Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current in Amperes - An Illustrated Chart
Uploaded by
Rafaelo09Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current in Amperes - An Illustrated Chart
Uploaded by
Rafaelo09Copyright:
Available Formats
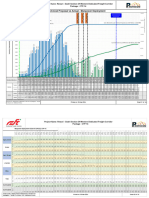
CURRENT IN AMPERES
100000
10000
20000
30000
40000
50000
60000
70000
80000
90000
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
1000 1000
2-200E
2-250E
2-300E
900 900
100E
125E
150E
175E
200E
250E
300E
800 800
10E
13E
15E
20E
25E
30E
40E
50E
65E
80E
3E
5E
7E
700 700
600 600
500 500
400 400
300 300
200 200
100 100
90 90
80 80
70 70
60 60
50 50
40 40
30 30
20 20
10 10
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
TIME IN SECONDS
TIME IN SECONDS
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
.9 .9
.8 .8
.7 .7
.6 .6
.5 .5
.4 .4
.3 .3
.2 .2
.1 .1
.09 .09
.08 .08
.07 .07
.06 .06
.05 .05
.04 .04
.03 .03
.02 .02
.01 .01
5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
20000
30000
40000
50000
60000
70000
80000
90000
100000
CURRENT IN AMPERES
MINIMUM MELTING TIME-CURRENT CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
SMD® FUSE UNITS—S&C STANDARD SPEED
BASIS—These fuse units are tested in accordance with the proce- when one or more fuse units have blown. Sometimes a selected ampere rating will fail to meet the coordi-
dures described in ANSI Standard C37.41-1981, and they are rated nation requirements in any available speed. In this case the selec-
COORDINATION—Any preloading reduces melting time. While this
to comply with ANSI Standard C37.46-1981. As required by these tion of another ampere rating for either the protecting or protected
phenomenon is especially pronounced in other makes of fuses
standards, the minimum melting current is not less than 200% of fuse usually will satisfy all requirements.
having minimum melting currents appreciably less than 200% of
fuse-unit ampere rating, and the minimum melting curves are based
rating, the effect of preloading must nonetheless be determined for Do not assume that other fuses that do not employ S&C’s silver,
on tests starting with the fuse unit at an ambient temperature of
the S&C fuse units represented by these curves (see S&C Data helically coiled fusible element construction can better resolve a
25°C and no initial load.
Bulletin 210-195) and adjustments to these curves must be made: coordination impasse than the use of another ampere rating in one
CONSTRUCTION—Fusible elements for fuse units rated 3E through 1. When close coordination is required; of the S&C speed options. Such other fuses, including “time-lag”
7E amperes are nickel-chrome, under controlled tension; fusible 2. When, regardless of the preciseness of coordination, the fuse speeds, “super-slow” speeds, and “high-surge” speeds, require the
elements for fuse units rated 10E through 300E amperes are silver, unit is subjected to temporary overloads. use of “safety-zone” or setback allowances and, in addition, they
helically coiled. All are of solderless construction. have larger construction tolerances (plus 20% in current; plus 40%
There are cases where the coordination requirements may be
in terms of time). The application of these two factors will give a time
TOLERANCES—Curves are plotted to minimum test points. Max- very exacting, for example, in coordinating a transformer primary
interval between the adjusted minimum melting curve and the total
imum variations expressed in current values are: fuse with a secondary breaker and a source-side breaker. The time
clearing curve greater than in the case of S&C speed options.
Plus 10% for 10E through 300E ampere ratings. interval between the operating characteristics of the two breakers
Plus 15% for 5E through 7E ampere ratings. may be very narrow. Under these circumstances there must be an
Plus 20% for 3E ampere rating. extremely short time interval between the minimum melting and the
FUSE UNITS AVAILABLE—
total clearing characteristics of the fuse.
APPLICATION—Like all high-voltage fuses, these fuse units are
Type Kv Nom. Ratings Ampere Ratings
intended to accommodate overloads, not to interrupt them. Accord- The fuse units represented by these curves possess this short
SMD-1Aa . . . . . . . . . . . . 34.5 through 69 .............3E through 200E
ingly, they feature fusible elements which are designed with a min- time interval feature, since—having a nondamageable fusible ele-
SMD-1A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115/138 .................10E through 100E
imum melting current of 200% of the fuse-unit ampere rating (for ment of precise construction—they require:
SMD-2Ba . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69........................3E through 300E
fuse units rated 100 amperes or less) or 220% of the fuse-unit 1. As little as 10% total tolerance in melting current—compared to
SMD-2Ba . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115 and 138................3E through 250E
ampere rating (for fuse units rated over 100 amperes). As a result, the 20% tolerance of many fuses (20% and 40% respectively
SMD-2Ca . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34.5 and 46 ................3E through 300E
these fuse units have considerable peak-load capabilities; however, in terms of time).
