Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITIL v3 Differences
Uploaded by
waheguru009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITIL v3 Differences
Uploaded by
waheguru009Copyright:
Available Formats
ITIL: The Key Differences Between Versions 2 and 3
A brief History of ITIL
First published in the late 1980s, ITIL started as a project to document best practices in IT. Since that time it
has become known worldwide as the most credible framework for IT Service Management and is now an
international standard (ISO IEC 20000).
The second version of ITIL was published in 2000 and then in 2004 work commenced on the ITIL version 3.
The project has involved extensive consultations with thousands of global ITSM Practitioners from the public
and private sectors, vendors, qualification bodies, exam institutes and education providers.
Key Changes:
• Move towards a service-driven lifecycle approach
• More prescriptive guidance
• Demonstration of return on investment
Key Evolutional Changes in ITSM Philosophy:
Business and IT – From Alignment to Integration
For many years, we have been discussing the topic of how to align business and IT objectives. We have
done this from the assumption that while business and IT share the same corporate brand, they are
somehow two separate and very distinct functions.
However, when does the line between the business process and its supporting technology begin to fade to a
point where there is no longer a true ability to separate or revert back to manual options?
If you consider banking as an example, the financial management business processes and their supporting
technologies are now so inter-dependent that they are inseparable. It is due to this growing realisation that
the term alignment is being replaced with the concept of integration.
From Value Chain Management to Value Service Network Integration
When reading ITIL v2, you get the perception that the business and IT relationship is primarily about a
business customer being supported by a single internal IT service provider (Value Chain Management). Little
acknowledgement or guidance is provided about the reality of life never being quite that simple.
Today’s business and IT relationship for service provision is much more complicated and complex than the
concept of a single provider meeting all business needs. We need to consider that yes, there are internal IT
functions, but some are found within a business unit structure where others are providing a shared service
model to multiple business units.
Add to this the option of using different external outsourcing options or leveraging software as a service
(SaaS) model and what you end up with is what ITIL v3 refers to as an Integrated Value Service Network.
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 1
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
From Linear Service Catalogues to Dynamic Service Portfolios
While ITIL has always been referred to as an IT Service Management Framework, the primary focus up until
now has been on the ten Service Support and Delivery processes. In previous versions of ITIL, the concept
of a "service" has almost been an afterthought or at least something you would get to later.
Consider that in ITIL v2 the process of Service Level Management has, as one of its many deliverables, a
Service Catalogue which can be summarised from the theory as a brochure of IT Services. Where IT
publishes the services it provides with their default characteristics and attributes or Linear Service
Catalogue.
In contrast to this, a Dynamic Service Portfolio can be interpreted as the product of a strategic process
where service strategy and design conceive of and create services that are built and transitioned into the
production environment based on business value. From this point, an actionable service catalogue
represents the published services and is the starting point or basis for service operations and ongoing
business engagement.
The services documented in this catalogue are bundled together into fit-for-purpose offerings that are then
subscribed to as a collection and consumed by business units.
From Integrated Processes to The Service Management Lifecycle
Based on publicly available information, we know the ITIL v3 core books are structured around a Service
Lifecycle.
This new structure organises the processes we understand from ITIL v2 with additional content. While
processes are important, they are secondary and only exist to plan for, deliver and support services. This
moves the importance and profile of the Service Catalogue from being an accessory of the Service Level
Management process to being the corner stone of ITSM.
As organisations evolve from a technology focus to a service orientation focus, these core changes to ITIL
provide the context and ability to support this emerging reality.
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 2
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
New areas in ITIL v3 (Core publications)
Core ITIL v2 – All processes Core ITIL v3 – Lifecycle Comments
except Service Desk approach
Service Desk Service Desk The focus remains the same
Incident Management Incident Management Request The addition of an optional request
Fulfilment fulfilment process
Problem Management Problem Management Remains the same but is only
covered as an overview
Change Management Change Management Slight changes in terminology i.e.
CAB/EC – ECAB
Release Management Release and Deployment Release and deployment covered
Management as an overview only but an
introduction of the V model is best
introduced here
Configuration Management Service Asset and Service Assets are included with
Configuration Management Configuration. Covered as an
overview
Service Level Management Service Portfolio Management Focus is on the Lifecycle approach
and not the process of SLM.
