Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spectros
Uploaded by
Vishal SahuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spectros
Uploaded by
Vishal SahuCopyright:
Available Formats
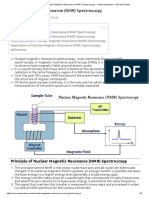
SPECTROSCOPY Spectroscopy is a branch of science that deals with the study of interaction of electro-magnetic radiations with matter.
The most important consequence of such interaction is that energy is either released or absorbed by the matter in discrete amount called as quanta. The emission and absorption process takes place through the electromagnetic spectrum from gamma ray region to radio-frequency region. Spectroscopy is one of the most important tools for the study of molecular and atomic structure and is applicable to a wide range of sample. It is studied under two heads:1). Atomic spectroscopy: - It is a branch of spectroscopy that deals with the interaction of electro-magnetic radiation of atoms which arte in their lowest energy state. 2). Molecular spectroscopy: - It is the branch of spectroscopy that deals with the study electro-magnetic radiation of molecules. Molecular spectra extend from visible light region through infra-red region into microwave region. The instrument that records the intensity of radiation is called as spectrophotometer or simply spectrometer. NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy):It is the branch of spectroscopy in which radio frequency waves induced transitions in magnetic energy levels of nuclei of molecules. The magnetic energy levels are created by keeping nuclei in magnetic field. Without magnetic field they posses same energy and transition is not possible. When magnetic field is applied, then transitions take place in different energy levels. NMR spectroscopy gives following information: (1)- The different chemical environment of different protons present in a molecule. (2)- The relation between number of signals in spectra and the number of different types of protons. (3)- Position of the signals (kinds of protons). (4)- Intensity of the signals. (5)- Splitation of signals and area under the peak. Number of signals (Equivalent and non-equivalent protons):In a given molecule proton ion same environment and same applied magnetic field strength are called as magnetically equivalent protons while protons in different environment and different applied magnetic field strength are called as magnetically non equivalent protons.
The number of signals in NMR spectra tells how many types of protons are present in the molecule. Each signal in NMR spectra is corresponding to the set of equivalent protons.
You might also like
- NMR Case Studies: Data Analysis of Complicated MoleculesFrom EverandNMR Case Studies: Data Analysis of Complicated MoleculesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioenergetic AssignmentDocument16 pagesBioenergetic Assignmentshanza FaheemNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument35 pagesSpectrosLoren Victoria AgbayNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument23 pagesNuclear Magnetic ResonanceDavid OsasNo ratings yet
- Written Report NMR SpectrometryDocument6 pagesWritten Report NMR SpectrometryRye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy)Document3 pagesNMR Spectroscopy)smart ptmNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument31 pagesNuclear Magnetic ResonanceDrPrashant ShihoraNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Kerja Instrumen Spektroskopi: 1. Spektrofotometer UV-VisDocument10 pagesPrinsip Kerja Instrumen Spektroskopi: 1. Spektrofotometer UV-ViswardaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument46 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaAnubhav VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument10 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosLaura CelisNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument7 pagesSpectrosSuraj RarathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1a PDFAmber FatimaNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Historical Background of NMR Spectroscopy: (Chapter - 01) Introduction 1Document36 pages1.1. Historical Background of NMR Spectroscopy: (Chapter - 01) Introduction 1Amber FatimaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 4: NMR Analysis of A Constitutional IsomerDocument18 pagesEXPERIMENT 4: NMR Analysis of A Constitutional IsomerDhiyyah Mardhiyyah100% (1)
- CHE 276 PPT - Introduction To Organic SpectrosDocument8 pagesCHE 276 PPT - Introduction To Organic SpectrosEmmy OlabosipoNo ratings yet
- SpectroDocument3 pagesSpectroAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- NMR Workshop ReportDocument18 pagesNMR Workshop ReportmrtharamNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of TheDocument51 pagesSpectroscopy: Spectroscopy Is The Study of ThePalwan SaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Analytical Techniques SPJDocument13 pagesChapter-9 Analytical Techniques SPJAvesh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMRDocument15 pagesProton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMRJes AnthonyNo ratings yet
