Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cisterne Mozga
Uploaded by
Turkalj IvanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisterne Mozga
Uploaded by
Turkalj IvanCopyright:
Available Formats
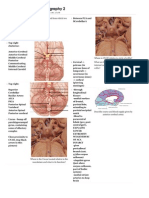
1. Posterior fossa cisterns 1. Cisterna magna a.k.a. cerebellomedullary cistern; posterior to medulla and clivus; location of PICA 2.
. Prepontine cistern CN 5 and 6, basilar artery, AICA 3. medullary cistern anterior to medulla; vertebral arteries; anterior and posterior spinal arteries, PICA, CN 12 4. Cerebellopontine cistern CN 5, 7 and 8, AICA 5. superior cerebellar cistern between tentorium and vermis, connects with quadrigeminal cistern anterosuperiorly; superior cerebellar artery, superior vermian veins 2. suprasellar (basal) cisterns 1. Interpeduncular cistern CN 3, basilar artery, SCA, PCA, Pcomm, basal vein of Rosenthal 1. Lilliquists membrane is an arachnoidal sheet that extends from the dorsum sellae to the anterior edge of the mamillary bodies; separates the interpeduncular and chiasmatic cisterns; forms a competent barrier in 10-30% of the population 2. Chiasmatic cistern located below the optic chiasm; ICA, ACA, MCA, Pcomm, anterior choroidal artery 3. Mesencephalic cisterns 1. Ambient cistern sheet like subarachnoid extensions around the midbrain, continuous with quadrigeminal cistern; CN 4 and 6, PCA, SCA 2. Quadrigeminal cistern a.k.a. cistern of great cerebral vein; connects ambient and superior cerebellar cisterns; pineal, vein of Galen, PCA 3. velum interpositum above third ventricle; below corpus callosum and fornix, anterior continuation of quadrigeminal cistern; internal cerebral veins, branches of anterior and posterior choroidal arteries 4. Cistern of the lamina terminalis: ACA and frontopolar artery 5. Callosal cistern above corpus callosum, between and below cingulated gyri 6. Crural cistern located between cerebral peduncle and uncus; PCA and anterior choroidal artery 7. Suprasellar cistern 8. Carotid cistern
You might also like
- Brain Cisterns: Suresh Bishokarma, MCH (Neurosurgery NinasDocument50 pagesBrain Cisterns: Suresh Bishokarma, MCH (Neurosurgery NinasntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- CSF SpacesDocument55 pagesCSF SpacesRitu pantaNo ratings yet
- The Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument12 pagesThe Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DIndra HadianditeNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply NeuroDocument60 pagesBlood Supply NeuroFatima FalahNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Brain & Spinal Cord by DR SarwarDocument52 pagesBlood Supply of The Brain & Spinal Cord by DR SarwarashrafNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryDocument5 pagesAnatomical Observations of The Subarachnoid Cisterns of The Brain During SurgeryMatheus FernandesNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Brain: Gigi Fernandez-Agbisit, MD Pediatric NeurologistDocument40 pagesBlood Supply of The Brain: Gigi Fernandez-Agbisit, MD Pediatric NeurologistVivien EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Vascular of BrainDocument52 pagesLecture Vascular of BrainAditya Pramana KasidiNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Brain: by Dr. Noura El TahawyDocument100 pagesBlood Supply of The Brain: by Dr. Noura El TahawySureshNo ratings yet
- Review of Functional Neuroanatomy (7) CNS VascularizationDocument38 pagesReview of Functional Neuroanatomy (7) CNS VascularizationUunsariNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Brain and Dural Venous SinusesDocument68 pagesBlood Supply of The Brain and Dural Venous Sinusesأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal FluidDocument41 pagesSubarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal Fluidharjoth395No ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 Saraf C2Document111 pagesPemicu 4 Saraf C2CcNo ratings yet
- Brain Topography 2Document6 pagesBrain Topography 2Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Vascularizatia SNCDocument106 pagesVascularizatia SNCCiopraga IuliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Cerebrum: Neuroscience 1: Cerebral CirculationDocument11 pagesLecture 11: Cerebrum: Neuroscience 1: Cerebral CirculationAudrey Nicole LisingNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument49 pagesBlood Supply of BrainDarling Sevenfoldism SynysterNo ratings yet