Service Level Management
Included is Supplier Management
Supplier Management and Service Portfolio Management
Financial Management for IT Financial Management for IT Main concepts are unchanged but
Services Services the focus is more on economics and
VOI
Capacity Management Capacity Management Capacity as an overview only there
is the introduction of Demand
Management at the Strategic level
in terms of Value to the Customer
Availability Management Availability Management Availability as an overview and the
introduction of Access Management
Access Management
IT Service Continuity IT Service Continuity ITSCM as an overview supporting
Management Management the Business Continuity
IT Security Management (EXIN IT Security Management The introduction of IT Security
only courses) Management, (Only EXIN included
this as a V2 process)
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 3
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
New areas in ITIL v3 (non-core publications)
Other Library Books v2-v3 additional scope Comments
Planning to Implement Service
Management
• What is the vision?
• Where are we now?
• Where do we want to
be?
• How do we get where
we want to be?
• How do we check our
milestones have been
reached?
• How do we keep the
momentum going?
ICT Infrastructure Management
• Design and Planning • Guidance for Service The ICTIM publication included
• Deployment Design many of the roles that are now
• Basis for Release and included as part of the V3 core.
• Operations
Deployment
• Technical Support
• IT Operations
• *Appendices Management
Security Management
Application Management
• Positioning of • Service Strategy basis Business value and the Service
Application Lifecycle are mentioned in the V2
Management Application Management publication
• Managing the business and these have been brought up-to-
value date in V3
• Aligning the delivery
strategy with key
business drivers and
organisational
capabilities
• The Application
Management Lifecycle
• Organising roles and
functions
• Control methods and
techniques
Business Perspective
Software Asset Management
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 4
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
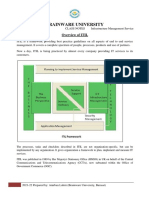
ITIL Qualifications
Structure
V2 Examinations ‘standalone’ V3 Examinations, points awarded toward an IT
Diploma
Foundation – pre-requisite for; Foundation– pre-requisite for;
Practitioners Capability – Process / Role based
Management – Lifecycle based
Managers IT Diploma
Advanced IT Diploma
Key focus for foundation qualification of each core publications
Service Strategy
• Service Management strategy and the links to other best practices and complementary standards
• Policy setting, Strategic Assets and objectives for services
• Market space, Provider types, Business case, Risks, Constraints, Value = Utility and Warranty
• Customer assets and Service assets, Service Models and Service Portfolio, which includes 3 areas,
what is being developed and in the pipeline i.e. requirements, what is currently being offered to the
customer i.e. Service Catalogue and what is being retired
• Planning and implementing service strategies
• Processes: Financial Management for IT Services, Demand Management
• Roles: Service Owner, Financial Manager, Demand Manager
Service Design
• 5 aspects of design in the Lifecycle
• The 4Ps – People, Process, Products, Partnerships
• Processes: Service Catalogue Management, SLM, Supplier Management, Availability Management,
Capacity Management, ITSCM, IT Security Management
• Roles: Design Manager, Service Level Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, Supplier Manager,
Process Owner (General)
Service Transition
• Managing new or a changed service change
• The ‘V’ Model or the Configuration and Test Model
• Processes: Change Management, Release and Deployment Management, Service Asset and
Configuration Management, Knowledge Management
• Roles: Change Manager, Release and Deployment Manager, Test and Validation Manager, Service
Asset Manager, Configuration Manager, Configuration Analyst, Configuration Administrator /
Librarian, Configuration Management System (CMS) / tools Administrator
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 5
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
Service Operation
• Managing services
• The 7Rs of Change Management
• Processes: Incident Management, Request Fulfilment, Problem Management, IT Operations
Management, Application Management, Technical Management, Event Management, Access
Management
• Roles: Service Desk, Incident Manager, Major Incident Manager, Problem Manager, Operations
Control roles – Mainframe team, Server Department, Desktop team, Storage team etc… Facilities
Management roles – Data centre team, power manager, fire systems manager etc…
Continual Service Improvement
• Project approach
• The 7 step improvement Process
• Types of metrics: Technology Process and Service
• Continual Service Improvement Model
• Process Improvement stages
• Deming Cycle
Further Information
ILX Group are a leading provider of ITIL training and consultancy services. If you would like to talk to a
training adviser about you requirements please call 01270 611600.
