Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAGE Is Sequence Sampling Technique in Which Very Short Sequence Tags Are Joined Into Long Concatamers
Uploaded by
Soumitra NathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAGE Is Sequence Sampling Technique in Which Very Short Sequence Tags Are Joined Into Long Concatamers
Uploaded by
Soumitra NathCopyright:
Available Formats
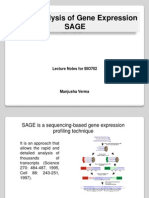
SAGE (Serial Analysis of Gene Expression)
SAGE is sequence sampling technique in which very short sequence tags are joined into long
concatamers. The size of the SAGE tag is optimal for high throughput analysis but genes can still be
identified unambiguously. A concatamer may contain more than 50 tags, and each SAGE sequence is
thus equivalent to more than 50 independent cDNA sequence experiments. SAGE is therefore
appropriate for the analysis of rare mRNAs.
SAGE (serial analysis of gene expression) is a sequence sampling technique that circumvents the
problems associated with random clone sequencing by sampling many different cDNAs in one
experiment. This is achieved by using very short ESTs and joining them into a long concatamer prior to
sequencing. The ESTs are just long enough to allow accurate and unambiguous gene identification.
The overall process of SAGE can be summarized as follows.
1. An mRNA population is reverse transcribe to generate cDNA, using a biotinylated oilgo dT-primer.
2. The cDNA is digested using restriction enzyme that cleaves very frequently, such as NlaIII, leaving 3’
fragments of few hundred base pairs labeled with biotin.
3. The 3’ end of cDNA is than captured and the other fragment is discarded.
4. The cDNA is divided into two pools, and each pool is ligated to a different linker (a ds oligonucleotide
with a specific overhang, in this case matching the overhang is generated by NlaIII). The linker carries an
internal recognition site for type II restriction enzymes such as FokI.
5. Cleavage with type II restriction enzyme generates a very short sequence tag attached to the linker,
and this known as a SAGE ditags.
6. The biotinylated fragments are discarded, and SAGE tags with different linkers are ligated tail to tail to
form dimmers called ditags.
7. The ditags are amplified by PCR using primer that anneals to the linkers.
8. The linker are removed using NlaIII and the ditags are randomly joined together in a long concatamer.
9. The concatamer is sequenced.
10. Sequence analysis identifies the tags and thus the associated mRNAs. The number of times each tag
appears in the concatamer is indicative of the mRNA abundance.
You might also like
- Sage Technology and Its ApplicationsDocument61 pagesSage Technology and Its Applicationsthamizh555No ratings yet
- Serial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Document34 pagesSerial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Rohit PhalakNo ratings yet
- SageDocument12 pagesSagelordniklausNo ratings yet
- Several Methods For Quantitative Analysis of The TranscriptomeDocument12 pagesSeveral Methods For Quantitative Analysis of The TranscriptomeSeeni BalajiNo ratings yet
- Intro REDocument5 pagesIntro REespada_fourNo ratings yet
- 1.2,3 DNA SequencingDocument64 pages1.2,3 DNA SequencingMansiNo ratings yet
- Deep Cap Analysis Gene Expression (CAGE) : Genome-Wide Identification of Promoters, Quantifi-Cation of Their Expression, and Network InferenceDocument4 pagesDeep Cap Analysis Gene Expression (CAGE) : Genome-Wide Identification of Promoters, Quantifi-Cation of Their Expression, and Network InferenceAaNo ratings yet
- Expression ProfilingDocument8 pagesExpression ProfilingSreedurgalakshmi KNo ratings yet
- Cloning StrategiesDocument35 pagesCloning Strategiesskmishra8467% (3)
- Construction of Genomic and cDNA Libraries-AmitDocument10 pagesConstruction of Genomic and cDNA Libraries-AmitPrashant BajpaiNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument36 pagesBiotechnologyFarwa JawadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsDocument11 pagesLecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsAngelica SmithNo ratings yet
- B4 Gene ArraysDocument15 pagesB4 Gene ArraysRizkia Milladina HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- The cDNA Library (Notes)Document9 pagesThe cDNA Library (Notes)sharadmore211No ratings yet
- Construction of Genomic LibraryDocument16 pagesConstruction of Genomic Librarysivagurunathan.P80% (5)
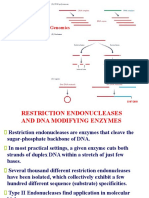
- Restriction - Endonucleases For Gene Manipulation - Unit 1 (Portion)Document17 pagesRestriction - Endonucleases For Gene Manipulation - Unit 1 (Portion)akshayaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology: Ashok Kumar (70700012) Ila Chawla (70700019)Document54 pagesGenetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology: Ashok Kumar (70700012) Ila Chawla (70700019)Harshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Transcriptom E: by Dr. Ina GargDocument60 pagesHuman Transcriptom E: by Dr. Ina GargIna GargNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Cloning TechnologyDocument71 pagesRecombinant DNA Cloning TechnologyRajkaran Moorthy100% (1)
- Gene Cloning StrategiesDocument35 pagesGene Cloning Strategiesnishit1990100% (2)
- Restriction Enzymes ActivityDocument7 pagesRestriction Enzymes ActivityDoree GlantzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - DNA Modifying EnzymesDocument64 pagesChapter 5 - DNA Modifying EnzymesLuong Nguyen50% (4)
- Recombinant Dna Technology: EcoriDocument2 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology: EcoriluisynonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Construction of DNA LibrariesDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Construction of DNA LibrariesvijikalkiNo ratings yet
- Bodhishukha School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument41 pagesBodhishukha School: Biology Investigatory ProjectParnadip PaulNo ratings yet
- L3-GeneTech DNA SequencingDocument83 pagesL3-GeneTech DNA SequencingSwayamNo ratings yet
