Professional Documents
Culture Documents
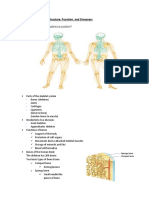
Parts of The Foot Bone
Uploaded by
Lady Daphne LandichoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of The Foot Bone
Uploaded by
Lady Daphne LandichoCopyright:
Available Formats
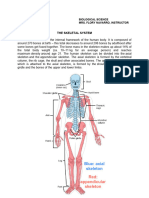
Parts of the Foot Bone: Tarsus the posterior half of the foot composed of seven tarsal bones: 1.
. Medial cuneiform 2. Intermediate cuneiform 3. Lateral cuneiform 4. Cuboid 5. Navicular 6. Talus 7. Calcaneus Metatarsals form the sole and are composed of 5 bones. Phalanges form the toes and are composed of 14 bones. Each toe has 3 phalanges with the exception of the great toe having only 2. Ligaments connects bones. Tendons attaches bone to a muscle allowing movements or a specific amount of elasticity
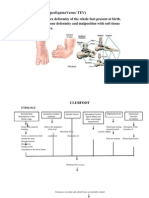
Pathophysiology Etiology The exact cause of this deformity is unknown. But suggestions or hypotheses of its disease process are the following: Genetic factor Abnormal tendon insertion Anomalous tendons may affect the alignment of the foot. Retracting fibrosis (myofibrosis) Collagen found in all ligaments and tendons are coiled and could be stretched with the exception of Achilles tendon (made up of tightly coiled collagen and cannot be stretched). Thickening and scarring of fibrous tissue could cause the twisted foot appearance. Neurogenic factors Innervation changes during the prenatal period could be due to the presence of neurologic events or disorder such as, spina bifida. Studies show that 35% of children with clubfoot have neurologicimpairment. Oligohydramnios Fluid leak during the prenatal period could cause restriction of fetal movements thereby, predisposing to a deformed foot. Developmental arrest of fetal development Disruption of the medial rotation of the fetal foot could result to a clubfoot condition. Diminished Vascular Circulation Disruption of the branches of the vascular supply of the lower extremity could contribute to misalignment of the foot.
In hip dislocation, the ball at the top of the thighbone (femoral head) does not sit securely in the socket (acetabulum) of the hip joint. Surrounding ligaments may also be loose and stretched. The ball may be loose in the socket or completely outside of it.
You might also like
- Lower LimbDocument53 pagesLower LimbRupesh M DasNo ratings yet
- Pes PlanusDocument6 pagesPes PlanusdeffyNo ratings yet
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesNo ratings yet
- Genovarum and GenovalgumDocument7 pagesGenovarum and GenovalgumVerli Fajriati NofliNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature, KyphoscoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosis: Spinal Curvature, Kyphoscoliosisiamweena17No ratings yet
- Assessment of Gait Disorders in ChildrenDocument3 pagesAssessment of Gait Disorders in ChildrenMadalina RarincaNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis PDFDocument19 pagesScoliosis PDFdallas100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Skeletal SystemPauline JoyceNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena KoushalNo ratings yet
- Assessment NX Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment NX Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLady Daphne LandichoNo ratings yet
- Bow Leg (Final) 3.9.20Document23 pagesBow Leg (Final) 3.9.20Gerald EthelieNo ratings yet
- Postural DeformitiesDocument37 pagesPostural DeformitiesBalram Jha80% (5)
- Cavus Foot 2015 Foot and Ankle ClinicsDocument13 pagesCavus Foot 2015 Foot and Ankle ClinicsRadu StoenescuNo ratings yet
- Club FootDocument5 pagesClub FootNika Joy Cabrera AlarconNo ratings yet
- Ankle and FootDocument31 pagesAnkle and FootmetoNo ratings yet
- Clubfoot: Bicol University Tabaco Campus Department of Nursing Tabaco CityDocument5 pagesClubfoot: Bicol University Tabaco Campus Department of Nursing Tabaco CitymikutekiNo ratings yet
- Adult Acquired Flatfoot DeformityDocument9 pagesAdult Acquired Flatfoot DeformityPutri ArthaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equino-Varus (Congenital Clubfoot) : by William Roy S. AgoncilloDocument8 pagesCongenital Talipes Equino-Varus (Congenital Clubfoot) : by William Roy S. AgoncilloWilliam AgoncilloNo ratings yet
- Congenital AbnormalitiesDocument37 pagesCongenital AbnormalitiesrezkadehaNo ratings yet
- ClubfootDocument5 pagesClubfootcreyannc0% (1)
- Exam 2 Study Guide (1146)Document7 pagesExam 2 Study Guide (1146)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- BulaloDocument7 pagesBulaloRobin HaliliNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: If Your Child Has Clubfoot, Here's What It Might Look LikeDocument112 pagesSymptoms: If Your Child Has Clubfoot, Here's What It Might Look LikeSantosh RudraNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH ASKEP SKOLIOSIS - KELOMPOK 3 - KELAS 2B - Yuk Bisa YukDocument37 pagesMAKALAH ASKEP SKOLIOSIS - KELOMPOK 3 - KELAS 2B - Yuk Bisa Yukfikri pratamaaaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument88 pagesThe Skeletal SystemjpotiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument31 pagesStructure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemSaminathan KayarohanamNo ratings yet
- Systems of The BodyDocument144 pagesSystems of The BodyTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- Fibular Hemimelia FAQsDocument11 pagesFibular Hemimelia FAQsLucila LugoNo ratings yet
- Normal Bone Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNormal Bone Anatomy and PhysiologyElsa GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Limb Length Discrepancy: Amputation Versus Reconstruction For Fibular HemimeliaDocument5 pagesLimb Length Discrepancy: Amputation Versus Reconstruction For Fibular HemimeliaAlfred JacksonNo ratings yet
- Tethered Cord SyndromeDocument10 pagesTethered Cord SyndromeLinda SugiartoNo ratings yet
- 30.ankle & Foot DiseasesDocument46 pages30.ankle & Foot DiseasesDuha HamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document27 pagesChapter 13Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus 222Document10 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus 222jjjj30No ratings yet
- Appendicular & LimbDocument29 pagesAppendicular & LimbPeter PrestonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Congenital Bone DisorderDocument100 pagesLecture 6 Congenital Bone DisorderWilson HalimNo ratings yet
- Human Skeleton: Navigation SearchDocument7 pagesHuman Skeleton: Navigation SearchvinaiyaNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Bone Serves To Protect The Internal Organs Such As The Small Intestine and ColonDocument2 pagesPelvic Bone Serves To Protect The Internal Organs Such As The Small Intestine and Colonde andryNo ratings yet
- Patho ClubfootDocument5 pagesPatho ClubfootKim LegastoNo ratings yet
- Easy Skeletal SystemDocument106 pagesEasy Skeletal SystemmikiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesAnatomy Test 1 ReviewRj GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemlorence.13911No ratings yet
- Dr. Jufri Latief (Neuromuskuler Problems)Document28 pagesDr. Jufri Latief (Neuromuskuler Problems)EmirNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spondylosis Case Study CT2Document27 pagesLumbar Spondylosis Case Study CT2hnihnn02No ratings yet
- Internal RotationDocument15 pagesInternal RotationBrian ChimpmunkNo ratings yet
- ClubfootDocument9 pagesClubfootLorebell100% (5)
- Organic Matrix: 1. According To Shape and SizeDocument9 pagesOrganic Matrix: 1. According To Shape and SizePrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Premedical Biology: Motor MechanismDocument44 pagesPremedical Biology: Motor MechanismsheenaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equino Varus (Ctev) - Nur HanisahDocument11 pagesCongenital Talipes Equino Varus (Ctev) - Nur HanisahNur HanisahNo ratings yet
- Blount's Disease (Textbook)Document17 pagesBlount's Disease (Textbook)Fadzhil AmranNo ratings yet
- Talipes Deformity or ClubfootDocument5 pagesTalipes Deformity or ClubfootcrisolandNo ratings yet
- Knee Anatomy & Disorders: By: Nour Abu Al-Sha'arDocument28 pagesKnee Anatomy & Disorders: By: Nour Abu Al-Sha'arAlisha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Wprkshop Ppt... 01Document53 pagesWprkshop Ppt... 01Varun ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- pGALS Examination OSCE GuideDocument18 pagespGALS Examination OSCE GuideFanny PritaningrumNo ratings yet
- Presentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. AnsariDocument48 pagesPresentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. Ansarimohammad farhanNo ratings yet
- A. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Document8 pagesA. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Kim LiatNo ratings yet
- Blount's Disease (Textbook)Document17 pagesBlount's Disease (Textbook)Fadzhil AmranNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesBones in The Body 1. Skull: Skeletal SystemSolemnly SwearrNo ratings yet
- Bio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesBio1 BSN 1 Skeletal SystemCamela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- Development of LimbsDocument29 pagesDevelopment of LimbsAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
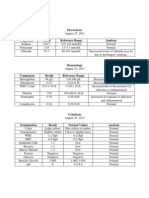
- Laboratory ExaminationsDocument1 pageLaboratory ExaminationsLady Daphne LandichoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Deep Brain & WhipplesDocument8 pagesCase Analysis - Deep Brain & WhipplesLady Daphne LandichoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExaminationsDocument1 pageLaboratory ExaminationsLady Daphne LandichoNo ratings yet
- Surgical TechniqueDocument1 pageSurgical TechniqueLady Daphne LandichoNo ratings yet