Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suggested+Solutions+V1+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+Electricity+G Level
Uploaded by
Epic WinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Suggested+Solutions+V1+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+Electricity+G Level
Uploaded by
Epic WinCopyright:
Available Formats
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
Directions Please Write your name on all of the papers on your table, NOW! Test time Resources 14:00-15:20 November 4, 2009 Calculators, and Formulas for the National Test in Mathematics Courses A & B, and the formula sheet for Physics A, FYANV-College. You may also use your personalized blue-booklet. The booklet must have your name and no calculations or solution to any problem are supposed to be on it. The test is a G-level test and consists of a total of 25 questions. Most of problems are multiple-choice. Answer all of questions. Below each problem some space is provided. You are required to show your calculations. The VG-MVG-level test is given on Friday November 9, 2009.
The test:
Score
The maximum score is 53 points.
Mark levels The maximum number of points you can receive for each solution is indicated after each problem. G: 28 points VG: MVG: Have Fun Behzad Only the marked problems in the box below will be graded. Electrostatics:ES DC DC DC DC DC DC ES ES ES Ch 16-19 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Total Minimum G 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 1 2 2 28 14 2 15 2 16 2 17 2 18 2 19 2 20 3 21 1 22 2 23 3 24 2 25 2
53 25 27
ES ES ES ES DC DC DC ES ES ES ES DC ELECTRICITY
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
1/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
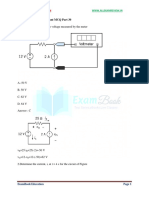
Base your answers to the problems 1-4 on the figure below which illustrates two point charges Q1 = 5.0 C and Q2 = 5.0 C . The charges are pinned to the page of the paper, and therefore are stationary.
D
Q1 = 5.0 C 5.0 cm
Q2 = 5.0 C
5.0 cm
[1]
1. At which point the magnitude of the electric field is zero? a. b. c. d. e.
A B
C
D
None [1] Answer: Alternative b: at the point B
Why? Explain.
The electric field E1 due to the charge Q1 = 5.0 C is to the right, and that of Q2 = 5.0 C is to the right at point B . Due to the symmetry of the problem, the magnitude of them are equal. The resultant electric field is therefore zero. 2. At which point the electric potential is zero? a. b. c. d. e. [1]
A B
C
D
None [1] Answer: Alternative e: None.
Why? Explain.
Due to the fact that both charges are positive, and electric potential is scalar, the electric potential due to them is positive and nonzero at any point in space. 3. If a unit positive charge move from the point A to the point C , the potential energy of the charge [2] a. b. c. d. e. increases decreases first increases, then decreases first decreases, then increases remains constant through out the journey. Answer: Alternative d: first decreases, then increases.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
2/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
4. Moving Q1 = 5.0 C and Q2 = 5.0 C away from each other would cause their electric potential energy to [1] a. b. c. d. e. increase decrease first increase, then decrease first decrease, then increase remain constant through out the journey. [1] Answer: Alternative b: decrease.
Why? Explain.
The potential energy of the system is E PE = k is the distance between them. E PE = k
r : if r increases E PE = k
Q1 Q2 will decrease. r
Q1 Q2 is inversely proportional to r
Q1 Q2 , where r = 0.100 m r
Answer questions 5-8 based on the circuit below where R1 = R2 = R3 = 2.0 , and
R4 = R5 = 4.0 .
A
R1 V = 8.0 V
A1
R2
R3
R4
R5
A5
5. The equivalent resistance of the circuit is a. b. c. d. e.
16.0 0.50 2 .0 0.25 4 .0
[1]
Why? Show your calculations below. [2]
Answer: Alternative c: Req = 0.50
The resistors are in parallel. Therefore the equivalent resistance of the circuit is:
1 1 1 1 1 1 = + + + + Req R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 6 2 6+2 8 1 1 = + + + + = + = + = = =2 = 2 Req = Req 2 2 2 4 4 2 4 4 4 4 4 Req 2