If you would like to keep up to date on all developments in ITIL please visit our resource centre:
http://www.ilxgroup.com/itil-v3-resources.htm
© Copyright ILX Group plc, 2007 Page 6
ILX Group plc. Registered in England & Wales No. 03525870. Registered Office: One London Wall, London, EC2Y 5AB.
You might also like
- Itil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeDocument16 pagesItil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeAhmed M. EzzatNo ratings yet
- Itil Best Practices - OEM 10gDocument26 pagesItil Best Practices - OEM 10gMohammed JawaidNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Service ManagementDocument5 pagesInformation Technology Service ManagementChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- "ITIL Coming of Age With V3": Author: Prakash SharmaDocument5 pages"ITIL Coming of Age With V3": Author: Prakash SharmaGomathy PadmaNo ratings yet
- ITIL Framework for Effective IT Service ManagementDocument30 pagesITIL Framework for Effective IT Service ManagementYátish BáthlaNo ratings yet
- Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument114 pagesLva1 App6892 PDFVishwanatham RamanaNo ratings yet
- ITIL BasicsDocument5 pagesITIL BasicsSubroto BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- ITIL® Maturity Model: PublicDocument14 pagesITIL® Maturity Model: PublicforbiswajitNo ratings yet
- Ebook-TOPdesk-BestPractices-Service-Management INGLESDocument47 pagesEbook-TOPdesk-BestPractices-Service-Management INGLESAntonio Eduardo da CostaNo ratings yet
- Itil PDFDocument25 pagesItil PDFRavi ChandranNo ratings yet
- ITIL Best PracticesDocument12 pagesITIL Best PracticesTariq GurooNo ratings yet
- BOOT CAMP (DAY 1) (Autosaved)Document157 pagesBOOT CAMP (DAY 1) (Autosaved)Ashish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- ITIL White Paper v1Document3 pagesITIL White Paper v1hahnj02100% (1)
- Itil and Iso 20000Document56 pagesItil and Iso 20000Anshuman Tiwari100% (2)
- Introduction To ITIL: An Overview of The Fundamentals of ITILDocument9 pagesIntroduction To ITIL: An Overview of The Fundamentals of ITILRaghuvamsi KandukuriNo ratings yet
- ITIL COBIT and ISODocument5 pagesITIL COBIT and ISOkirui kipronohNo ratings yet
- Axelos - Itil The BasicsDocument6 pagesAxelos - Itil The Basicstest userNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Prasanta Kumar Sahu: ITIL - IT Service ManagementDocument64 pagesPresented By: Prasanta Kumar Sahu: ITIL - IT Service ManagementTripathy Kumar Sarthak100% (1)
- ITIL 2011 Foundation Training: ITIL School of ExcellenceDocument97 pagesITIL 2011 Foundation Training: ITIL School of ExcellenceVenki VenkiNo ratings yet
- ITIL - TrainingCourseDocument111 pagesITIL - TrainingCourseKikeNo ratings yet
- ISO 20000: A Look into the Future of IT Service ManagementDocument51 pagesISO 20000: A Look into the Future of IT Service Managementsaieesha2012_8036449No ratings yet
- SDA - ITIL 4 BrochureDocument9 pagesSDA - ITIL 4 BrochureALEX RICHAR SILVA GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Brainware University: Overview of ITILDocument7 pagesBrainware University: Overview of ITILabcdNo ratings yet
- RKT Itsm OverviewDocument71 pagesRKT Itsm OverviewMohammed Anwer KaleemNo ratings yet
- ITIL & ServiceDesk PlusDocument40 pagesITIL & ServiceDesk PlusArthur EkowNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Learning Course - Day1Document32 pagesITIL 4 Foundation Certification Learning Course - Day1royvan000100% (2)
- Business Value in Implementing A Standard ITSM SystemDocument6 pagesBusiness Value in Implementing A Standard ITSM SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Itil - Help or Hindrance?: Management and Infrastructure SIG MeetingDocument26 pagesBeginners Guide To Itil - Help or Hindrance?: Management and Infrastructure SIG MeetingSurinder DalalNo ratings yet
