Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grundy Map
Grundy Map
Uploaded by
Belinda Allen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe document compares three curriculum models: technical, practical, and emancipatory. The technical model has an empirical/analytic focus and is objectivist, rule-based, and control-oriented. The practical model has a historical/hermeneutic focus and is constructivist and judgement-based. The emancipatory model has a critical/reflective focus and is transformational, with a social-critical perspective and emphasis on empowerment through dialogue.
Original Description:
Original Title
grundy_map
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document compares three curriculum models: technical, practical, and emancipatory. The technical model has an empirical/analytic focus and is objectivist, rule-based, and control-oriented. The practical model has a historical/hermeneutic focus and is constructivist and judgement-based. The emancipatory model has a critical/reflective focus and is transformational, with a social-critical perspective and emphasis on empowerment through dialogue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageGrundy Map
Grundy Map
Uploaded by
Belinda AllenThe document compares three curriculum models: technical, practical, and emancipatory. The technical model has an empirical/analytic focus and is objectivist, rule-based, and control-oriented. The practical model has a historical/hermeneutic focus and is constructivist and judgement-based. The emancipatory model has a critical/reflective focus and is transformational, with a social-critical perspective and emphasis on empowerment through dialogue.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
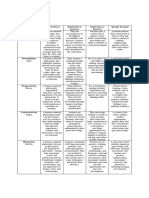
Comparison of curriculum models
Chart by Belinda Allen, UNSW, after Grundy, S. 1987. Curriculum: Product or praxis?
The Falmer Press , London/New York.
Cognitive interests framework (Habermas 1972)
Empirical/analytic Historical/hermeneutic Critical/reflective
TECHNICAL PRACTICAL EMANCIPATORY
CURRICULUM
OBJECTIVISM CONSTRUCTIVISM TRANSFORMATIONAL
assessment of product assessment of process self/peer assessment
CHARACTERISTICS CHARACTERISTICS CHARACTERISTICS
positivist learning-centred social-critical
rule-based judgement-based perspective
control-oriented shared control learners as
objective (Tyler) reflective participants
systems interpretative learners as teachers
management subjective and vv
(Rowntree) (Stenhouse) critical pedagogy
power outside the empowerment
classroom through dialogue
(Freire)
ENACTED AS ENACTED AS ENACTED AS
focus on product focus on meaning- negotiated curriculum
pseudo-scientific making problematisation of
difficut to adapt to teacher-determined learning/ teaching
new situations (via judgement) situation
ideas-oriented process-oriented learner control
prescriptive relation objectives as action on reflection
in theory ‘hypotheses’ tested socially-constructed
subject to in classroom meaning-making
supervision evaluative relation emancipatory relation
in theory in theory
context-sensitive
You might also like
- ACTIVITY 2 - Philosophical and Theoretical Orientations To TeachingDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 2 - Philosophical and Theoretical Orientations To TeachingAngel Nicolin Suyman100% (1)
- Comparison of Attributes of Educational PhilosophiesDocument1 pageComparison of Attributes of Educational PhilosophiesSelepas Hujan100% (3)
- Rethinking Evaluation For Promoting Self-Regulated LearningDocument29 pagesRethinking Evaluation For Promoting Self-Regulated LearningRaul Polanco M.No ratings yet
- Lfhers: ConstructivismDocument17 pagesLfhers: ConstructivismDada Aguilar DelgacoNo ratings yet
- Toward A Post Method Pedagogy 160214183540Document22 pagesToward A Post Method Pedagogy 160214183540Fabiana MariazziNo ratings yet
- Management-Of-Inst - 083047Document25 pagesManagement-Of-Inst - 083047ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Matrix No. Author's Name Title Year Findings InstrumenDocument9 pagesLiterature Review Matrix No. Author's Name Title Year Findings InstrumenYONG CHIAN RU MoeNo ratings yet
