Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adsorption Exp Calculations
Uploaded by
Dilip Singh ChoudharyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adsorption Exp Calculations
Uploaded by
Dilip Singh ChoudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculations:
We have the volume of NaOH used for titrating the equilibrium solution of acetic acid (with
activated charcoal) and hence we can calculate the equilibrium concentration of acetic acid C’
We know that,
N1V1= N2V2 ………(1)
Here,
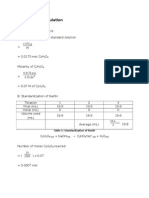
N1 = Normality of NaOH solution =0.1N
N2 = Normality of sample (equilibrium solution of acetic acid) =?
V1 = volume of NaOH used for titrating the sample (in ml)
V2 = volume of sample taken = 10 ml
0.1 * V1 = N2 * 10
C’ = N2 = 0.01* V1 (normality and molarity is same for acetic acid) …(2)
With the help of equation (2) we can calculate the equilibrium concentration of acetic acid
and then.
We used 250 ml of acetic acid solution , so mass of solute adsorbed is
x = (C0 – C’)*0.250*60 gm ; (mol. Wt. of acetic acid = 60) .……..(3)
Weight of activated charcoal m = 2 gm
(x/m) = [(C0 – C’)*0.250*60] / 2 ……….(4)
By using the eq. (2) and eq. (4) & observation table , we calculate the values of C’ and
x/m. and draw the table given below,
Intial Volume equilibrium
concentration of NaOH concentration
S.No. x/m log (C’) log(x/m)
of acetic acid used V1 of acetic acid
C0 (in M) (in ml) C’ (in M)
1. 0.0625 5.5 0.055 0.05625 -1.2596 -1.2498
2. 0.125 11.0 0.11 0.1125 -0.9586 -0.9488
3. 0.25 22.9 0.229 0.1575 -0.6402 -0.8027
4. 0.5 46.0 0.46 0.3 -0.3372 -0.5229
5. 1.0 95.0 0.95 0.375 -0.0223 -0.426
Now Freundlich adsorption isotherm equation given by
n
(x/m) = k*C’ …….(5)
By taking log of the eq.(5)
log(x/m) = logk + n*logC’ .....…(6)
Here,
(x/m) = amount of the solute solute adsorbed per gram of adsorbent
x = mass of adsorbate (in gm)
m = mass of adsorbent (in gm)
C’ = equilibrium concentration of acetic acid
k & n are constant
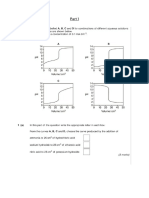
Equation (6) shows a linear equation , by using table draw a graph between
log (x/m) and logC’ [logC’ as a abscissa and log(x/m) as a ordinate.]
and get the intercept and slope..
from the graph,
slope of the graph = n = 0.668
intercept of graph = logk = -0.359
k = 10-0.359
k= 0.4375
You might also like
- Flas K# Mass of Charcoa L (G) Initial Concentrati On of Acoh (M) Volume of Naoh Used (ML) Run 1 Run 2Document2 pagesFlas K# Mass of Charcoa L (G) Initial Concentrati On of Acoh (M) Volume of Naoh Used (ML) Run 1 Run 2shaiNo ratings yet
- Choba 408 EXP 2Document12 pagesChoba 408 EXP 2Choba Tapaphiwa ChobaNo ratings yet
- NCHE312Document11 pagesNCHE312Charmaine MoyoNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Acetic Acid On Charcoal SurfaceDocument3 pagesAdsorption of Acetic Acid On Charcoal SurfaceDrGaurav Rajput100% (1)
- Safonification Conductometrically SS-13062021 UploadDocument3 pagesSafonification Conductometrically SS-13062021 UploadNerdNo ratings yet
- Exp5 Baru..Document13 pagesExp5 Baru..ibrahimkhadijah100% (41)
- Determination of Composition of Complexes Using Jobs Method (1) NoDocument10 pagesDetermination of Composition of Complexes Using Jobs Method (1) NoCh Safdar FarukhNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment AdsorptionDocument7 pagesLab Experiment AdsorptionchiragdbeckNo ratings yet
- Adsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuDocument7 pagesAdsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuZhu Chen ChuanNo ratings yet
- SKL 1013 (Laboratory Report 1)Document12 pagesSKL 1013 (Laboratory Report 1)Raajeshwary.TNo ratings yet
- Practical LabDocument7 pagesPractical Labdaudiali2002No ratings yet
- Exp-4 Date-Adsorption of Acetic Acid On Activated Charcoal: TheoryDocument4 pagesExp-4 Date-Adsorption of Acetic Acid On Activated Charcoal: TheorySUDIPA KONERNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 (Recovered)Document36 pagesExperiment 7 (Recovered)Manda BaboolalNo ratings yet
- App05 Vir 2013Document3 pagesApp05 Vir 2013kagisokhoza000No ratings yet
- EXP 5 KoloidDocument12 pagesEXP 5 KoloidLau Yong HuiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Kimia Fisika Adsorpsi Pada Larutan: Oleh Gian Habli Maulana 161424011Document10 pagesLaporan Praktikum Kimia Fisika Adsorpsi Pada Larutan: Oleh Gian Habli Maulana 161424011giangantengNo ratings yet
