesY0405 2 md1hthaier4062No ratings yet
- (Ii) Eequatorial : (Ii) E¡xial and For Short Dipole, E¡xial and For Short Dipole EequatorialDocument4 pages(Ii) Eequatorial : (Ii) E¡xial and For Short Dipole, E¡xial and For Short Dipole EequatorialRussia ServerNo ratings yet
- Assign 1 Soln 2014Document5 pagesAssign 1 Soln 2014Sumeyya NuruNo ratings yet
- Laser SafetyDocument21 pagesLaser Safetymeharsaleemi.14No ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law: F K Q Q R K KDocument4 pagesCoulomb's Law: F K Q Q R K KJoan BalendrezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 Example ProblemsDocument2 pagesLesson 27 Example Problemsspamhere1977No ratings yet
- Physics SolutionsDocument4 pagesPhysics SolutionsTammy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Em Waves JeeDocument14 pagesEm Waves JeeTobiramaNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.86Document2 pagesProblem 3.86Luis Gustavo Pilco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5: E (4.0 N/C) Î (2.0 N/C) ĴDocument4 pagesProblem Set 5: E (4.0 N/C) Î (2.0 N/C) ĴMahid DandamunNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Phs122Document52 pagesElectric Field Phs122Danika LoavesNo ratings yet
- 0.2m M 0.3kg/s 0.25 M M 0.2kg/s 460 K 310 K 400 KDocument3 pages0.2m M 0.3kg/s 0.25 M M 0.2kg/s 460 K 310 K 400 KAusan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cap. 32 PDFDocument75 pagesCap. 32 PDFwallaNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolDocument9 pagesHW 1 SolNatalia AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Chap23 10Document10 pagesChap23 10litrakhanNo ratings yet
- Homework (Lecture 4)Document31 pagesHomework (Lecture 4)anh anhNo ratings yet
- Test 1 SolutionDocument7 pagesTest 1 SolutionJake WischnefskiNo ratings yet
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- E2 121 09-PreviewDocument14 pagesE2 121 09-PreviewTremendous JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems For Chapter 22Document6 pagesSelected Problems For Chapter 22kevin.sanghyunNo ratings yet
- Fall 2014 HW 11 SolnsDocument22 pagesFall 2014 HW 11 Solnsaleman844No ratings yet
- Epotential2015 IRSDocument9 pagesEpotential2015 IRS吳俊陞No ratings yet
- Electric Fields: Chapter 21 KindaDocument18 pagesElectric Fields: Chapter 21 Kindaapi-96362001No ratings yet
- Full Download Quantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Quantum Mechanics 6th Rae Solution Manual PDF Full Chaptertortuous.osmiousr3v45i100% (21)
- p112 Lecture2Document22 pagesp112 Lecture2Othniel SulpicoNo ratings yet
- Phys12 SM Unit3 RDocument34 pagesPhys12 SM Unit3 RAdarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- L05S ch25 PDFDocument23 pagesL05S ch25 PDFGella QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Solution For Plasma PhysicDocument5 pagesSolution For Plasma Physicms_geo100% (6)
- Solucionario Chapter 15 Pag 21-35Document15 pagesSolucionario Chapter 15 Pag 21-35web SoftNert ChileNo ratings yet
- 최신대학물리학2 19Document16 pages최신대학물리학2 19minsukkim2323No ratings yet
- Chapter6 7thDocument14 pagesChapter6 7thMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- K Q Q R: General Physics 2Document4 pagesK Q Q R: General Physics 2Jolina MalanumNo ratings yet
- Poynting Vector E and BDocument4 pagesPoynting Vector E and BDao ZhangNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Chapter 23Document5 pagesPhysics Questions Chapter 23hamadaxx2000100% (1)
- 2 Electric FieldDocument2 pages2 Electric FieldsamanthaNo ratings yet
- Review Physics 3Document24 pagesReview Physics 3Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument14 pagesCoulomb's LawSpoodsNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 1 SolutionDocument17 pagesPhysics Assignment 1 SolutionKaniyan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Phys12 SM 07 6Document7 pagesPhys12 SM 07 6Adi SinghNo ratings yet
- Midterm 01 Physics 2 UTDocument8 pagesMidterm 01 Physics 2 UTJonathan OrNo ratings yet
- Additional Problems Electric Field Intensity: GivenDocument2 pagesAdditional Problems Electric Field Intensity: GivenJosua SaysonNo ratings yet
- HW 01 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW 01 SolutionPotatoes123No ratings yet
- Compile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviDocument10 pagesCompile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviSelma Regita MahardiniNo ratings yet
- Chap15 s08 ProbsDocument7 pagesChap15 s08 ProbsyiiviiezzNo ratings yet
- ch25 PDFDocument21 pagesch25 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - TutorialDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - TutorialDavidNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p105Document1 pageProblem21 p105IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p101Document1 pageProblem21 p101IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 95Document1 pageProblem21 95IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p104Document1 pageProblem21 p104IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 98Document1 pageProblem21 98IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 93Document1 pageProblem21 93IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p102Document1 pageProblem21 p102IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 94Document1 pageProblem21 94IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 99Document1 pageProblem21 99IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 p100Document1 pageProblem21 p100IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 