Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tablet Composition
Uploaded by
Enrique_iranieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tablet Composition
Uploaded by
Enrique_iranieCopyright:
Available Formats
Tablet composition
Diluent (frtunningsmedel, utspdningsmedel) Dicalcium phosphate Lactose Mannitol Starch Magnesium stearate Cellulose Diluent properties * To provide improved cohesion * To allow direct compression manufacturing * To enhance flow * To adjust weight of tablet as per die capacity Lubricant (glidmedel, smrjmedel) Magnesium stearate (especially in tablet formulations) Lubricant properties: * Improves flow properties of granules * Reduces powder adhesion onto the dies and punches * Reduces punsch and die wear * Faciliates tablet ejection from the die * Water insoluble ( difficult to wet) Glidant Talc Sweetener Aspartame Mannitol Bulking agent (gr partiklarna strre s att man ser nr mnet r lst) Mannitol Antimicrobial perservative Benzyl alhocol Propyl Methyl Benzyl Antiadherent Colloidal silica Sodium lauryl sulfate Cornstarch Stearates
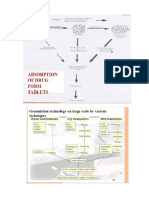
Antiadherent * Aiding picking by puches * Avoiding sticking to die walls Colourants * Facilitate identification of similar looking products with in a product line to avoid confusion * To overcome colour change on aging * To enhance the aesthetic appearance of the product to have better patient compliance * For brand image in the market Pregelatinized Starch can be used as a (multifunctional excipient): * Disintegrant * Flow aid * Diluent * Tablet binder Tablet disintegrant Starch Cellulose Alignates Ion-echange resins Chelating agents (wetting agent) Aids water uptake and thereby enhancing disintegration and assisting in drug dissolution. Chelator Tartaric Acid Granule formation steps 1) Nucleation 2) Transition 3) Ball growth Colorant Indigotine Erythrosin Tartrazine Emulsifying agent Other names: Wetting agents, surfactants, surfactive agents. It lowers the surface and interfacial tension. These agents permit more inimate contact between an aqueous phase and a lipid phase. Emulsifying agents Soaps
Sodium lauryl sulfate Dioctyl sodium
You might also like
- Laundry Detergents Formulation With ExplanationsDocument13 pagesLaundry Detergents Formulation With Explanationsramu_uppada89% (9)
- ExcipientsDocument40 pagesExcipientsLidya Ameliana100% (1)
- Dishwashing LiquidDocument3 pagesDishwashing LiquidTots Holares100% (6)
- Types of ExcipientsDocument3 pagesTypes of ExcipientsNarasimha RajuNo ratings yet
- Tablets NotesDocument56 pagesTablets NotesLakshmi Kumari100% (1)
- TabletsDocument104 pagesTabletsWalaa abo foolNo ratings yet
- Validasi TabletDocument79 pagesValidasi TabletZein Mxrc BdgNo ratings yet
- Tablet Ingredients: Pharmaceutical Technology I PHARM 2322 byDocument42 pagesTablet Ingredients: Pharmaceutical Technology I PHARM 2322 bySuzie JayNo ratings yet
- Exp Pharmainfo NetDocument56 pagesExp Pharmainfo NetVijay Mallavarapu0% (1)
- Perc Aka PanDocument16 pagesPerc Aka PanASOMA Z.No ratings yet
- TabletDocument80 pagesTabletParizal Very100% (4)
- TabletsDocument117 pagesTabletscontactamit_shah100% (1)
- Technology of Making Tablets: Murat KizaibekDocument79 pagesTechnology of Making Tablets: Murat KizaibekSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Tablets Mod 4Document15 pagesTablets Mod 4Manasvi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument46 pagesPharmaceutical ExcipientsMasum HossinNo ratings yet
- C-8 TabletDocument129 pagesC-8 TabletLareina Uy Calubad67% (3)
- Introduction To TabletsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Tabletssyedamaryamali19No ratings yet
- Tablets TextDocument18 pagesTablets TextarunbaskaranjNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GEA Courtoy: Presented by Presenter: Sangram KendreDocument79 pagesPresentation On GEA Courtoy: Presented by Presenter: Sangram KendreSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Ipqcsoliddosageforms 210223184929Document43 pagesIpqcsoliddosageforms 210223184929dr Amr Aly ReshaNo ratings yet
- ExcipientsDocument13 pagesExcipientsMahbubur Rahman RubonNo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage Form Part 2Document44 pagesSolid Dosage Form Part 2Claire Marie AlvaranNo ratings yet
