Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nylon - : Plastic Molecular Weight
Uploaded by
Stela WinxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nylon - : Plastic Molecular Weight
Uploaded by
Stela WinxCopyright:
Available Formats
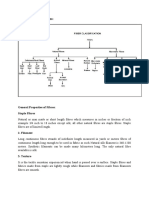
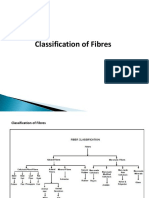
Nylon-;
Any synthetic plastic material composed of polyamides of high molecular weight and usually, but not always, manufactured as a fibre. Nylons were developed by Du Pont in the 1930s. The successful production of a useful fibre by chemical synthesis from compounds readily available from air, water, and coal or petroleum stimulated expansion of research on polymers, leading to a rapidly growing family of synthetics.
Cotton-;
Seed-hair fibre of various plants of the genus Gossypium, in the mallow family, native to most subtropical countries. One of the world's leading agricultural crops, cotton is plentiful and economically produced, making cotton products relatively inexpensive. The fibres can be made into a diverse array of fabrics suitable for a great variety of apparel, home furnishings, and industrial
uses. Cotton fabrics can be extremely durable and are comfortable to wear.
JuteEither of two herbaceous annuals (Corchorus capsularis and C. olitorius, in the linden family), or their fibre. Jute has been grown and processed in the Bengal area of India and Bangladesh since ancient times. Its biggest use is in burlap sacks and bags, which are used to ship and store many agricultural products. High-quality jute cloths are used as backing for tufted carpets and hooked rugs. Coarser jute fibres are made into twines, rough cordage, and doormats.
Woolen-;
Animal fibre that is the protective covering, or fleece, of sheep or such other hairy mammals as goats and camels.Wool is warm and lightweight
and takes dyes well. Woolen yarns, usually made from shorter fibres, are thick and full and are used for such items as tweed fabrics and blankets. Worsteds usually are made from longer fibres..
You might also like
- Raw MaterialsDocument104 pagesRaw MaterialsGarima BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Textiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesFrom EverandTextiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesNo ratings yet
- Textile - WikipediaDocument58 pagesTextile - WikipediaNani100% (1)
- Spinning, Dyeing and Weaving: Essential Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandSpinning, Dyeing and Weaving: Essential Guide for BeginnersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Economic Botany Fibres GuideDocument109 pagesEconomic Botany Fibres Guidesggdgd100% (1)
- FIBERDocument9 pagesFIBERnaivaanNo ratings yet
- Types of Textile IndustryDocument4 pagesTypes of Textile IndustryJanet Paletta100% (2)
- 1) Cotton: Cotton Is A Soft, Fluffy StapleDocument5 pages1) Cotton: Cotton Is A Soft, Fluffy StapleMayank Mohan VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Fibres Used in TextilesDocument12 pagesPlant and Animal Fibres Used in Textilesvenka07No ratings yet
- Origin of FibreDocument10 pagesOrigin of FibreShyam ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Textile Fibers StudyDocument9 pagesTextile Fibers StudyAbid hasanNo ratings yet
- CIT Campus, No 136/ 137, Ramchandrapur, Jatni, Khurda, Bhubaneswar 752050 Website: WWW - Nift.ac - inDocument9 pagesCIT Campus, No 136/ 137, Ramchandrapur, Jatni, Khurda, Bhubaneswar 752050 Website: WWW - Nift.ac - inPragya JainNo ratings yet
- Textile - WikipediaDocument10 pagesTextile - WikipediaMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Fabric Science Assignment 1 On "Hemp" & "Bamboo" Cohesiveness PropertyDocument10 pagesFabric Science Assignment 1 On "Hemp" & "Bamboo" Cohesiveness PropertyaadishNo ratings yet
- TDT 151 Lecture Notes 2022Document44 pagesTDT 151 Lecture Notes 2022Ollè WorldwideNo ratings yet
- Abirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessDocument76 pagesAbirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Abirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessDocument76 pagesAbirami Exports Manufacturing ProcesseswariNo ratings yet