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
3/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
6. The Ammeter A shows: a. b. c. d. e.
2 .0 A 4 .0 A 8 .0 A 16.0 A 1 .0 A
[1]
Why? Show your calculations below. [1]
Ohms law: V = RI I =
Answer: Alternative d: I = 16.0 A
V 8.0 = = 16.0 A R 0.50
[1]
7. The Ammeter A1 shows: a. b. c. d. e.
2 .0 A 4 .0 A 8 .0 A 16.0 A 1 .0 A
Why? Show your calculations below. [2]
First method:
Answer: Alternative b: I1 = 4.0 A
The resistances are in parallel. Therefore, the potential difference between their terminal are :
V1 = V2 = V3 = V4 = V5 = 8.0 V
Ohms law: V1 = R1 I1 I1 = Second method: We may solve the problem logically. 16.0 A is divided to five parts. More current passes through the line with lesser resistance. Therefore 4.0 A passes through R1 = R2 = R3 = 2.0 and 2.0 A passes through
V1 8.0 = = 4 .0 A R1 2.0
R4 = R5 = 4.0 .
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
4/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
8. The Ammeter A5 shows: a. b. c. d. e.
2 .0 A 4 .0 A 8.0 A 16.0 A 1 .0 A
[1]
Why? Show your calculations below.
[2]
Answer: Alternative a: I 5 = 2.0 A
The resistances are in parallel. Therefore, the potential difference between their terminal are :
V1 = V2 = V3 = V4 = V5 = 8.0 V
Ohms law: V5 = R5 I 5 I 5 =
V5 8.0 = = 2 .0 A R5 4.0
9. The power and voltage on the light bulb read 400 W 240V. How many amperes will follow through the light [1] bulb if it is connected to 220 V ? a. b. c. d. e.
88 000 A 1 .8 A 0.55 A 2 .5 A 0.55 mA
Why? Show your calculations below. [1]
Answer: Alternative b: I = 1.8 A
P =V I I =
P 400 = = 1.8 A V 220
[1]
10. At 0.9 kr / kwh , what does it cost to use a 2000 W hair dryer for 30 min ? a. b. c. d. e.
0.9 kr 1.8 kr 5.4 kr 6 kr 2.7 kr
Why? Show your calculations below.[1]
Cost = (2 kw)(0.5 h )(0.9 kr / kwh ) = 0.9 kr
Answer: Alternative a: Cost = 0.9 kr
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
5/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
11. What is the approximate electrostatic force between the electron and proton of a Hydrogen atom? We may assume the average distance of the electron from the nucleus of hydrogen atom is 0.53 10 10 m . [1/0] a. 8.2 10 8 N attractive. b. 8.2 10 8 N repulsive. c. 8.2 108 N attractive. d. 8.2 108 N repulsive. Answer: a: 8.2 10 8 N attractive
QQ 1.6 10 19 F = k 1 2 2 = 9.0 109 r 0.53 10 10
( (
) )
2
= 8.2 10 8 N
12. Two identical metallic sphere carry charges Q1 = 10.0 mC and Q2 = 4.0 mC . The spheres are brought together, and then separated. The final charge on each sphere will be: [1] a. b. c. d. e.
6.0 mC 3.0 mC 14.0 mC 6.0 mC 0 .0
Why? Show your calculations below. [1]
Answer: Alternative b: 3.0 mC
The total charge of the system is Q = Q1 + Q2 = 10.0 4.0 = 6.0 mC . When the two identical metallic spheres are brought together, and then separated, the total charge of 6.0 mC will be divided equally, each Q 6.0 mC = 3.0 mC . = having the electric charge of 2 2
13. Both the Van de Graff generator and the lady in the picture are charged. Why does her hair stands out? Explain. [2/0] Answer: The lady in the picture and therefore her hair are charged. The charges on the each hair are of the same sort, and due to the fact that like charges repel each others, each hair is repelled by the hairs around it. The lighter her hair is the more dramatic is the rising of her hair.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
6/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
14. When you bring a charged insulator rod close to a thin stream of tap water. The stream of water is affected by the charged rod. Why? Explain. [2/0] Answer: Water molecule is polarized, i.e. one side of a water molecule is more positive than the other side of it. When a charged rod gets near the thin water stream, due to the fact that water molecules are all polarized, and due to the fact that opposite charges attract, water stream is attracted to the charged rod.