- cDNA LibraryDocument10 pagescDNA LibraryjanapriyaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDocument8 pagesContinuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDebapriya HazraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 PresentationDocument47 pagesChapter 18 PresentationNealNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Deals With Problems of Heredity and VariationDocument37 pagesGenetics: Deals With Problems of Heredity and VariationjdazuelosNo ratings yet
- cDNA, cDNA Library and CloningDocument70 pagescDNA, cDNA Library and CloningDerick SemNo ratings yet
- 2859 764 4 61932GeneticEngineeringDocument40 pages2859 764 4 61932GeneticEngineeringAman HoodaNo ratings yet
- Bacaan SlideDocument11 pagesBacaan SlidemuhnameiskristinNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Molecular Biology (COMPLETE)Document51 pagesTechniques in Molecular Biology (COMPLETE)Endik Deni NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Poulain2017NanoCAGE A Method For The Analysis of Coding and Noncoding 5'-Capped TranscriptomesDocument53 pagesPoulain2017NanoCAGE A Method For The Analysis of Coding and Noncoding 5'-Capped TranscriptomesKito TongHuiNo ratings yet
- Cloning StrategiesDocument41 pagesCloning StrategiesKumar Aavula100% (2)
- Kloning Gen: Penyusunan Pustaka GenomikDocument79 pagesKloning Gen: Penyusunan Pustaka GenomikEndah Dwi sitaresmiNo ratings yet
- The Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequence-Tagged SitesDocument7 pagesThe Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequence-Tagged SitesPisi MicaNo ratings yet
- Traditional CloningDocument2 pagesTraditional Cloningshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- Shotgun SequencingDocument29 pagesShotgun SequencingKhyati JoshiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Workbook UpdateDocument36 pagesGenetics Workbook UpdateLauren WinnettNo ratings yet
- Molecular Marker: Study NotesDocument14 pagesMolecular Marker: Study NotesSasikala RajendranNo ratings yet
- 1 Enzimas IDocument55 pages1 Enzimas IconstanzaNo ratings yet
- Revised TERM PAPERDocument19 pagesRevised TERM PAPERVikal RajputNo ratings yet
- Perspectives: Rna-Seq: A Revolutionary Tool For TranscriptomicsDocument7 pagesPerspectives: Rna-Seq: A Revolutionary Tool For Transcriptomicsjubatus.libroNo ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument56 pagesGENETICSKeziah Tayco100% (1)
- Concise Notes Summary Genetic Engineering PCRDocument26 pagesConcise Notes Summary Genetic Engineering PCRVoice AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Screening of C-Dna Library Using Colony PCRDocument7 pagesScreening of C-Dna Library Using Colony PCRIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Construction of Genomic Library - The Idea of Amplifying Very Large Mixtures of DNA Fragments andDocument18 pagesConstruction of Genomic Library - The Idea of Amplifying Very Large Mixtures of DNA Fragments andPrabhjot Brar100% (1)
- DNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNADocument16 pagesDNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNAmohamedtnsNo ratings yet
- A Combinatorial Approach To Hybrid Enzymes Independent of DNA HomologyDocument5 pagesA Combinatorial Approach To Hybrid Enzymes Independent of DNA HomologyArdiellaputriNo ratings yet
- DNA LibraryDocument73 pagesDNA LibraryDGA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- cDNA Library - WikipediaDocument4 pagescDNA Library - WikipediaHkr GamingNo ratings yet
- Chia-Pet (Chromatin Interaction Analysis by Paired-End Tag Sequencing)Document13 pagesChia-Pet (Chromatin Interaction Analysis by Paired-End Tag Sequencing)Naresh Prasad SapkotaNo ratings yet
- History of Genetic Manipulation: Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument69 pagesHistory of Genetic Manipulation: Recombinant DNA TechnologyBagus WijayaNo ratings yet
- Block II Lecture 1: Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument42 pagesBlock II Lecture 1: Recombinant DNA TechnologyRitesh Chandrakant SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Ant Dna TechnologyDocument18 pagesAnt Dna Technologysa2325No ratings yet
- Cloning Tech GuideDocument40 pagesCloning Tech GuideioncacaciosuNo ratings yet
- Supporting Information: Supplementary Note 1 Encoding: Data To DNA SequencesDocument25 pagesSupporting Information: Supplementary Note 1 Encoding: Data To DNA Sequencesweixing wangNo ratings yet
- DNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensFrom EverandDNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensNo ratings yet
- 2021 LifeDocument17 pages2021 LifeSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Role of Cadmium and Lead Tolerant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Seedling Germination of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Document5 pagesRole of Cadmium and Lead Tolerant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Seedling Germination of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Soumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of Metal-Tolerant and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria From Soil Samples of Cachar District of Assam, IndiaDocument9 pagesIsolation and Identification of Metal-Tolerant and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria From Soil Samples of Cachar District of Assam, IndiaSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Me NTH ADocument4 pagesMe NTH ASoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument2 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Structure of TCR: T - Cell ReceptorDocument2 pagesStructure of TCR: T - Cell ReceptorSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- The Human Genetic Code - The Human Genome Project and BeyondDocument6 pagesThe Human Genetic Code - The Human Genome Project and BeyondKovács Árpád FerencNo ratings yet
- Genetics-Virology of EDocument2 pagesGenetics-Virology of ESoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Paper 18Document6 pagesPaper 18Soumitra NathNo ratings yet
- DockingDocument7 pagesDockingSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Overview On BioinformaticsDocument23 pagesOverview On BioinformaticsSoumitra NathNo ratings yet