- Knitting Assignment-Types of TextilesDocument32 pagesKnitting Assignment-Types of TextilesOwaiste0% (1)
- Statement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaDocument7 pagesStatement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaMark Angelo DiazNo ratings yet
- Textile Fibres Classification PPT 1Document43 pagesTextile Fibres Classification PPT 1tutu1990100% (4)
- Textile Fundamentals: Project On Fibre ClassificationDocument7 pagesTextile Fundamentals: Project On Fibre ClassificationAnubhav kashyapNo ratings yet
- Classification of FibresDocument12 pagesClassification of FibresARYAN RATHORENo ratings yet
- Mineral: RayonDocument3 pagesMineral: RayonArctic OceanNo ratings yet
- Plant: Verification NeededDocument1 pagePlant: Verification NeededEmdadul HoqNo ratings yet
- Engleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarDocument6 pagesEngleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarAndrea VekarićNo ratings yet
- Various Fabrics of IndiaDocument12 pagesVarious Fabrics of IndiaManasviNo ratings yet
- Properties Natural FibresDocument46 pagesProperties Natural FibresanishaNo ratings yet
- Processing and Production of WoolDocument10 pagesProcessing and Production of WoolrohishaakNo ratings yet
- Textile Industry - 01 LectureDocument40 pagesTextile Industry - 01 Lectureisabelism100% (1)
- Advanced Technologies For Textile and Fashion IndustryDocument5 pagesAdvanced Technologies For Textile and Fashion Industryfamilia -gentileNo ratings yet
- CottonDocument2 pagesCottonXeniya777No ratings yet
- Ntural and Man Made FibreDocument46 pagesNtural and Man Made FibreRemyaNo ratings yet
- SivanesanDocument42 pagesSivanesanKp PrakashNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Notes 1Document3 pagesFibre To Fabric Notes 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- SUNI - Classification and Types of Clothing FibersDocument32 pagesSUNI - Classification and Types of Clothing FibersJoseph MontainNo ratings yet
- Importance of Fibers in Textiles: Kavitha RajanDocument44 pagesImportance of Fibers in Textiles: Kavitha RajankavineshpraneetaNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Fibre PlantsDocument18 pagesUnconventional Fibre PlantsRajendra Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document62 pagesProject 2kuttappanvanneriNo ratings yet
- Cotton FiberDocument10 pagesCotton Fibermalikarslanali621No ratings yet
- Hotextile Lecture 2Document12 pagesHotextile Lecture 2fatima hussainNo ratings yet
- History of FabricDocument3 pagesHistory of Fabricudana0% (1)
- CoirDocument9 pagesCoirJulie MarieNo ratings yet
- Fiber Plants & DiscussionDocument10 pagesFiber Plants & DiscussionvishcrimeNo ratings yet
- Plant: Vicuña WoolDocument2 pagesPlant: Vicuña WoolArctic OceanNo ratings yet
- FIBRE (Power Point)Document54 pagesFIBRE (Power Point)MonirHossainNo ratings yet
- Jute and CottonDocument15 pagesJute and CottonDeepika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Raw Silk Production and Reeling IndustryDocument142 pagesRaw Silk Production and Reeling IndustryAdita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Natural Fibres 2Document26 pagesNatural Fibres 2Kebede kasaNo ratings yet
- Cotton Hai YeDocument7 pagesCotton Hai Yerahul0751No ratings yet
- History of Textile Production (Inglés) (Artículo) Autor Escuela Secundaria de Textil de LiberecDocument6 pagesHistory of Textile Production (Inglés) (Artículo) Autor Escuela Secundaria de Textil de LiberecRicardo SantosNo ratings yet
- Fiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Document18 pagesFiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Mahadi HabibNo ratings yet
- Textile Fiber Intro PDFDocument30 pagesTextile Fiber Intro PDFmoorthy_sweety43075% (8)
- TextileDocument6 pagesTextileBilla DamamiNo ratings yet
- Textiles Research TaskDocument8 pagesTextiles Research TaskKalleeNo ratings yet
- 7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalDocument101 pages7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalAdityaNo ratings yet
