Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Joval Tan
Uploaded by
Joval TanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Joval Tan
Uploaded by
Joval TanCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: Risk for High blood After 8 hours INDEPENDENT: Provides basis After 8 hours of
“Bakit kaya prone pressure (HBP) of nursing Define and state the for nursing
madalas ako behavior or hypertension interventions, limits of desired BP. understanding interventions,
mahilo?” (Why do I related to means high the patient Explain elevations of BP, the patient was
always feel dizzy?) as lack of pressure will verbalize hypertension and its and clarifies able to
verbalized by the knowledge (tension) in the understanding effect on the heart, misconceptions verbalize
patient. about the arteries. Arteries of the disease blood vessels, and also understanding
disease are vessels that process and kidney, and brain. understanding of the disease
carry blood from treatment Assist the patient in that high BP can process and
OBJECTIVE: the pumping regimen. identifying exist without treatment
Request for heart to all the modifiable risk symptom or even regimen.
information. tissues and factors like diet high when feeling
Agitated organs of the in sodium, saturated well.
behavior body. High fats and cholesterol. These risk
Inaccurate blood pressure Reinforce the factors have
follow through does not mean importance of been shown to
of instructions. excessive adhering to contribute to
emotional tension, treatment regimen hypertension.
although and keeping follow Lack of
emotional up appointments. cooperation is
tension and Suggest frequent common reason
V/S taken as stress can position changes, for failure of
follows: temporarily leg exercises when antihypertensive
T: 37.2 increase blood lying down. therapy.
P: 84 pressure. Decreases
R: 18 Normal blood and a blood peripheral
BP: 180/110 pressure is pressure of venous pooling
below 120/80; 140/90 or above that may be
blood pressure is considered potentiated by
between 120/80 high. An vasodilators and
and 139/89 is elevation of the prolonged sitting
called "prehypertension", systolic and/or or standing.
and a blood diastolic blood Two years on
pressure of pressure moderate low
140/90 or above increases the salt diet may be
is considered risk of sufficient to
high. An developing control mild
elevation of the heart (cardiac) hypertension.
systolic and/or disease, kidney Caffeine is a
diastolic blood (renal) disease, cardiac stimulant
pressure hardening of the and may
increases the arteries adversely affect
risk of (atherosclerosis cardiac function.
developing or Alternating rest
heart (cardiac) arteriosclerosis), and activity
disease, kidney eye damage, increases
(renal) disease, and stroke tolerance to
hardening of the (brain damage). activity
arteries These progression.
(atherosclerosis complications of Community
or hypertension resources like
arteriosclerosis), are often health centers
eye damage, referred to as programs and
and stroke end-organ check ups are
(brain damage). damage helpful in
These because controlling
complications of damage to hypertension.
hypertension these organs is
are often the end result of
referred to as chronic (long
end-organ duration) high
damage blood pressure.
