0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views8 pagesGraphing Issues with sin 63x Function
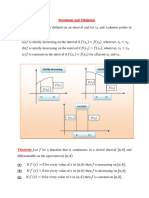
The document provides examples of graphs of functions f(x) and discusses their key properties in intervals based on the values of f'(x) and f''(x). It examines cases where f'(x) is 0, positive, or negative, and where f''(x) is positive, negative, or changes sign, indicating points of inflection. The graphs shown have maxima, minima, points of inflection, and indications of concavity. Misdrawing an inflection point can alter the overall shape of the graph.
Uploaded by
api-3738981Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Graphing Strategies,
- Applications of Derivatives,
- Graphing Quadratic Functions,
- Derivative Analysis,
- Graphing Derivatives,
- Graphing Errors,
- Increasing and Decreasing Func…,
- Graphing Maximums,
- Graphing Functions,
- Critical Points
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views8 pagesGraphing Issues with sin 63x Function
The document provides examples of graphs of functions f(x) and discusses their key properties in intervals based on the values of f'(x) and f''(x). It examines cases where f'(x) is 0, positive, or negative, and where f''(x) is positive, negative, or changes sign, indicating points of inflection. The graphs shown have maxima, minima, points of inflection, and indications of concavity. Misdrawing an inflection point can alter the overall shape of the graph.
Uploaded by
api-3738981Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Graphing Strategies,
- Applications of Derivatives,
- Graphing Quadratic Functions,
- Derivative Analysis,
- Graphing Derivatives,
- Graphing Errors,
- Increasing and Decreasing Func…,
- Graphing Maximums,
- Graphing Functions,
- Critical Points