Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mantoux Wallchart
Mantoux Wallchart
Uploaded by
Rhea DerijeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mantoux Wallchart
Mantoux Wallchart
Uploaded by
Rhea DerijeCopyright:
Available Formats
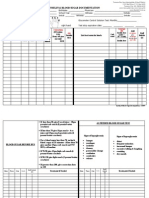
Mantoux tuberculin skin test
Administration
For each patient, conduct a risk assessment that takes into consideration recent exposure, clinical conditions that increase risk for TB disease if infected, and the programs capacity to deliver treatment for latent TB infection to determine if the skin test should be administered.
2
1
Reading
Interpretation
The skin test should be read between 48 and 72 hours after administration. A patient who does not return within 72 hours will probably need to be rescheduled for another skin test.
Skin test interpretation depends on two factors: Measurement in millimeters (mm) of the induration Persons risk of being infected with TB and progression to disease if infected The three cut points below should be used to determine whether the skin test reaction is positive. A person with a positive reaction should be referred for a medical evaluation for latent TB infection and appropriate follow-up and treatment if necessary. A measurement of 0 mm or a measurement below the defined cut point for each category is considered negative.
1 Locate and clean injection site
2 to 4 inches below elbow joint
Inspect site
Visually inspect site under good light Erythema (reddening of the skin) _ do not measure
Place forearm palm side up on a firm, well-lit surface Select an area free of barriers (e.g., scars, sores) to placing and reading Clean the area with an alcohol swab
Induration of 5 mm is considered positive in
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected persons Recent contacts of TB case patients
Induration (hard, dense, raised formation)
Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with prior TB
Patients with organ transplants and other immunosuppressed patients (e.g., receiving the equivalent of 15 mg/d of prednisone for 1 month or more)
Prepare syringe
Check expiration date on vial and ensure vial contains tuberculin (5 TU per 0.1 ml) Use a single-dose tuberculin syringe with a - to -inch, 27-gauge needle with a short bevel Fill the syringe with 0.1 ml of tuberculin
Palpate induration
Induration of 10 mm is considered positive in
Recent immigrants (i.e., within the last 5 years) from countries with a high prevalence of TB
Use fingertips to find margins of induration
Injection drug users Residents and employees* of the following high-risk congregate settings: - prisons and jails - nursing homes and other long-term facilities for the elderly - hospitals and other health care facilities - residential facilities for patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) - homeless shelters Mycobacteriology laboratory personnel Persons with the following clinical conditions that place them at high risk: - silicosis - diabetes mellitus - chronic renal failure - some hematologic disorders (e.g., leukemias and lymphomas) - other specific malignancies (e.g., carcinoma of the head, neck, or lung) - weight loss of 10% of ideal body weight - gastrectomy - jejunoileal bypass Children 5 years of age Infants, children, and adolescents exposed to adults at high risk for developing active TB
0.1 ml
Inject tuberculin
5 to 15 Angle Intradermal Inject ion
3
Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Tissue
15 5
Mark induration
Use fingertip as a guide for marking widest edges of induration across forearm
Insert slowly, bevel up, at a 5- to 15-degree angle
4
Needle bevel can be seen just below skin surface After injection, a tense, pale wheal should appear over the needle
Induration of 15 mm is considered positive in
Measure induration (not erythema)
Place 0 ruler line inside left dot edge
Persons with no known risk factors for TB
Read ruler line inside right dot edge (use lower measurement if between two gradations on mm scale)
Check skin test
* For employees who are otherwise at low risk for TB and who are tested as part of an infection control screening program at the start of employment, a reaction of 15 mm is considered positive. Some health care workers participating in an infection control screening program may have had an induration 0 mm that was considered negative at baseline. If these health care workers have an increase in induration size upon subsequent testing, they should be referred for further evaluation.
Wheal should be 6 to 10 mm in diameter. If not, repeat test at a site at least 2 inches away from original site
Record measurement of induration in mm
If no induration, record as 0 mm Do not record as positive or negative Only record measurement in mm
Record information
Record all the information required for documentation by your institution (e.g., date and time of test administration, injection site location, lot number of tuberculin)
Note: Reliable administration and reading of the tuberculin skin test involves standardization of procedures, training, supervision, and practice. Always follow your institutions policies and procedures regarding infection control, evaluation, and referral. Also remember to provide culturally appropriate patient education before and after administration, reading, and interpretation of the skin test.