89Document1 pageProblem21 89IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 91Document1 pageProblem21 91IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 86Document1 pageProblem21 86IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 87Document1 pageProblem21 87IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 88Document1 pageProblem21 88IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 85Document1 pageProblem21 85IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 82Document1 pageProblem21 82IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 70Document1 pageProblem21 70IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 79Document1 pageProblem21 79IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 80Document1 pageProblem21 80IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 77Document1 pageProblem21 77IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 75Document1 pageProblem21 75IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 74Document1 pageProblem21 74IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 73Document1 pageProblem21 73IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 72Document1 pageProblem21 72IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 71Document1 pageProblem21 71IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 68Document1 pageProblem21 68IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 64Document1 pageProblem21 64IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 66Document1 pageProblem21 66IENCSNo ratings yet
- Problem21 69Document1 pageProblem21 69IENCSNo ratings yet
- SAP S4 HANA LSMW ProcessDocument39 pagesSAP S4 HANA LSMW Processcendrine djukemNo ratings yet
- M2 - Variables, Measurements and Data CollectionDocument54 pagesM2 - Variables, Measurements and Data CollectionAzer Asociados SacNo ratings yet
- MR J3 A Instruction ManualDocument460 pagesMR J3 A Instruction ManualVictor Manuel Perez EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Torsion ShaftDocument6 pagesTorsion ShaftmichaelNo ratings yet
- Code Coupling For Simulation of Flow-Induced Vibrations: Elisabeth LONGATTE Fabien HUVELIN Mhamed SOULIDocument28 pagesCode Coupling For Simulation of Flow-Induced Vibrations: Elisabeth LONGATTE Fabien HUVELIN Mhamed SOULIAshraf S. HusseinNo ratings yet
- Online 6kVA: 94% Eficacia Factor de Potencia de 0.9 (4.5kW deDocument2 pagesOnline 6kVA: 94% Eficacia Factor de Potencia de 0.9 (4.5kW deVictor BlancoNo ratings yet
- EMD 645 Parts Catalog 302 Part 1Document164 pagesEMD 645 Parts Catalog 302 Part 1KarlaFernanda Roque Rodriguez0% (1)
- Ttester enDocument125 pagesTtester enDiego García MedinaNo ratings yet
- Astrology & I Ching - How Life WorksDocument97 pagesAstrology & I Ching - How Life Worksajakuk100% (2)
- CVG 2132-Lec 2 - Engineering Units & Water Chemistry - StudentDocument47 pagesCVG 2132-Lec 2 - Engineering Units & Water Chemistry - StudentOusama KadriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Measurements & UncertaintyDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Measurements & Uncertaintysofiea hazriNo ratings yet
- Hamacher. On Celan's TodtnaubergDocument41 pagesHamacher. On Celan's Todtnaubergkukaandmika100% (1)
- Oil Immersed Type Power TransformerDocument17 pagesOil Immersed Type Power TransformerRafaela Ribeiro de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- S120 Communication FCT Man 0620 en-USDocument246 pagesS120 Communication FCT Man 0620 en-USadnane adNo ratings yet
- 1999 - TMTT Packaged Semiconductor Laser Optical Phase-Locked Loop (OPLL) For Photonic Generation, Processing and Transmission of Microwave SignalsDocument8 pages1999 - TMTT Packaged Semiconductor Laser Optical Phase-Locked Loop (OPLL) For Photonic Generation, Processing and Transmission of Microwave SignalsshahabniaziNo ratings yet
- RTOS VxWorksDocument8 pagesRTOS VxWorksAshraful HimelNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 12th Dec 2022 Shift-4 by CrackuDocument29 pagesSSC CGL 12th Dec 2022 Shift-4 by CrackuKukuNo ratings yet
- ARK Intel CPU Products ComparisonDocument2 pagesARK Intel CPU Products Comparisonkhopdi_number1No ratings yet
- One LineDocument7 pagesOne LineTerpal PlusNo ratings yet
- GVF Asparagus Cart 11050Document2 pagesGVF Asparagus Cart 11050Carlos CubaNo ratings yet
- Editable Test Item Analysis Template Sy 2022 2023Document6 pagesEditable Test Item Analysis Template Sy 2022 2023Michelle Rivel TallerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geometry ProofsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Geometry ProofsNaufalzzNo ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Document5 pagesFHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Zheng Kit OoiNo ratings yet
- Activity 6-3 Name: Joella Mae Escanda Section: B 1. Which Is More Soluble, Calcium Hydroxide or Copper (I) Bromide? JustifyDocument3 pagesActivity 6-3 Name: Joella Mae Escanda Section: B 1. Which Is More Soluble, Calcium Hydroxide or Copper (I) Bromide? JustifyJOELLA MAE ESCANDANo ratings yet
- Metacentric HeightDocument9 pagesMetacentric HeightNUR BADRINA NABILAH ZURIZALNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTSDocument7 pagesASSESSMENTSJohn Michael BolocNo ratings yet
- Normality Study AddaDocument26 pagesNormality Study AddaTammanurRaviNo ratings yet
- A Power-Law Model of Psychological Memory Strength in Short - and Long-Term RecognitionDocument11 pagesA Power-Law Model of Psychological Memory Strength in Short - and Long-Term RecognitioneastareaNo ratings yet