Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rd ESO Adj Order Lesson1
Uploaded by
Branka GavrilovichCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3rd ESO Adj Order Lesson1
Uploaded by
Branka GavrilovichCopyright:
Available Formats
In English, it is common to use more than one adjective before a noun -- for example, "He's a silly young
fool," or "she's a smart, energetic woman." When you use more than one adjective, you have to put them in
the right order, according to type. This page will explain the different types of adjectives and the correct
order for them.
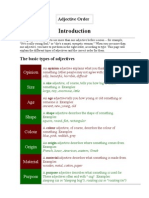
The basic types of adjectives
An opinion adjective explains what you think about something (other people may
Opinion not agree with you). Examples:
silly, beautiful, horrible, difficult
A size adjective, of course, tells you how big or small something is. Examples:
Size large, tiny, enormous, little
An age adjective tells you how young or old something or someone is. Examples:
Age ancient, new, young, old
A shape adjective describes the shape of something. Examples:
Shape square, round, flat, rectangular
A colour adjective, of course, describes the colour of something. Examples:
Colour blue, pink, reddish, grey
An origin adjective describes where something comes from. Examples:
Origin French, lunar, American, eastern, Greek
A material adjective describes what something is made from. Examples:
Material wooden, metal, cotton, paper
A purpose adjective describes what something is used for. These adjectives often
Purpose end with "-ing". Examples:
sleeping (as in "sleeping bag"), roasting (as in "roasting tin")
Some examples of adjective order
Opinion Size Age Shape Colour Origin Material Purpose
a silly young English man
a huge round metal bowl
a small red sleeping bag
You might also like
- Adjective Categories and ExerciseDocument2 pagesAdjective Categories and ExerciseKaren WestNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument1 pageAdjectivesapi-241242931No ratings yet
- Adjective Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAdjective Lesson Planstem73No ratings yet
- The Basic Types of AdjectivesDocument1 pageThe Basic Types of AdjectivesĐhamar HashiramaNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order PPDocument5 pagesAdjective Order PPJulio Armenta TorresNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument1 pageAdjective OrderamentisNo ratings yet
- Order of AdjetivesDocument5 pagesOrder of AdjetivesCarlos MinanoNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order UseDocument4 pagesAdjective Order UseNatalia StincaNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order Part 1Document2 pagesAdjective Order Part 1Byron PachacamaNo ratings yet
- Order of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesOrder of AdjectivessooghayNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Adjectives ExplainedDocument1 pageDescriptive Adjectives Explainediw2fualNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order Guide - Learn the Correct Order for Multiple AdjectivesDocument3 pagesAdjective Order Guide - Learn the Correct Order for Multiple AdjectivessafloviNo ratings yet
- Order of Adjective: Nama: Mirza Pratama Kelas: 2 EGB Nim: 061340411654Document3 pagesOrder of Adjective: Nama: Mirza Pratama Kelas: 2 EGB Nim: 061340411654mirza052No ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument17 pagesAdjectivesIlmz Vilma Manait - CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument17 pagesAdjectivesIlmz Vilma Manait - CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- Is A Word That Modifies A Noun or Pronoun. It Is Used To Tell Which One, What Kind, How Many, or How Much About Nouns and PronounsDocument17 pagesIs A Word That Modifies A Noun or Pronoun. It Is Used To Tell Which One, What Kind, How Many, or How Much About Nouns and PronounsIlmz Vilma Manait - CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument24 pagesAdjective Order113sonia113100% (3)
- 0 PDFDocument1 page0 PDFMaylen FerminNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument5 pagesAdjective OrderKat_23No ratings yet
- Orden de Adjetivos-RufinoDocument1 pageOrden de Adjetivos-Rufinoyupi_futbolNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order ExplainedDocument3 pagesAdjective Order ExplainedDiyantoNo ratings yet
- The Basic Types of Adjectives: OpinionDocument4 pagesThe Basic Types of Adjectives: OpinionAndree PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order Trird GradeDocument2 pagesAdjective Order Trird GradeNerioBurgaNo ratings yet