For more information on tuberculosis, visit www.cdc.gov/tb
TM
TB Elimination
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Acid Alkaline Foods ChartDocument4 pagesAcid Alkaline Foods Charthealthalkaline100% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DMT PowerpointDocument21 pagesDMT Powerpointapi-3843268680% (1)
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Study Guideangieswenson100% (4)
- Surgery Clerkship ManualDocument29 pagesSurgery Clerkship ManualAndro GalaxNo ratings yet
- InstrumentsDocument135 pagesInstrumentsdoctor-to-be100% (1)
- A Snapshot of Demand For Adult-Use Cannabis in IllinoisDocument27 pagesA Snapshot of Demand For Adult-Use Cannabis in IllinoisTodd FeurerNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Homoeopathy in SarcoidosisDocument77 pagesEfficacy of Homoeopathy in SarcoidosisDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- Insulin & Blood Sugar DocumentationDocument2 pagesInsulin & Blood Sugar DocumentationeirnkathNo ratings yet
- Claiming Disability Living Allowance On Dual Diagnosis GroundsDocument8 pagesClaiming Disability Living Allowance On Dual Diagnosis GroundsMark SmidoNo ratings yet
- Finding Low-Cost Dental Care: National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)Document2 pagesFinding Low-Cost Dental Care: National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)P D SpencerNo ratings yet
- VBAC ScoreDocument3 pagesVBAC ScorepraburastraNo ratings yet
- Prescription Drug Abuse in Los Angeles County: Background and Recommendations For ActionDocument20 pagesPrescription Drug Abuse in Los Angeles County: Background and Recommendations For ActionSouthern California Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Script God's GiftDocument5 pagesScript God's GiftDATProudctionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science Form 1Document19 pagesChapter 1 Science Form 1Che SalNo ratings yet
- 1349072656CV Dr. Shaheen N KhanDocument17 pages1349072656CV Dr. Shaheen N KhanTanveer Abbas JafriNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation OrifDocument27 pagesCase Presentation OrifANJELO CYRUS BIARES GARCIANo ratings yet
- Faccioni Assisted and Resisted Methods For Speed Development Part 1Document5 pagesFaccioni Assisted and Resisted Methods For Speed Development Part 1MNo ratings yet
- Great Dane Full ContractDocument9 pagesGreat Dane Full Contractapi-391051712No ratings yet
- Lucy Basset Hound Rescue Medical RecordsDocument6 pagesLucy Basset Hound Rescue Medical Recordsnagpalpalak77No ratings yet
- 1-10 Aphorisms of Organon of MedicineDocument5 pages1-10 Aphorisms of Organon of MedicinedevainetNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cloning Vectors PDFDocument44 pages1 - Cloning Vectors PDFUsman ShamshadaliNo ratings yet
- Drugs and The Brain - CourseraDocument5 pagesDrugs and The Brain - CourseraSinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia in Cattle PDFDocument33 pagesRegional Anesthesia in Cattle PDFNiaz AsgharNo ratings yet
- Pearson CnsDocument19 pagesPearson CnsMohammed Mohammed EldeibNo ratings yet
- Justification For MonetizationDocument3 pagesJustification For MonetizationCharina Balunso100% (1)
- Method Development and Validation of Uv Spectrophotometric Methods For The Estimation of Darunavir in Bulk and Its Pharmaceutical Dosage FormDocument8 pagesMethod Development and Validation of Uv Spectrophotometric Methods For The Estimation of Darunavir in Bulk and Its Pharmaceutical Dosage FormBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Herbesser IVDocument24 pagesHerbesser IVsuho exoNo ratings yet
- GDD Implan Dengan Pemasangan LIO Sekunder Iris Claw Retro Pupillary Pada Pasien Pasca Vitrektomi LianiDocument11 pagesGDD Implan Dengan Pemasangan LIO Sekunder Iris Claw Retro Pupillary Pada Pasien Pasca Vitrektomi LianivellafebrinaefitaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument29 pagesGas Exchange in HumansLizzy AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Kekuatan Material: Oleh: Drs. Djony Izak Rudyardjo, M.Si Prodi S-1 TeknobiomedikDocument34 pagesKekuatan Material: Oleh: Drs. Djony Izak Rudyardjo, M.Si Prodi S-1 TeknobiomedikEva FahmadiyahNo ratings yet