- Answer Questions For Vinegar Analysis - Exp.7Document2 pagesAnswer Questions For Vinegar Analysis - Exp.7sanaaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Ans To Stoichiometry Supplemtary QN - 2012Document5 pages01 - Ans To Stoichiometry Supplemtary QN - 2012caspersoongNo ratings yet
- Aicd and Base Mega Teacher 2022Document85 pagesAicd and Base Mega Teacher 2022KhensaniNo ratings yet
- Theory: Adsorption Isotherm: Adsorption Isotherm Describes TheDocument9 pagesTheory: Adsorption Isotherm: Adsorption Isotherm Describes TheSakib PkNo ratings yet
- MolarityDocument2 pagesMolarityIel FedericoNo ratings yet
- CALCULATIONSDocument3 pagesCALCULATIONSgoabaone kgopaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Aim: To Determine The Adsorption of Aqueous Acetic Acid by Activated Charcoal and To Study The Adsorption IsothermDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 Aim: To Determine The Adsorption of Aqueous Acetic Acid by Activated Charcoal and To Study The Adsorption Isothermtashi dendupNo ratings yet
- Determination of Acetic Acid of Vinegar (CAPE LAB)Document3 pagesDetermination of Acetic Acid of Vinegar (CAPE LAB)AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Exam1 02A PDFDocument6 pagesExam1 02A PDFCrizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- Adsorption Lab ManualDocument6 pagesAdsorption Lab ManualSatyamGuptaNo ratings yet
- Concentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveDocument9 pagesConcentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveAhZaiSkyNo ratings yet
- Data Dan Perhitungan P11Document5 pagesData Dan Perhitungan P11Shinta SetyowatiNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem #3Document15 pagesSample Problem #3Dozdi67% (6)
- University of Sabratha Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument8 pagesUniversity of Sabratha Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringMarNo ratings yet
- Foster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Document7 pagesFoster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Cole FosterNo ratings yet
- M20 Stoichiometry CalculationsDocument25 pagesM20 Stoichiometry CalculationsPurple Girl2255No ratings yet
- MS Excel BiochemistryDocument5 pagesMS Excel BiochemistryMarie St. Louis100% (1)
- S.4 Mole (2) + TitrationDocument27 pagesS.4 Mole (2) + TitrationS4C07 Lai Yik TsunNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Bachelor Science (Hons) Applied Chemistry (As 245) CMT555 Electrochemistry and Corrosion ScienceDocument10 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Bachelor Science (Hons) Applied Chemistry (As 245) CMT555 Electrochemistry and Corrosion ScienceNabilah HarisNo ratings yet
- Data Results Lab 8Document5 pagesData Results Lab 8Jane RihanNo ratings yet
- Aas ManualDocument2 pagesAas ManualCharitra Prakash ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Nitrite Ion Contents in Meat Sample by UV Vis Spectroscopy Method Results and DiscussionDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Nitrite Ion Contents in Meat Sample by UV Vis Spectroscopy Method Results and DiscussionANH NGUYỄN HUỲNH MINHNo ratings yet
- Iodine Clock LabDocument5 pagesIodine Clock LabHuang AmandaNo ratings yet
- Langmuir Adsorption IsothermDocument3 pagesLangmuir Adsorption IsothermUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument5 pagesAcid-Base TitrationNor Shahira KamaruzmanNo ratings yet
- S7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSDocument7 pagesS7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSFatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- BCH1104 Assignment Physical ChemistryDocument4 pagesBCH1104 Assignment Physical ChemistryElias BonkeNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document6 pagesExp 2KnobalukeshNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - CEB2093 - Reaction Engineering 2Document10 pagesTest 1 - CEB2093 - Reaction Engineering 2Ahmed AlwaqediNo ratings yet
- The Mole Part 1Document8 pagesThe Mole Part 1Daniel BerryNo ratings yet
- ADSORPTIONDocument6 pagesADSORPTIONSatyamGupta0% (1)
- Assignment 1: 01. Practical: Determination of End Point of Titration Using PH MeterDocument9 pagesAssignment 1: 01. Practical: Determination of End Point of Titration Using PH Metertheepak rajkeethanNo ratings yet
- BCBM 659 - Lab 3Document18 pagesBCBM 659 - Lab 3Nick Morettin0% (1)
- Report 4 Group 5 1Document6 pagesReport 4 Group 5 1HƯNG LIÊU MẠNHNo ratings yet
- Data and Results Computations Expt5Document6 pagesData and Results Computations Expt5John Pierre JerusalemNo ratings yet
- The Conductance of Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesThe Conductance of Strong and Weak Electrolytessexycassie100% (6)