- Constructing Multiple-Choice Items To Measure Higher-Order ThinkiDocument14 pagesConstructing Multiple-Choice Items To Measure Higher-Order Thinkirehan azizNo ratings yet
- Behavioral TheoriesDocument1 pageBehavioral TheoriesJasmin GregorioNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Ilan, Kyle Angela - Activity1Document5 pagesPractical Research 2 - Ilan, Kyle Angela - Activity1Kyle Angela IlanNo ratings yet
- EDCC115 Unit 3 2023Document13 pagesEDCC115 Unit 3 2023Sinovuyo MshweshweNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 16 Summary ReportDocument5 pagesTOPIC 16 Summary ReportRyan Philippe RelovaNo ratings yet
- EDU101 Assignment 1 Spring 2019Document5 pagesEDU101 Assignment 1 Spring 2019Muhammad YasinNo ratings yet
- The Art of Teaching ScienceDocument32 pagesThe Art of Teaching ScienceSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- A Mixed Methods Study On The Influence of Feedback Source and Curriculum Type On Creative Development in Middle Childhood Across Two CountriesDocument20 pagesA Mixed Methods Study On The Influence of Feedback Source and Curriculum Type On Creative Development in Middle Childhood Across Two Countriesapi-536883471No ratings yet
- Scully, D. (2017) - Constructing Multiple-Choice Items To Measure Higher-Order Thinking. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 22 (4), 2.Document13 pagesScully, D. (2017) - Constructing Multiple-Choice Items To Measure Higher-Order Thinking. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 22 (4), 2.ING4 Labs0% (1)
- Adult Learning: From Theory To ApplicationDocument8 pagesAdult Learning: From Theory To ApplicationasifNo ratings yet
- EDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Document4 pagesEDUC 103 Module 2 2T 2018 2019Pau CervantesNo ratings yet
- Dev't ReadingDocument16 pagesDev't ReadingPee BaradasNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Infographics by Slidesgo Copy Compressed 1 1Document32 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Infographics by Slidesgo Copy Compressed 1 1Jasmine Nicole OsallaNo ratings yet
- PDF TEAM3 STUDYGUIDE ProfEd102Document44 pagesPDF TEAM3 STUDYGUIDE ProfEd102Duhreen Kate CastroNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Perspectives: Compiled by Irfan Fajrul FalahDocument12 pagesCurriculum Perspectives: Compiled by Irfan Fajrul FalahIrfan Fajrul FalahNo ratings yet
- ProEd 6Document1 pageProEd 6Jirah Joy PeañarNo ratings yet
- The Cognitive Perspective On LearningDocument10 pagesThe Cognitive Perspective On LearningDoraNo ratings yet
- Utew 311 Assignment 1 PPT Presentation - 4Document12 pagesUtew 311 Assignment 1 PPT Presentation - 4MphoNo ratings yet
- The 5 Phases of InquiryDocument14 pagesThe 5 Phases of InquiryAbebe Tilahun KNo ratings yet
- A Mixed Methods Study On The Influence of Feedback Source On Creative Development in Middle ChildhoodDocument13 pagesA Mixed Methods Study On The Influence of Feedback Source On Creative Development in Middle Childhoodapi-536883471No ratings yet
- The Role of Assessment in A Learning Culture. ShepardDocument11 pagesThe Role of Assessment in A Learning Culture. ShepardMariana CarignaniNo ratings yet
- Learning Outputs in Comparative Philosophies in EducationDocument8 pagesLearning Outputs in Comparative Philosophies in EducationArman Berina CortezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Pedagogies 5 Day FDPDocument23 pagesTeaching Pedagogies 5 Day FDPYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- Educ 327Document44 pagesEduc 327manlanothammillanNo ratings yet
- Thinking Skills and Creativity: Martín Cáceres, Miguel Nussbaum, Jorge Ortiz TDocument18 pagesThinking Skills and Creativity: Martín Cáceres, Miguel Nussbaum, Jorge Ortiz TdillaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches in Secondary in Social Studies - Proper LectureDocument8 pagesTeaching Approaches in Secondary in Social Studies - Proper LectureAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sparks-Langer and Colton - Synthesis On Research On Teacher Reflective ThinkingDocument9 pagesSparks-Langer and Colton - Synthesis On Research On Teacher Reflective Thinkingophelia elisa novitaNo ratings yet