- Add NotesDocument1 pageAdd Notesraynold raphaelNo ratings yet
- Order-of-AdjectivesDocument34 pagesOrder-of-Adjectivesmarklayug621No ratings yet
- Which Is The Correct Order?Document4 pagesWhich Is The Correct Order?Lulu RoNo ratings yet
- Ordering Adjectives: I Can Order Adjectives in Sentences According To Conventional PatternsDocument23 pagesOrdering Adjectives: I Can Order Adjectives in Sentences According To Conventional PatternsJERALD HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Variation Through ExpansionDocument49 pagesVariation Through ExpansionJean Claude JavierNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument20 pagesPart of SpeechAyu Putri Aryati100% (1)
- Pinion Size Age Shape Colour Origin Material Purpose: Some Examples of Adjective OrderDocument11 pagesPinion Size Age Shape Colour Origin Material Purpose: Some Examples of Adjective OrderChristine BeltranNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Describe or Give Information About Nouns or PronounsDocument6 pagesAdjectives Describe or Give Information About Nouns or PronounsNor Hazila Mah HassanNo ratings yet
- What Do You Think ?Document21 pagesWhat Do You Think ?widi boerdanNo ratings yet
- Types of AdjectivesDocument6 pagesTypes of AdjectivesAkram SyamelNo ratings yet
- English Adjectives OrderDocument5 pagesEnglish Adjectives OrderFlaviaNo ratings yet
- Adjetives and AdverbsDocument7 pagesAdjetives and AdverbsSantiago PosadaNo ratings yet
- Adjective Lesson Plan - English Adjectives Activity: Opinion Size Age Shape Colour Origin Material PurposeDocument3 pagesAdjective Lesson Plan - English Adjectives Activity: Opinion Size Age Shape Colour Origin Material PurposemewaberiNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument22 pagesAdjective OrderRolly PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Adjective Word Order: Poor Okay Good Great AwesomeDocument2 pagesAdjective Word Order: Poor Okay Good Great Awesomewilliam felisildaNo ratings yet
- Order of Adjectives: Name: Fiola Finandakasih J1A112 020 Class: ADocument4 pagesOrder of Adjectives: Name: Fiola Finandakasih J1A112 020 Class: AFiola FinandakasihNo ratings yet
- Group AdjectivesDocument1 pageGroup AdjectivesrosarioNo ratings yet
- Adjectives OrderDocument1 pageAdjectives OrderDavid Yacchirema SilvaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives ActivitiesDocument8 pagesAdjectives Activitiesnobia jabeenNo ratings yet
- Background of The ProblemsDocument3 pagesBackground of The ProblemsRiski HeriyandaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Types of Adjectives: Opinio N SizeDocument3 pagesThe Basic Types of Adjectives: Opinio N SizeTeresaGilabertNo ratings yet
- The Basic Types of Adjectives: OpinionDocument12 pagesThe Basic Types of Adjectives: OpinionfacteNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument10 pagesAdjectivesAzmi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech English GrammerDocument16 pagesPart of Speech English GrammerSumang GjmNo ratings yet
- Contents NewDocument9 pagesContents NewBella PutriNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument4 pagesAdjective OrderSimone SantosNo ratings yet
- What Is An AdjectiveDocument4 pagesWhat Is An AdjectiveTyasmeita14No ratings yet
- English Orde of Adjective 2Document2 pagesEnglish Orde of Adjective 2inda_yolandaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives: Purpose. Some of These Categories Are (Roughly in The Order in Which Adjectives Are UsedDocument10 pagesAdjectives: Purpose. Some of These Categories Are (Roughly in The Order in Which Adjectives Are UsedSheylaMoralesNo ratings yet
- Order of AdjectivesDocument19 pagesOrder of AdjectivesPeterus BalanNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Order 2020Document4 pagesAdjectives and Order 2020Sofia SalasNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and InterjectionsDocument23 pagesAdjectives and InterjectionsGabriel DiazNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order GuideDocument5 pagesAdjective Order GuideFider Saputra TNo ratings yet
- U 3 Handout 9 Differnt Kinds of Nouns and AdjectivesDocument4 pagesU 3 Handout 9 Differnt Kinds of Nouns and AdjectivesMuhammad Mubasher AliNo ratings yet
- Adjective OrderDocument3 pagesAdjective OrderEstǝfaníaRojasAvendañoNo ratings yet
- English Composition & Style: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandEnglish Composition & Style: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNo ratings yet