- Perhitungan: Mol M X LDocument10 pagesPerhitungan: Mol M X Lfitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- Experiment Four - SchemeDocument4 pagesExperiment Four - SchemepeterokotettehNo ratings yet
- Results and CalculationsDocument5 pagesResults and CalculationsGriezmann HaziqNo ratings yet
- Rate Expression and Order of ReactionDocument3 pagesRate Expression and Order of ReactionMartha PrawiradirdjaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Determination of An Unknow PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry The Determination of An Unknow PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- (Answer Key) Calculation Exercise - 元素の貓 - 免費dse化學練習Document6 pages(Answer Key) Calculation Exercise - 元素の貓 - 免費dse化學練習Belladonna Lee100% (1)
- Titration Practice Questions NewDocument14 pagesTitration Practice Questions NewDeneil WalkerNo ratings yet
- Irshad KamilDocument11 pagesIrshad Kamilprakshid3022100% (1)
- Concept of InsuranceDocument4 pagesConcept of InsuranceNazrul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Thinking Out LoundDocument2 pagesThinking Out LoundExita ConiaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Community OutreachDocument3 pages12 - Community OutreachAdam ThimmigNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Document4 pagesA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinNo ratings yet
- 2002PCDFCADocument78 pages2002PCDFCATin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hard Rock Tunnelling MethodsDocument20 pagesHard Rock Tunnelling Methodskiranism0% (1)
- Lithium Dongjin 48v100ahDocument5 pagesLithium Dongjin 48v100ahmk7718100% (1)
- Thermo Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermo Exam QuestionssiskieoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFDocument28 pages2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFMahnoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractDocument14 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractMary SheshiraNo ratings yet
- Ingles - 1 - Bach - Modulo - 2 (20 - 21)Document32 pagesIngles - 1 - Bach - Modulo - 2 (20 - 21)John Alex Almeida50% (2)
- OXE Training - Complete (2011)Document94 pagesOXE Training - Complete (2011)Dhexter Villa75% (4)
- Aggregate Turf PavementDocument6 pagesAggregate Turf PavementDevrim GürselNo ratings yet
- Drive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Document90 pagesDrive Engineering - Practical Implementation SEW Disc Brakes 09202218 - G1Anonymous ntE0hG2TPNo ratings yet
- Pre-Colonial Philippine ArtDocument5 pagesPre-Colonial Philippine Artpaulinavera100% (5)
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Document79 pagesRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoNo ratings yet
- Harvester Main MenuDocument3 pagesHarvester Main MenuWonderboy DickinsonNo ratings yet
- Times Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Document49 pagesTimes Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Joseph HoukNo ratings yet
- Set B Cluster 3 (Final) (Aug102015)Document4 pagesSet B Cluster 3 (Final) (Aug102015)Kuo Sarong100% (1)
- Comprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire TruckDocument79 pagesComprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire Truckbhupendra singh sengarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesSyllabus Financial AccountingHusain ADNo ratings yet
- Shock Cat 2009Document191 pagesShock Cat 2009gersonplovasNo ratings yet
- Waste SM4500-NH3Document10 pagesWaste SM4500-NH3Sara ÖZGENNo ratings yet
- Check To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsDocument48 pagesCheck To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsarunchockanNo ratings yet
- Statistics For EconomicsDocument58 pagesStatistics For EconomicsKintu GeraldNo ratings yet
- Lattner HRT Power Plus Operations ManualDocument42 pagesLattner HRT Power Plus Operations Manualsabir_munnaNo ratings yet
- Basic DWDM Components.Document16 pagesBasic DWDM Components.Pradeep Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Shib Mandir, PO-Kadamtala Dist-Darjeeling WB - 734011 JC 18, 3RD Floor, Sector - III Salt Lake City, Kolkata 700098Document7 pagesShib Mandir, PO-Kadamtala Dist-Darjeeling WB - 734011 JC 18, 3RD Floor, Sector - III Salt Lake City, Kolkata 700098Rohit DhanukaNo ratings yet
- 1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018Document5 pages1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018PRO ECUNo ratings yet