SMD-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69........................3E through 300E
they should never be exposed to loading in excess of the peak-load 2. No “safety-zone” or setback allowances.
SMD-50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34.5 through 69 .............5E through 100E
capabilities listed in S&C Data Bulletin 210-190.
This narrow time band normally will provide the desired coordi- a These curves are also applicable to previous designs desig-
Since fuse units having nickel-chrome or silver element con- nation. If the selected S&C Standard Speed fuse unit does not meet
nated SMD-1, SMD-2, SMD-2A, and SMD-2B.
struction are not subject to damage by aging or transient overcur- the coordination requirements, check to see if the same ampere
rents, it is unnecessary to replace unblown fuse units of either of rating in the S&C Slow Speed or S&C Very Slow Speed will satisfy.
these constructions in single-phase or three-phase installations
Supersedes TCC No. 153-1 dated 1-25-88 c1988
TCC NUMBER 153-1
s S&C ELECTRIC COMPANY • Chicago
S&C ELECTRIC CANADA LTD. • Toronto
Page 1 of 1
August 29, 1988
You might also like
- TCC Number 153 2 PDFDocument1 pageTCC Number 153 2 PDFOmar VazquezNo ratings yet
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyEddy UberguagaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Tripping Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyDocument1 pageMinimum Tripping Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyEddy UberguagaNo ratings yet
- 165 6 PDFDocument1 page165 6 PDFGonzalo Peñafiel CondoriNo ratings yet
- Current in Amperes ChartDocument1 pageCurrent in Amperes ChartEddy UberguagaNo ratings yet
- 165 6 2Document1 page165 6 2Carlos A. Carpio CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Fault Tamer Fuse LimitersDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Fault Tamer Fuse LimitersStoner WddNo ratings yet
- TCC Number 450 8 PDFDocument1 pageTCC Number 450 8 PDFjavier jimenez rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Smu Fuse Units For Voltage-Transformer Applications-S&C Standard SpeedDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Smu Fuse Units For Voltage-Transformer Applications-S&C Standard SpeedObed GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Melting Time-Current Characteristic CurvesDocument1 pageMinimum Melting Time-Current Characteristic CurvesObed GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Available Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Document1 pageAvailable Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)jurica_2006No ratings yet
- Available Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Document1 pageAvailable Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Amr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Shift index curve for long-time overcurrent protectionDocument1 pageShift index curve for long-time overcurrent protectionPrathap KumarNo ratings yet
- Multiples of Ground Fault Pickup SettingDocument1 pageMultiples of Ground Fault Pickup SettingjosehenriquezsotoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive guide to circuit breaker ground trip element settingsDocument2 pagesComprehensive guide to circuit breaker ground trip element settingsjurica_2006No ratings yet
- Long-time delay curve shift index for high ambient temperaturesDocument1 pageLong-time delay curve shift index for high ambient temperaturesBolivar MartinezNo ratings yet
- GES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingDocument1 pageGES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingAdolfo Sotomayor BurgosNo ratings yet
- GES-6122C: Multiples of Current RatingDocument1 pageGES-6122C: Multiples of Current RatingAdolfo Sotomayor BurgosNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ConductosDocument8 pagesCatalogo ConductosCarlos ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Shift Index Temperature ChartDocument1 pageShift Index Temperature ChartBolivar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Current Rating Multiples ChartDocument1 pageCurrent Rating Multiples ChartAmr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Situación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Oriente 14junio2021Document40 pagesSituación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Oriente 14junio2021cdc.inmunopreveniblesNo ratings yet
- DES-095B: Approximately (0.784-Actual Pickup)Document1 pageDES-095B: Approximately (0.784-Actual Pickup)shrikanth5singhNo ratings yet
- Situación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Norte 17junio2021Document49 pagesSituación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Norte 17junio2021cdc.inmunopreveniblesNo ratings yet