- Itil CobitDocument16 pagesItil CobitrashmimehNo ratings yet
- Introducing ITIL Best Practices For IT Service Management: Presentation Will Begin at 9:00 AmDocument90 pagesIntroducing ITIL Best Practices For IT Service Management: Presentation Will Begin at 9:00 Amearth2783No ratings yet
- ITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital AgenciesDocument6 pagesITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital Agenciesroyvan000No ratings yet
- Classifying ITIL ProcessesDocument10 pagesClassifying ITIL ProcessesJailton NonatoNo ratings yet
- ITIL Capacity ManagementDocument34 pagesITIL Capacity Managementmohamad7khadir7No ratings yet
- The Itil FrameworkDocument3 pagesThe Itil Frameworkinsomniac432No ratings yet
- Implementing IT Service Management StandardsDocument57 pagesImplementing IT Service Management Standardsandank Lallana100% (1)
- ITIL4 Foundation Session1Document38 pagesITIL4 Foundation Session1ahmed.abdelsatar.itNo ratings yet
- ITIL Self-Assessment Approach For Small and MediumDocument7 pagesITIL Self-Assessment Approach For Small and MediumaminaNo ratings yet
- IT Governance-UMB 17122016Document30 pagesIT Governance-UMB 17122016Niputu CintyadewiNo ratings yet
- What's New in ITIL V3Document2 pagesWhat's New in ITIL V3Marlon RicafortNo ratings yet
- ITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital AgenciesDocument6 pagesITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital AgenciesVamsi aravetiNo ratings yet
- ITIL® vs. ISO/IEC 20000: Similarities and Differences & Process MappingDocument9 pagesITIL® vs. ISO/IEC 20000: Similarities and Differences & Process MappingmixuviNo ratings yet
- Ebk It Infrastructure Library OverviewDocument11 pagesEbk It Infrastructure Library OverviewAllen Earl Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) : Driving Business Growth Through ITDocument8 pagesIT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) : Driving Business Growth Through ITmkolapoNo ratings yet
- Service Transition by SNOWDocument10 pagesService Transition by SNOWVijay JainNo ratings yet
- Service Design by SNOWDocument12 pagesService Design by SNOWVijay JainNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 FoundationDocument5 pagesITIL 2011 FoundationDenz TajoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Service Management and ITILDocument27 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Service Management and ITILvenki_hinfotechNo ratings yet
- 04 It Infrastructure Library Overview Service OperationDocument11 pages04 It Infrastructure Library Overview Service OperationSijilNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Learning Course - Day1Document32 pagesITIL 4 Foundation Certification Learning Course - Day1royvan000100% (5)
- ITILOverviewDocument29 pagesITILOverviewCeci ADNo ratings yet
- ITIL History and Best PracticesDocument17 pagesITIL History and Best PracticesQolbyYostraEvantAdhaNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Operation Describes Best Practice ForDocument1 pageITIL Service Operation Describes Best Practice ForKartik ShastriNo ratings yet
- 2ITIL Overview IssueDocument101 pages2ITIL Overview IssueAiman SubzposhNo ratings yet
- IT and Business Process Performance Management: Case Study of ITIL Implementation in Finance Service IndustryDocument8 pagesIT and Business Process Performance Management: Case Study of ITIL Implementation in Finance Service IndustrysenegebreNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Service Management ISO 20000-1Document40 pagesInformation Technology Service Management ISO 20000-1ikbalNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Context: 1.1.5 Target AudienceDocument1 page1.2 Context: 1.1.5 Target AudienceKartik ShastriNo ratings yet