- ExcipientsDocument20 pagesExcipientsSolomonNo ratings yet
- Roleof ExipiantsDocument8 pagesRoleof ExipiantsRafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Neccesity of Auxiliaries in DyeingDocument3 pagesNeccesity of Auxiliaries in DyeingMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Formulation Excipients of TabletsDocument10 pagesFormulation Excipients of TabletsatjaiNo ratings yet
- Paint and Coatings Additivesformulating With MikeDocument7 pagesPaint and Coatings Additivesformulating With Mikerndsb.aopNo ratings yet
- TabletDocument14 pagesTabletIVLS AKCPNo ratings yet
- 3 Hinds - Flour Tortilla Extensibility & TranslucencyDocument34 pages3 Hinds - Flour Tortilla Extensibility & TranslucencyUname EpithetoNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Prepared By: Roshni Mehta PHD Research Scholar Guided By: Dr. Yamini Shah Associate ProfessorDocument169 pagesTablets: Prepared By: Roshni Mehta PHD Research Scholar Guided By: Dr. Yamini Shah Associate ProfessorMithu SarkerNo ratings yet
- Tablet Manufacture Formulation and ProcessingDocument45 pagesTablet Manufacture Formulation and ProcessingSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pharmaceutical Tecnology: (Essentials)Document44 pagesIndustrial Pharmaceutical Tecnology: (Essentials)Selvakumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Tablet ExcipientsDocument15 pagesTablet ExcipientsFarhatNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptDocument72 pagesPharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptFANTANo ratings yet
- By Chetana ModiDocument30 pagesBy Chetana ModiGadi Srinath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Development of Orally Disintegrating and Dispersible TabletsDocument60 pagesChallenges in Development of Orally Disintegrating and Dispersible TabletsAhmad AinurofiqNo ratings yet
- Printing Paste IngredientsDocument10 pagesPrinting Paste Ingredientsloki bNo ratings yet
- Tide PowderDocument7 pagesTide PowderDuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument32 pagesPharmaceutical ExcipientsrandatagNo ratings yet
- Tablets-Part IIDocument42 pagesTablets-Part IIali.menem15No ratings yet
- Tablet FinalDocument104 pagesTablet FinalAngela PagalilauanNo ratings yet
- ORAL DISINTEGRATING TABLETS 2020-Converted-CompressedDocument43 pagesORAL DISINTEGRATING TABLETS 2020-Converted-CompressedAnisaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Tiga Jenis UtamaDocument20 pages3 - Tiga Jenis UtamaLaras SubektiNo ratings yet
- Lubricants in Pharmaceutical Solid Oral Dosage FormDocument3 pagesLubricants in Pharmaceutical Solid Oral Dosage Formqaz_qazNo ratings yet
- 10 Marks)Document4 pages10 Marks)Mussa MwaitolageNo ratings yet
- Dosage FormsDocument42 pagesDosage FormsArpita VermaNo ratings yet
- Stability Considerations For All Dosage Forms of DrugsDocument3 pagesStability Considerations For All Dosage Forms of DrugsAshraf ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Printing ThickenersDocument14 pagesPrinting ThickenersGrady YohanNo ratings yet
- Tablet CoatingDocument7 pagesTablet CoatingLakmi Nurul UciiNo ratings yet
- ExcipientDocument6 pagesExcipientnevelle4667No ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Tablets-FINAL PARTDocument11 pagesManufacturing of Tablets-FINAL PARTbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Organic Coatings: Paints Varnishes Enamels LacquersDocument20 pagesOrganic Coatings: Paints Varnishes Enamels LacquersMadhavanIceNo ratings yet
- Additives Quiz 3Document9 pagesAdditives Quiz 3BEA RADANo ratings yet
- L3 PDFDocument8 pagesL3 PDFSadeq Al-tmimiNo ratings yet
- Components of A Dosage FormDocument56 pagesComponents of A Dosage FormAlapinos CrunzNo ratings yet
- The Role of Disintegrants in Solid Oral Dosage ManufacturingDocument17 pagesThe Role of Disintegrants in Solid Oral Dosage ManufacturingRhosuna Aina0% (1)
- PH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesDocument11 pagesPH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesKrsna NaveraNo ratings yet
- Veegum & XanthanDocument27 pagesVeegum & XanthanConcept77No ratings yet