- H NMRDocument34 pagesH NMRbsmalah11alroxnamNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesDocument2 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy - Instrumentation - Microbe Notesjimgitonga100% (2)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 3be574aa E12a 4ba6 80f6 573389d5c75dDocument11 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 3be574aa E12a 4ba6 80f6 573389d5c75dBeamlak MarelignNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Document26 pagesAtomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1Hammed LawalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance - WikiDocument16 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance - Wiki12BAcNo ratings yet
- NMR ReichiDocument186 pagesNMR ReichiJanni ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- IR by Faisal Hassnai PDFDocument12 pagesIR by Faisal Hassnai PDFMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Ch09-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Mass SpectrometryDocument47 pagesCh09-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Mass SpectrometryVicky Faras Barunson PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument25 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosFalak Naz100% (1)
- What Is It?Document6 pagesWhat Is It?PharmaEducationNo ratings yet
- Raman Spectros PDFDocument14 pagesRaman Spectros PDFTanvi BattaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFDocument43 pagesSpectroscopy Revised 10oct22 PDFGundanNo ratings yet
- X RaysDocument7 pagesX RaysHarshmeek KaurNo ratings yet
- Module-1Principles of SpectrosDocument9 pagesModule-1Principles of SpectrosveronislisteningNo ratings yet
- NMR For BSCDocument13 pagesNMR For BSCmalluchaithra88_3587No ratings yet
- Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy - WikipediaLuan D SouzaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance IntroDocument17 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Introlisan2053No ratings yet
- Objectives of The StudyDocument24 pagesObjectives of The Studysanjeev1962kumarNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy: The TheoryDocument4 pagesNMR Spectroscopy: The Theoryoliv1aNo ratings yet
- NMRDocument17 pagesNMRSourabhNo ratings yet
- NMR - A ThesisDocument4 pagesNMR - A ThesisJ KNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDocument17 pagesUnit VI Molecular Spectroscopy: Physical ChemistryDewal Deshmukh100% (1)
- 2005 Encansci Twyman Aes1 Elsev PDFDocument9 pages2005 Encansci Twyman Aes1 Elsev PDFPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ijrra 07 03 02 PDFDocument5 pagesIjrra 07 03 02 PDFAnonymous kd6WjmxTIFNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy IntroDocument43 pagesSpectroscopy Introshruti shahNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy: Koradiya Ketan N. Inorganic Chemistry, Reg. Roll No-5, Bhavnagar University, Bhavnagar-05Document41 pagesNMR Spectroscopy: Koradiya Ketan N. Inorganic Chemistry, Reg. Roll No-5, Bhavnagar University, Bhavnagar-05Koradiya Ketan NNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 1Document35 pages07 Chapter 1shashi kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is NMRDocument9 pagesWhat Is NMRNishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chm580 NMRDocument8 pagesChm580 NMRNorHidayu Azmi50% (2)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Radiation TechniquesDocument15 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance and Radiation TechniquesMathavaraja JeyaramanNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectroscopy: PrincipDocument38 pagesNMR Spectroscopy: Principandi evi febriantiNo ratings yet
- Infrared SperctrosDocument16 pagesInfrared SperctrosroyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Student CD IBID PRESS CH 12 SummaryDocument5 pagesChemistry Student CD IBID PRESS CH 12 SummaryFranklin garryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectrochemical MethodsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Spectrochemical MethodsSean CollinsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Document24 pagesUnit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Akshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument4 pagesPhysical ChemistryBablu RajputNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: 1.1. BackgroundDocument4 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: 1.1. BackgroundFalak NazNo ratings yet
- Smita S. Mandal (Chemistry)Document19 pagesSmita S. Mandal (Chemistry)cytrfNo ratings yet
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.From EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.No ratings yet