- ITIL EssentialsDocument130 pagesITIL Essentialsnahid423100% (1)
- Mathematical Methods for Economics: Calculating DerivativesDocument8 pagesMathematical Methods for Economics: Calculating DerivativesLennard PangNo ratings yet
- Book of RecordsDocument395 pagesBook of RecordsareyoubeefinNo ratings yet
- Planning, organizing, staffing and directing roles in education administrationDocument1 pagePlanning, organizing, staffing and directing roles in education administrationtheresaNo ratings yet
- Emerson Electric Financial Statement AnalysisDocument6 pagesEmerson Electric Financial Statement Analysismwillar08No ratings yet
- Event Concept Paper Edited1Document20 pagesEvent Concept Paper Edited1Tyler HerroNo ratings yet
- Customer equity value and lifetime revenue importanceDocument10 pagesCustomer equity value and lifetime revenue importanceSniper ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Bukit Asam Anual ReportDocument426 pagesBukit Asam Anual Reportwandi_borneo8753No ratings yet
- Cathay Pacific v. VasquezDocument2 pagesCathay Pacific v. Vasquezrgtan3No ratings yet
- Tensor Catalogue USA PDFDocument72 pagesTensor Catalogue USA PDFdavev2005No ratings yet
- US Economics Digest: The 2014 FOMC: A New Cast of CharactersDocument10 pagesUS Economics Digest: The 2014 FOMC: A New Cast of CharactersGlenn ViklundNo ratings yet
- FINAL ASEAN Handbook 01 - Engineering ServicesDocument92 pagesFINAL ASEAN Handbook 01 - Engineering ServicesGerry GsrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, Problem 5.: Common Multiple of The Lives of The AlternativesDocument7 pagesChapter 5, Problem 5.: Common Multiple of The Lives of The AlternativesMishalNo ratings yet
- Distridution and Channel MemberDocument6 pagesDistridution and Channel Memberabdulhaq4No ratings yet
- Kasneb Entrepreneurship and Communication For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Section 1 Question OneDocument1 pageKasneb Entrepreneurship and Communication For More Free Past Papers Visit May 2014 Section 1 Question OneTimo PaulNo ratings yet
- Platinum Gazette 29 July 2011Document12 pagesPlatinum Gazette 29 July 2011Anonymous w8NEyXNo ratings yet
- QTC Cert Module 2 CPQDocument41 pagesQTC Cert Module 2 CPQjalaj01No ratings yet
- SACCO Budgeting and Business Planning ManualDocument54 pagesSACCO Budgeting and Business Planning ManualFred IlomoNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument32 pagesExecutive SummaryMuhammad ZainNo ratings yet
- Cheniere Energy Valuation ModelDocument11 pagesCheniere Energy Valuation Modelngarritson1520100% (1)
- Ryan M Scharetg TMobile BillDocument3 pagesRyan M Scharetg TMobile BillJonathan Seagull LivingstonNo ratings yet
- Cleansheet Target CostingDocument4 pagesCleansheet Target CostingrindergalNo ratings yet
- Silicon Valley Community Foundation 2008 990Document481 pagesSilicon Valley Community Foundation 2008 990TheSceneOfTheCrimeNo ratings yet
- 02 Kanto Region (Kaigofukushishi) 12000017Document4 pages02 Kanto Region (Kaigofukushishi) 12000017bnp2tkidotgodotidNo ratings yet
- Suzlon EnergyDocument32 pagesSuzlon EnergymysterydevilNo ratings yet
- Internship Report of State Bank of Pakistan KarachiDocument180 pagesInternship Report of State Bank of Pakistan KarachixavanahNo ratings yet
- KFC Case Study by MR OtakuDocument36 pagesKFC Case Study by MR OtakuSajan Razzak Akon100% (1)
- Flavia CymbalistaDocument3 pagesFlavia Cymbalistadodona7772494No ratings yet
- BSC Hospital 1Document24 pagesBSC Hospital 1sesiliaNo ratings yet
- Life After Seafaring A Guide To Post Sea CareersDocument4 pagesLife After Seafaring A Guide To Post Sea CareersJeric SorianoNo ratings yet
- Client Info Sheet - PR PetroleumDocument4 pagesClient Info Sheet - PR PetroleumAnonymous E5GfQD7dhZNo ratings yet