because
damage to
these organs is
the end result of
chronic (long
duration) high
blood pressure.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hypertensionderic98% (124)
- Hypertension PamphletDocument2 pagesHypertension PamphletNikki RicafrenteNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Drenaj LimfaticDocument71 pagesDrenaj LimfaticGugiu Bogdan Ștefan90% (20)
- Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts - 2nd EditionDocument257 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Concepts - 2nd EditionAbel GarcíaNo ratings yet
- NCP PPHDocument2 pagesNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesAcute Gastroenteritisreejay123No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionBlessie FernandezNo ratings yet
- ASSESMENTDocument2 pagesASSESMENTgep4617_rayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- High Blood PressureDocument2 pagesHigh Blood PressureKreisl DizonNo ratings yet
- CCM HypertensionDocument1 pageCCM Hypertensionaba766467No ratings yet
- NCP-DP NCM112LecDocument4 pagesNCP-DP NCM112LecShane CabucosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 HypertensionDocument3 pagesChapter 31 HypertensionVen SemillaNo ratings yet
- Velez College - Nursing F. Ramos ST., Cebu CityDocument26 pagesVelez College - Nursing F. Ramos ST., Cebu Cityfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERDocument6 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERCarla LimNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionjonathanNo ratings yet
- Hypertension ReviewerDocument9 pagesHypertension Reviewermecleo93No ratings yet
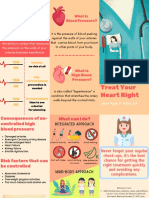
- Hypertensive BrochureDocument2 pagesHypertensive BrochureKyle FelixNo ratings yet
- NCP For Dizziness and HeadacheDocument4 pagesNCP For Dizziness and Headachekarthi karthi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: M.L.HDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: M.L.HNicolne LorraineNo ratings yet
- Ncma215 - Nutrition Counseling and Dietary InstructionsDocument1 pageNcma215 - Nutrition Counseling and Dietary InstructionsChesca DomingoNo ratings yet
- What Is Blood PressureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Blood PressureTazneem Apostol EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1Niña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidDocument7 pagesFinal Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidMor Shi DA BalutintikNo ratings yet
- Baber ReqDocument3 pagesBaber ReqRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanElaine P. RoqueNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesHypertension: Nursing Care PlansSamah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDocument3 pagesBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeNo ratings yet
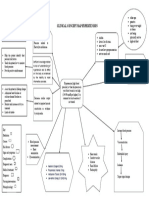
- Concept Map Joshua ValdrizDocument1 pageConcept Map Joshua ValdrizJoshua ValdrizNo ratings yet
- PHY4283 Physics in Medicine (Lecture 6)Document32 pagesPHY4283 Physics in Medicine (Lecture 6)Henry LauNo ratings yet
- Stroke and High Blood Pressure Ucm - 493407Document2 pagesStroke and High Blood Pressure Ucm - 493407TariqNo ratings yet
- NCP #2Document2 pagesNCP #2Faith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure (Hyperten Sion)Document2 pagesHigh Blood Pressure (Hyperten Sion)CHARLHYN GRACE BISNARNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Role of Homeopathy in The Treatment of HypertensionDocument5 pagesRole of Homeopathy in The Treatment of HypertensionArturo ChiribogaNo ratings yet
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+HypertensionDocument9 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+HypertensionAcell Molina EMNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 pagesNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure: 10 Steps To Lower And Manage Your Blood Pressure NaturallyFrom EverandBlood Pressure: 10 Steps To Lower And Manage Your Blood Pressure NaturallyNo ratings yet
- The High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!From EverandThe High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!No ratings yet
- Causes of High Blood Pressure: Natural Blood Pressure Solutions and RemediesFrom EverandCauses of High Blood Pressure: Natural Blood Pressure Solutions and RemediesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Dash Diet Cookbook: Easy and Healthy Dash Diet Recipes to Lower Your Blood Pressure. 7-Day Meal Plan and 7 Simple Rules for Weight LossFrom EverandDash Diet Cookbook: Easy and Healthy Dash Diet Recipes to Lower Your Blood Pressure. 7-Day Meal Plan and 7 Simple Rules for Weight LossNo ratings yet
- Natural High Blood Pressure Solutions: Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally Using Diet And Natural Remedies Without MedicationFrom EverandNatural High Blood Pressure Solutions: Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally Using Diet And Natural Remedies Without MedicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Complete Guide to Hypertension & High Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis, Treatments & CuresFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Hypertension & High Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis, Treatments & CuresNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: How to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally and Prevent Heart DiseaseFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: How to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally and Prevent Heart DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Beating High Blood Pressure Naturally: Your Complete Guide to Self-Care, Healthy Eating, and Herbal Remedies: Self Care, #1From EverandBeating High Blood Pressure Naturally: Your Complete Guide to Self-Care, Healthy Eating, and Herbal Remedies: Self Care, #1No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally With Essential Oil: What Hypertension Is, Causes of High Pressure Symptoms and Fast RemediesFrom EverandHow to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally With Essential Oil: What Hypertension Is, Causes of High Pressure Symptoms and Fast RemediesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lower Your High Blood Pressure Naturally - How To Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationFrom EverandLower Your High Blood Pressure Naturally - How To Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Way to Reverse Heart Disease Naturally: Beyond the Hypertension Hype: Why Drugs Are Not the AnswerFrom EverandThe Amazing Way to Reverse Heart Disease Naturally: Beyond the Hypertension Hype: Why Drugs Are Not the AnswerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Reducing Blood Pressure Naturally: Do You Suffer From High Blood Pressure? Do You Feel Like This 'Silent Killer' Might Be Stalking You? Have you been diagnosed or pre-hypertension and hypertension?From EverandReducing Blood Pressure Naturally: Do You Suffer From High Blood Pressure? Do You Feel Like This 'Silent Killer' Might Be Stalking You? Have you been diagnosed or pre-hypertension and hypertension?No ratings yet
- The HeartDocument7 pagesThe HeartJoval TanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewerDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Reviewerbrianwenceslao4100% (3)
- Electromagnetic Energy Flow and The Poynting VectorDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Energy Flow and The Poynting VectorJoval TanNo ratings yet
- Dissociative AmnesiaDocument7 pagesDissociative AmnesiaJoval TanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Planned BehaviorDocument33 pagesTheory of Planned BehaviorAyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Verse ChoirDocument2 pagesVerse ChoirJoval TanNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument3 pagesAortic StenosisZweNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 28Document31 pagesDownloadfile 28Chowdhury Mohammed Tawhid TasneefNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument5 pagesEcghappy100% (1)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMyocardial InfarctionLetecia MooreNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFDocument12 pagesBiology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFFarah100% (1)
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument35 pagesPulmonary HypertensionKea Keleste DetablanNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument8 pagesAortic Stenosisdr.moni.co.ukNo ratings yet
- Kehamilan & Penyakit JantungDocument23 pagesKehamilan & Penyakit JantungSyifa NurainiNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Parameters To Guide Fluid Therapy: Review Open AccessDocument9 pagesHemodynamic Parameters To Guide Fluid Therapy: Review Open AccessClaudioValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Document36 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Nafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Blood Vessel and LymphaticsDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Blood Vessel and LymphaticsvisaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Extra Edge Topics For NEET 2020Document6 pagesBiology - Extra Edge Topics For NEET 2020alishNo ratings yet
- Case Reports of Left Atrial Myxoma in Elderly and ChildrenDocument5 pagesCase Reports of Left Atrial Myxoma in Elderly and Childrenbri bugelNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Atresia With An Intact Ventricular Septum: Preoperative Physiology, Imaging, and ManagementDocument12 pagesPulmonary Atresia With An Intact Ventricular Septum: Preoperative Physiology, Imaging, and ManagementGusti Ayu Radhitia OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Master File - ChronicDocument671 pagesMaster File - ChronicsubhojitnayekNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMyocardial InfarctionMark Emil BautistaNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia: Heart (Myocardial) InfarctionDocument4 pagesAcute Leukemia: Heart (Myocardial) InfarctionSisham SubediNo ratings yet
- Beyond Wedge: Clinical Physiology and The Swan-Ganz CatheterDocument12 pagesBeyond Wedge: Clinical Physiology and The Swan-Ganz Catheterkromatin9462No ratings yet
- AIPMT 2013 Code W1 Question PaperDocument43 pagesAIPMT 2013 Code W1 Question PaperNageswarNo ratings yet
- Oxy CadDocument21 pagesOxy CadrlinaoNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument18 pagesCPRSwamy MmsNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia SiteDocument23 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia Sitebenypermadi100% (1)
- Accsap 10 VHDDocument94 pagesAccsap 10 VHDMuhammad Javed Gaba100% (2)
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument11 pagesMedical AbbreviationsbtraNo ratings yet
- Bams AllxcfgxfDocument104 pagesBams AllxcfgxfRaheel Bhai0% (1)
- Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesAngina PectorisDr AUNo ratings yet
- Mindmap CVS Liana Naamnih Group3Document1 pageMindmap CVS Liana Naamnih Group3Liana NaamnehNo ratings yet
- Pass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Document26 pagesPass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Ahmad Shokry100% (1)