- Fiber CropsDocument3 pagesFiber Cropsmalath bash100% (1)
- Introduction To YarnDocument18 pagesIntroduction To YarnAbhradeep BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- A Study On Employees Administration in Sri Karpagam Organic Cotton KarurDocument68 pagesA Study On Employees Administration in Sri Karpagam Organic Cotton KarurMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Intro Textile Ij Mam 201 - AMTDocument72 pagesIntro Textile Ij Mam 201 - AMTMd. Sabbir Sabbir HossainNo ratings yet
- (A) Study On Impact Analysis of Microfinance On Poverty ReductionDocument65 pages(A) Study On Impact Analysis of Microfinance On Poverty ReductionSankalpa RimalNo ratings yet
- Murrel Farming PDFDocument10 pagesMurrel Farming PDFshridhanNo ratings yet
- Mezzogiorno PrimaryDocument1 pageMezzogiorno PrimarychrisZENGOOD tvNo ratings yet
- Ortoire River Basin WWDocument10 pagesOrtoire River Basin WWAlex Rosa100% (1)
- List of Greek and Latin Roots in English PDFDocument39 pagesList of Greek and Latin Roots in English PDFMvrnaidu MithraNo ratings yet
- Consumer Trends: Cooking Oils in Hong KongDocument21 pagesConsumer Trends: Cooking Oils in Hong Kongativ29No ratings yet
- Hacienda LuisitaDocument94 pagesHacienda LuisitanathNo ratings yet
- Technology AssessmentDocument6 pagesTechnology AssessmentTanmay PandyaNo ratings yet
- Anu FFDocument185 pagesAnu FFIron hippoNo ratings yet
- Resource and Development Next Topper ClassDocument18 pagesResource and Development Next Topper Classanath4714No ratings yet
- 1.1 Minimum Wage - PhilippinesDocument6 pages1.1 Minimum Wage - PhilippinesInhenyero TsupiteroNo ratings yet
- 10tauto Generated Amazon Forest Fire What It Tells Us About DeforestationDocument4 pages10tauto Generated Amazon Forest Fire What It Tells Us About DeforestationАндрей КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- HISTORY OF ABEOKUTA, THE CAPITAL OF OGUN STATE IN NIGERIADocument10 pagesHISTORY OF ABEOKUTA, THE CAPITAL OF OGUN STATE IN NIGERIAOgunsanya Enitan100% (1)
- Global Bee Colony Disorder and Threats Insect PollinatorsDocument16 pagesGlobal Bee Colony Disorder and Threats Insect PollinatorsannaphNo ratings yet
- Winged Bean High Protien Crop For The TropicsDocument58 pagesWinged Bean High Protien Crop For The TropicsplutocowNo ratings yet
- Merle, Robert - Malevil (v1.0)Document437 pagesMerle, Robert - Malevil (v1.0)Adam Šantić50% (2)
- Proceedings Tri-State Dairy Nutrition ConferenceDocument140 pagesProceedings Tri-State Dairy Nutrition Conferencepedro41No ratings yet
- Conveyors or Conveyor SystemDocument10 pagesConveyors or Conveyor SystemmotilalNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 English ActivitiesDocument2 pagesGrade 3 English Activitiessylvia nkambiNo ratings yet
- Survival and Dissemination of Plant PathogensDocument24 pagesSurvival and Dissemination of Plant PathogensSuprabuddha KunduNo ratings yet
- Mayang's Kutkutin in A JarDocument4 pagesMayang's Kutkutin in A JarKapitan SinoNo ratings yet
- Jack's Game - SupaduDocument16 pagesJack's Game - SupaduYakeline LópezNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-1.bijayananda Sahoo 2.jibesh Kumar Mohapatra 3.naresh Kumar Sahoo 4.soumya Surajit BiswalDocument37 pagesPresented By:-1.bijayananda Sahoo 2.jibesh Kumar Mohapatra 3.naresh Kumar Sahoo 4.soumya Surajit BiswaljibeshmNo ratings yet
- Cashew PriceDocument17 pagesCashew Price李今洋100% (2)
- Off-Farm and TE Getahun GemechuDocument61 pagesOff-Farm and TE Getahun GemechuZerihun SisayNo ratings yet
- Case 14 - Maple Leaf Consumer Foods - Fixing Hot DogsDocument3 pagesCase 14 - Maple Leaf Consumer Foods - Fixing Hot DogsRoseAnnGatuzNicolas100% (1)
- Agricultural TenancyDocument20 pagesAgricultural TenancyJel LyNo ratings yet
- Care Sheet Parrots and ParakeetsDocument5 pagesCare Sheet Parrots and ParakeetsNina Sapphire100% (1)
- Experienced Agricultural ResumeDocument4 pagesExperienced Agricultural ResumeDanny R. SalvadorNo ratings yet
- PSCLE General Paper 2012, Mar 23Document10 pagesPSCLE General Paper 2012, Mar 23Naps Library100% (2)