- TCC Number 115 4Document1 pageTCC Number 115 4Dennis RimandoNo ratings yet
- Des-095b - Long TimeDocument1 pageDes-095b - Long Timeshrikanth5singhNo ratings yet
- DES-101B: Multiple of Trip Rating PlugDocument1 pageDES-101B: Multiple of Trip Rating Plugjurica_2006No ratings yet
- Daily COVID-19 cases, deaths and recoveries from June 24 to July 16, 2021Document8 pagesDaily COVID-19 cases, deaths and recoveries from June 24 to July 16, 2021John Y FadrilanNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Overview: Dekalb County Residents With at Least 1 DoseDocument4 pagesVaccination Overview: Dekalb County Residents With at Least 1 DoseZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- Multiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit BreakersDocument1 pageMultiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit BreakersAmr AhmedNo ratings yet
- Curvas FusiblesDocument2 pagesCurvas FusibleswilmerNo ratings yet
- Long-time delay shift index chartDocument1 pageLong-time delay shift index chartMUSIC ELECNo ratings yet
- Monitoring EWDocument2 pagesMonitoring EWrfq2brd2ttNo ratings yet
- Multiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit Breakers Q LineDocument1 pageMultiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit Breakers Q LineMUSIC ELECNo ratings yet
- Model 9F54Dfc Series: Current in AmperesDocument1 pageModel 9F54Dfc Series: Current in AmperesPaulo H TavaresNo ratings yet
- KM. 27 E. AGUINALDO HIGHWAY GENERATOR SETSDocument1 pageKM. 27 E. AGUINALDO HIGHWAY GENERATOR SETSJOHN MICHAEL MADLAINGNo ratings yet
- 2016CT Compressor Specs at GlanceDocument4 pages2016CT Compressor Specs at GlanceabsahkahNo ratings yet
- Site Plan + Luas - 230426 - 223115Document1 pageSite Plan + Luas - 230426 - 223115J.T HalohoNo ratings yet
- Arabian Construction Company: Ruwais Igd 4Th NGL Train Project - Civil & BuildingsDocument1 pageArabian Construction Company: Ruwais Igd 4Th NGL Train Project - Civil & BuildingsJule Lobres0% (1)
- Kerja-Kerja Menaiktaraf Sistem Takungan Air Mentah Di Mukasauk Loji Rawatan Air (Lra) Kina Benuwa, Wilayah Persekutuan LabuanDocument1 pageKerja-Kerja Menaiktaraf Sistem Takungan Air Mentah Di Mukasauk Loji Rawatan Air (Lra) Kina Benuwa, Wilayah Persekutuan LabuanFarith AkbarNo ratings yet
- FSXA Quick Selection Chart TitleDocument2 pagesFSXA Quick Selection Chart TitleEmmanuel Ber SNo ratings yet
- Dekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyDocument13 pagesDekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- PARAN3E ExerciseNo2 Layout1Document1 pagePARAN3E ExerciseNo2 Layout1Mickaela Kassandra ParanNo ratings yet
- Nifty Technical AnalysisDocument136 pagesNifty Technical Analysisapi-3728932No ratings yet
- Master Plan 2022 - Koordinat - Papadino-ModelDocument1 pageMaster Plan 2022 - Koordinat - Papadino-ModelASNo ratings yet
- 2017CT CompressorSpecsAtAGlanceDocument4 pages2017CT CompressorSpecsAtAGlanceMadhana GopalNo ratings yet
- ADA Index and Sample Output PDFDocument8 pagesADA Index and Sample Output PDFKavita GohelNo ratings yet
- Power Point UASDocument1 pagePower Point UASNurul KhatimahNo ratings yet
- Struc TureDocument1 pageStruc TureAnh GiangNo ratings yet
- Daily COVID-19 UpdateDocument3 pagesDaily COVID-19 UpdateFikri MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 5.0 Ton at 600mm Load Center: SH1F4-1 / 13 Apr. '10Document30 pages3.5 5.0 Ton at 600mm Load Center: SH1F4-1 / 13 Apr. '10JulianoNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis - Charts, Trends & Patterns: Presented by Jayanthi Premkumar 0991014Document26 pagesTechnical Analysis - Charts, Trends & Patterns: Presented by Jayanthi Premkumar 0991014ruckumaaluNo ratings yet
- A5. Manpower Deployment Plan - Histogram (2)Document4 pagesA5. Manpower Deployment Plan - Histogram (2)vasavavatsaNo ratings yet
- Office A1 PDFDocument1 pageOffice A1 PDFalfredo agsunodNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor PlanDocument1 pageGround Floor Plansydney augustNo ratings yet
- MXD 3Document1 pageMXD 3Cesars TacussisNo ratings yet
- Asignación de Persinal Y Curva "S"Document2 pagesAsignación de Persinal Y Curva "S"RoberChavarríaCastañedaNo ratings yet
- 5 HVPT2 15Document2 pages5 HVPT2 15Rafaelo09No ratings yet
- 5 HVPT2 15Document2 pages5 HVPT2 15Rafaelo09No ratings yet
- Capitalizing On Effective CommunicationDocument18 pagesCapitalizing On Effective CommunicationRafaelo09No ratings yet
- Science Social Studies: Tippy-Toe Chick, Go!Document6 pagesScience Social Studies: Tippy-Toe Chick, Go!Rafaelo09No ratings yet
- A Proposed Method For Processing Unbalanced Conditions and DC Offset Currents in Transient Stability AnalysisDocument6 pagesA Proposed Method For Processing Unbalanced Conditions and DC Offset Currents in Transient Stability AnalysisRafaelo09No ratings yet