- Sistem Ventrikel Dan LCSDocument22 pagesSistem Ventrikel Dan LCSsamiratumananNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument21 pagesBlood Supply of The Brainrey martinoNo ratings yet
- Circle WillisDocument42 pagesCircle WillisShazada KhanNo ratings yet
- ATA-PCA BypassDocument4 pagesATA-PCA Bypasskaan_yagmur7711No ratings yet
- Ventricles Sub ArachnoidspaceDocument41 pagesVentricles Sub ArachnoidspaceShivaranjani sakthivelNo ratings yet
- DR Sameeha KhanDocument69 pagesDR Sameeha KhanCristian O. Saavedra RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum - Dr. TalabuconDocument232 pagesCerebrum - Dr. TalabuconstudyproblemNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Anatomy: Ms CurriculumDocument29 pagesNeurovascular Anatomy: Ms CurriculumJack Jenkins0% (1)
- Neuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentDocument36 pagesNeuro 10 Cerebrovascular Supply StudentLeoNo ratings yet
- Meninges وهدانDocument10 pagesMeninges وهدانوسيم جمال مياسNo ratings yet
- The Cerebral Circulation and Cerebrovascular Disease I: AnatomyDocument24 pagesThe Cerebral Circulation and Cerebrovascular Disease I: AnatomyNazliah SyarbinNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 4Document12 pagesCapitulo 4Carla MonteroNo ratings yet
- 2 Arteres-Supratentorielles PDFDocument68 pages2 Arteres-Supratentorielles PDFMihai Soplica PancuNo ratings yet
- Cerebraal Spinal FluidDocument34 pagesCerebraal Spinal FluidElisa NNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood and Venous Drainage BrainDocument24 pagesArterial Blood and Venous Drainage BrainMahrukh RajputNo ratings yet
- Vascular Anatomy and CSF SpacesDocument64 pagesVascular Anatomy and CSF SpacesJha K SujitNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesThe Brain and Cranial NervesJet ToralbaNo ratings yet
- II - 22. Common Carotid Artery+ CNDocument3 pagesII - 22. Common Carotid Artery+ CNalllexissssNo ratings yet
- Brain CisternsDocument42 pagesBrain CisternsLepaca KliffothNo ratings yet
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1Document20 pages11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1checkmateNo ratings yet
- Intracranial ArteriesDocument98 pagesIntracranial ArteriesAgnesthesiaNo ratings yet
- yZGn9p PaudelDocument4 pagesyZGn9p PaudelAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- L1 Cerebrovascular Anatomy and Nerves of Lower LimbDocument48 pagesL1 Cerebrovascular Anatomy and Nerves of Lower LimbAshraf NabilNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Circulation: Presented BY Dr. Shambhu Shah 1 Yr P.G N.M.C THDocument14 pagesIntracranial Circulation: Presented BY Dr. Shambhu Shah 1 Yr P.G N.M.C THsheshNo ratings yet
- Cns Vascularization DR - Dianayu Hamama Pitra, SP.S, M.BiomedDocument43 pagesCns Vascularization DR - Dianayu Hamama Pitra, SP.S, M.BiomedHayaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Circulation Part 2Document12 pagesPosterior Circulation Part 2priyanka arunNo ratings yet
- Sosa 2016Document10 pagesSosa 201616fernandoNo ratings yet
- 6.cme Brain AnatomyDocument31 pages6.cme Brain AnatomyAidil IdhamNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument12 pagesBlood Supply of BrainSharon Rose Genita Medez100% (1)
- Lymphatic FilariasisDocument17 pagesLymphatic FilariasisSelvaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Conditions 4 StrokeDocument4 pagesNeurologic Conditions 4 StrokeEdward De LeonNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument2 pagesBlood Supply of BrainvmagtotoNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument55 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument75 pagesBlood Supply of BrainMurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 17 Brain VascularizationDocument86 pages17 Brain VascularizationMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument11 pagesBlood Supply of The Brainneleh grayNo ratings yet
- The Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal FluidDocument39 pagesThe Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal Fluidnurul rezki fitrianiazisNo ratings yet
- 1 BloodsupplyofbrainDocument36 pages1 Bloodsupplyofbrainsanofazal786No ratings yet
- Anatomy AxillaDocument2 pagesAnatomy AxillaFroi Jovanni PerezNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument11 pagesBrainBilal MashagebahNo ratings yet
- Internal CapsuleDocument24 pagesInternal CapsuleBimaIndraNo ratings yet