- Ed 2 Module 8 1Document5 pagesEd 2 Module 8 1Jimeniah Ignacio RoyoNo ratings yet
- Research Report PresentationDocument10 pagesResearch Report PresentationAdriana Elizabeth Cango PatiñoNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM IN ENGLISH 204 2023 2024 Term 2Document2 pagesFINAL EXAM IN ENGLISH 204 2023 2024 Term 2kbanez.bulNo ratings yet
- LOQ-model-of-science-teaching PendukungDocument8 pagesLOQ-model-of-science-teaching Pendukungkamilah kurniaNo ratings yet
- Project PresentationDocument10 pagesProject PresentationslypiekunNo ratings yet
- Telling Active Learning Pedagogies Apart - From Theory To Practice - Hood Cattaneo - Journal of New Approaches in Educational Research PDFDocument9 pagesTelling Active Learning Pedagogies Apart - From Theory To Practice - Hood Cattaneo - Journal of New Approaches in Educational Research PDFSam SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 EducPsychDocument5 pagesChapter 14 EducPsychAdam VidaNo ratings yet
- Handout1 Taxonomy Bloom Krathwohl SimpsonDocument7 pagesHandout1 Taxonomy Bloom Krathwohl SimpsonBruz SundayNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Procedures: Procedures: Procedures: Procedures: ProceduresDocument1 pageTeacher: Procedures: Procedures: Procedures: Procedures: Procedureselisha lasolaNo ratings yet
- INSTR6230 - LearningStyles - WP-2Document8 pagesINSTR6230 - LearningStyles - WP-2Mariya RyzhkovaNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles: Higher Education ServicesDocument8 pagesLearning Styles: Higher Education Servicesandi sri mutmainnaNo ratings yet
- Three Approaches To Curriculum Issue Traditional Approach Learner-Driven Approach Critical ApproachDocument4 pagesThree Approaches To Curriculum Issue Traditional Approach Learner-Driven Approach Critical ApproachReo Daryl Martinez PineraNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Focus On Curriculum Role of Teacher Teaching Methodologies Aims of Education Educational LeadersDocument2 pagesPhilosophy Focus On Curriculum Role of Teacher Teaching Methodologies Aims of Education Educational LeadersJanine Bernadette ChioNo ratings yet
- Module 1 List of Requirements and ActivitiesDocument2 pagesModule 1 List of Requirements and ActivitiesysabelletorranoNo ratings yet
- Article. Impact of Effective Communication, Achievement Sharing and Positive Classroom Environments On Learning PerformanceDocument12 pagesArticle. Impact of Effective Communication, Achievement Sharing and Positive Classroom Environments On Learning PerformanceDG AnnNo ratings yet
- Lima Fase InkuiriDocument16 pagesLima Fase InkuiriTri lestariNo ratings yet
- Constructivism As A Learning TheoryDocument6 pagesConstructivism As A Learning TheorydushyantNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Science Discourse in K-12 Urban Classrooms in The United States: Accounting For Individual, Collective, and Contextual FactorsDocument47 pagesA Systematic Review of Science Discourse in K-12 Urban Classrooms in The United States: Accounting For Individual, Collective, and Contextual FactorsChi AbagatNo ratings yet
- Valli's ReflectionDocument1 pageValli's ReflectionmirunahorgaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document5 pagesLesson 7Princess BilogNo ratings yet
- Pogoy Module 1Document5 pagesPogoy Module 1Nica PogoyNo ratings yet
- TeachertoolkitDocument6 pagesTeachertoolkitapi-379700595No ratings yet
- Schools of Thought in SLA: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and StructuralismDocument12 pagesSchools of Thought in SLA: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and StructuralismNinuk Retna SumiarsihNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Educational PsychologyDocument18 pagesContemporary Educational PsychologyMadrid MNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet