Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anthrax
Uploaded by
saint_peter_03Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anthrax
Uploaded by
saint_peter_03Copyright:
Available Formats
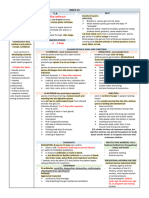
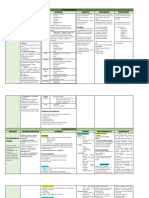
AGENT FACTORS CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX
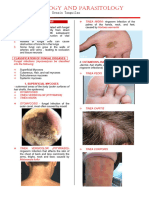
- Presence of Bacillus anthracis - Small pimple or macule appears 2-3 days after
- General characteristics of B. the entrance of microorganism
Without antibiotic treatment ->
anthracis - On 4th day a ring of vesicles develops around the
- Mode of transmission papule. Vesicular fluid may exude. complications : anthrax meningitis and
- anthrax sepsis -> DEATH
Incubation period - Mark edema starts to develop. Unless there is
secondary infection, there is no pus and the lesion is not
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS painful, although painful lymph adenitis may occur in the
- Prevalence among domestic herbivores inguinal area.
(including cattle, sheep, horses and goats) and - On the 5th to 7th day, the original papules ulcerate
wild herbivores. to form the characteristic eschar.
- Carcasses of infected animals provide - Clinical symptoms maybe severe if the lesion is
located in the face, neck or chest.
additional potential foci of contamination With antibiotic treatment-> neutralization
- In more severe forms, clinical findings are high
fever, toxaemia, regional painful lymphadenopathy and of anthrax toxin
HOST FACTORS extensive edema. Shock and death may also ensue.
- Agricultural cases which result most often INHALATION ANTHRAX
- Presenting symptoms resemble those of severe
from contact with animals that have anthrax viral respiratory diseases.
(e.g. during skinning, butchering or dissecting), - After one to three days of acute phase, increasing
from bites of contaminated or infected flies and fever dyspnea, stridor, hypoxia and hypotension occur
from consumption of contaminated meat usually leading to death within 24 hours.
GASTROINTESTINAL ANTHRAX
- Industrial cases which are associated with - Primary infection is initiated in the intestines
exposure to contaminated hides, goat hair, wool where the lesions are formed accompanied by
or bones hemorrhagic lymphadenitis.
- Symptoms include fever, nausea and vomiting,
abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and sometimes rapidly
developing ascitis.
PRE PATHOGENESIS PATHOGENESIS
BEFORE INFECTION INFECTION PROGRESS TERMINAL PROGRESS
- Immunize high-risk persons with cell free - Parenteral Penicillin G – 2 million units every - Anthrax spores can survive for long periods of
six hours, until edema subsides with subsequent time in the environment after release. Methods for
vaccine prepared from a culture filtrate containing
administration of oral penicillin to complete seven to cleaning anthrax-contaminated sites commonly use
the protection against antigen.
ten-day-course. oxidizing agents such as peroxides, and ethylene oxide
- Educate employees handling potentially - Patients who are sensitive to penicillin can be because these agents slowly destroy bacterial spores.
contaminated articles about modes of anthrax treated with erythromycin, tetracycline, or
transmission, care of skin abrasions and personal chloramphenicol.
cleanliness.
- Control dusts and properly ventilates in
- The body of the patient should be put in strict
quarantine. Full isolation of the body is important to
hazardous industries especially those that handle
prevent possible contamination of others. Protective,
raw animal materials. impermeable clothing and equipment such as rubber
- Promptly immunize and annually re-immunize gloves, rubber apron, and rubber boots with no
all animals at risk. perforations should be used when handling the body.
You might also like
- Med Surg (Midterm)Document9 pagesMed Surg (Midterm)Jennica BubanNo ratings yet
- Antrax LectureDocument49 pagesAntrax LecturefraolNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxanemenyee100% (2)
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxanemenyeeNo ratings yet
- Lec4 TransDocument23 pagesLec4 TransErika PatarayNo ratings yet
- Anthrax Icd-9 022 Icd-10 A22: Control Communicable Diseases ChinDocument5 pagesAnthrax Icd-9 022 Icd-10 A22: Control Communicable Diseases ChinSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- MICP Bacterial Infections s1Document12 pagesMICP Bacterial Infections s1Valerian VolkzkiNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxaristadevyaNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas - Medical Technology Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas - Medical Technology Diagnostic Microbiologythedarkwing100% (1)
- Diagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Venomous AnimalsDocument15 pagesVenomous AnimalsKaryl JoyNo ratings yet
- Anthrax 140129091950 Phpapp02Document28 pagesAnthrax 140129091950 Phpapp02Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Staphylococcus EpidermidisDocument19 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Staphylococcus EpidermidisThomas GealonNo ratings yet
- Anthrax: Biological WarfareDocument4 pagesAnthrax: Biological WarfarekhyzyrNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Skin 2Document42 pagesInfections of The Skin 2Kathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis Rabies Pediculosis Bubonic Plague Anthrax HelminthesDocument92 pagesSchistosomiasis Rabies Pediculosis Bubonic Plague Anthrax Helminthesaltairejoshua.jalbayNo ratings yet
- Anthrax Background Information: Bacillus AnthracisDocument3 pagesAnthrax Background Information: Bacillus AnthracisDhea.MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Topics For CA. (Yu)Document6 pagesTopics For CA. (Yu)Charlotte CorderoNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Zaidi Abd Hamid Pensyarah Pembantu PerubatanDocument31 pagesTetanus: Zaidi Abd Hamid Pensyarah Pembantu PerubatanSyasya NanaNo ratings yet
- Angiostronylus Cantonensis (Summary Report)Document2 pagesAngiostronylus Cantonensis (Summary Report)Iyah ChingNo ratings yet
- Disaster Caused BY Biological AgentsDocument25 pagesDisaster Caused BY Biological AgentsKaren Mae Dacoco MamuyacNo ratings yet
- Anthrax by JamesDocument34 pagesAnthrax by JamesJAMES NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- History of RabiesDocument23 pagesHistory of Rabiescolicot100No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument193 pagesCommunicable DiseaseLuvastranger Auger100% (2)
- Large A.medicine 4th YearDocument285 pagesLarge A.medicine 4th YearAssefaTayachewNo ratings yet
- BACILLUSDocument11 pagesBACILLUSFatima AbasovaNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lec 1Document11 pagesBacte Lec 12234382No ratings yet
- ANTHRAX and BRUCELLOSISDocument31 pagesANTHRAX and BRUCELLOSISMARK ARQUE LACANARIANo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxRizky Bayu AjieNo ratings yet
- Large Animal Medicine PPt2016Document221 pagesLarge Animal Medicine PPt2016kibrushe260No ratings yet
- Lec 15Document9 pagesLec 15surendradeora3628No ratings yet
- Anthrax - Business QueenslandDocument4 pagesAnthrax - Business QueenslandNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis PowerpointDocument32 pagesBacillus Anthracis PowerpointEnerose MagnoNo ratings yet
- Infestation: ScabiesDocument16 pagesInfestation: ScabiesBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument6 pagesAnthraxeutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Spore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria: Prof. Zainab A AldhaherDocument17 pagesSpore Forming Gram Positive Bacteria: Prof. Zainab A Aldhaherمروه عماد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Anthrax: SynonymsDocument4 pagesAnthrax: SynonymsVenkatapradeepNo ratings yet
- Common Mites (Arachnids) of Rabbits Common Mites (Arachnids) of Rabbits and Their Treatment and Their TreatmentDocument8 pagesCommon Mites (Arachnids) of Rabbits Common Mites (Arachnids) of Rabbits and Their Treatment and Their TreatmentMustafarNo ratings yet
- DIPTHERIADocument2 pagesDIPTHERIADr KhatidjaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 CD Vidlec 1-3 (+ Module Info)Document24 pagesWEEK 14 CD Vidlec 1-3 (+ Module Info)jmmacar19No ratings yet
- 2.06 - Bacterial InfectionsDocument8 pages2.06 - Bacterial InfectionsMaria CanabeNo ratings yet
- w2 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument3 pagesw2 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- W2 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument3 pagesW2 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (Heba)Document176 pagesBacteriology (Heba)irs531997No ratings yet
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- About The Diseases: AnthraxDocument2 pagesAbout The Diseases: Anthraxsasmita100% (1)
- Pathogens That Involve The SkinDocument57 pagesPathogens That Involve The SkinLeeShauran100% (2)
- 3.1. Gram Positive Rods-BacillusDocument32 pages3.1. Gram Positive Rods-Bacillusahmed mohammedNo ratings yet
- Pseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesDocument14 pagesPseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesTricia Mae JuanitasNo ratings yet
- Bacteria TableDocument4 pagesBacteria TableBrittany Lynn MyersNo ratings yet
- Tetanus in Farm AnimalsDocument7 pagesTetanus in Farm AnimalsIsrarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in MicroparaDocument7 pagesReviewer in MicroparaLore FraginalNo ratings yet
- Funda Lab - Prelim ReviewerDocument16 pagesFunda Lab - Prelim ReviewerNikoruNo ratings yet
- Advanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and HygieneDocument28 pagesAdvanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and Hygienejane entunaNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic Infections 10Document21 pagesZoonotic Infections 10Chaudhary AjayNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument19 pagesDermatologypkpmmc1957No ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- All You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseFrom EverandAll You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseNo ratings yet
- NazeerDocument23 pagesNazeerDrGurinder KanwarNo ratings yet
- Where Everything Is in Halves, by Gabriel Ojeda-SagueDocument22 pagesWhere Everything Is in Halves, by Gabriel Ojeda-SagueBe About It Press100% (1)
- Assessment of The Ears Rev 4-2013Document8 pagesAssessment of The Ears Rev 4-2013alphabennydelta4468No ratings yet
- Color Therapy GeneralDocument39 pagesColor Therapy GeneralNowo BudirahardjoNo ratings yet
- Guidance Notes Dog Breeding EstablishmentsDocument3 pagesGuidance Notes Dog Breeding EstablishmentsIuliana BodaNo ratings yet
- Wilderfeast Quickstart 1.0Document85 pagesWilderfeast Quickstart 1.0Chris Hughes100% (3)
- BotulismeDocument36 pagesBotulismeDienjhe Love BunzNo ratings yet
- I. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2Document115 pagesI. Review of Respiratory System A.ppt 2arielleortuosteNo ratings yet
- Tropical Medicine: Departement of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine USUDocument40 pagesTropical Medicine: Departement of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine USUSartika NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Worm Infestation and HomoeopathyDocument15 pagesWorm Infestation and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- Journal 1Document2 pagesJournal 1Intan KartikasariNo ratings yet
- Self Disseminating VaccinesDocument9 pagesSelf Disseminating VaccinesCaesar VranceanuNo ratings yet
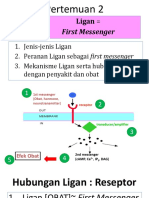
- 2 Ligan First MassengerDocument32 pages2 Ligan First MassengerikhararaNo ratings yet
- Herpes Antidote UnlockedDocument125 pagesHerpes Antidote Unlockedfcuevaspr180% (5)
- tmpB0AD TMPDocument10 pagestmpB0AD TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- About HyenaDocument24 pagesAbout HyenaRiswan Hanafyah Harahap0% (1)
- Kato Thick Kato KatzDocument3 pagesKato Thick Kato KatzジェスNo ratings yet
- Uwise HYDocument3 pagesUwise HYJack GuccioneNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Repot Text KLS 9Document14 pagesBahan Ajar Repot Text KLS 9Risya Ega Khailla100% (1)
- 20 Yoga Poses For Losing Weight Fast - 990Document22 pages20 Yoga Poses For Losing Weight Fast - 990Ku Esyra Hani Ku IshakNo ratings yet
- Roland Barthes - Steak and ChipsDocument3 pagesRoland Barthes - Steak and ChipsmishaiolandaNo ratings yet
- RSOM Mark SchemesDocument26 pagesRSOM Mark SchemesElaine Rosemary BruceNo ratings yet
- Moon DogDocument4 pagesMoon DogJairo FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Methemoglobin Reductase PathwayDocument2 pagesMethemoglobin Reductase PathwayinshNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Compiled Chintu Notes ..Document76 pagesClass 11 Compiled Chintu Notes ..Mohammed ArifuddinNo ratings yet
- 1 Slide BiasaDocument19 pages1 Slide BiasaFransiska Padma Dewi100% (1)
- Functions of The Respiratory PassagewaysDocument2 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory PassagewaysAdnin ShereenNo ratings yet
- Teachng DemoDocument32 pagesTeachng DemoNom NomNo ratings yet
- Nadi Shodhana (Stage 1)Document3 pagesNadi Shodhana (Stage 1)Béla JózsiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDDocument1 pageConcept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDBert Brian Bolido100% (1)