15. Two charged Ping-Pong balls separated by a distance of 2.00 m exert an electric force of 10.00 mN on each other. What will be the force if the Ping-Pong balls are brought closer, to a separation of 50.0 cm from each other? [1] a. 2.50 mN . b. 40.00 mN . c. 160.00 mN . d. 10.00 mN . Explain your reasoning: [1] Answer: Alternative c, i.e.: 160.00 mN .
The distance between the charges are decreased by a factor of four. The force between them will increase by a factor of 16.
F =k Q1Q2 QQ QQ QQ QQ Fnew = k 12 2 = k 1 2 2 = k 12 2 = 16 k 12 2 = 16 Fold 2 r rnew rold rold rold 16 4
16. How much work is required to move a single electron through a potential difference of 1.0 kV ? [1/0] a. 1.6 10 19 J . b. 1.6 10 22 J . c. 1.6 10 16 J . d. 1.0 103 J . Why? Show your calculations below. [1] Answer: Alternative c, i.e.: 1.6 10 16 J .
W = E PE = QV W = 1.0 103 1.6 10 19 = 1.6 10 16 J
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
7/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
17. Which circuit diagram shows voltmeter V and ammeter A correctly positioned to measure the total potential difference of the circuit and the current through each resistor? [2/0] A:
V
B:
R1 R2
R1
R2
C:
D:
R1
R2
R1
R2
A
V
Answer: Alternative B. Voltmeter must be in parallel, and ammeter must be in series in an electric circuit. 18. The internal resistance of an excellent voltmeter must be: a. Very small. b. Very large. Why? Explain. [1] Answer: Alternative b: Very Large
Voltmeter is always connected in parallel to the terminals of the electric device. By definition, the measuring device should not effect the system. Therefore, if the internal resistance of the voltmeter is very large, quite a small amount of current will pass the voltmeter, and therefore major part of the current will pass the electric device, and therefore voltmeter is going to measure the potential difference without effecting the system.
[1/0]
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
8/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
19. The diagram below represents currents in a segment of an electric circuit. What is the reading of the ammeter A ? [1/0] a. 1 mA . b. 2 mA . c. 3 mA . d. 4 mA e. 5 mA Why? Show your calculations below. Answer: Alternative d, i.e.: I = 4 mA [1]
7 mA 3 mA
A
2 mA
4 mA 5 mA
1 mA
The total amount of currents coming to a network must be equal to the total amount of currents leaving the point, i.e.:
4 + 2 + 3 + I = 5 + 1 + 7 mA 9 + I = 13 mA I = 13 9 mA = 4 mA
20. A positive charge Q1 = 5.0 C and a negative charge Q2 = 5.0 C are placed on a plane surface as illustrated in the figure below. A positive point charge is placed at the point P. The distance between PQ1 is exactly equal to the distance PQ2 . What is the direction of the resultant force on the point charge P? Explain [1] a. Towards a. b. Towards b. c. Towards c.
f g h a P d b c Q1
d. Towards d. e. Towards e. f. Towards f. g. Towards g. h. Towards h. Why? Explain. [2]
Q2
Answer: Towards f.
The force between P and Q1 = 5.0 C is repulsive, i.e.: it is in the direction g in the figure. But the force between P and Q2 = 5.0 C is attractive, i.e.: it is in the direction e in the figure. Due to the fact that both, distances and the magnitude of charges are identical, magnitudes of forces are the same: F1 = F2 Therefore, the resultant vector will be in the direction e.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
9/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
Base your answers to the problems 21-24 on the figure below which illustrates an electron projected into the region between two parallel charged plates which are 2.0 mm apart. The MN electric field between the plates is E = 2.0 C
2.0 mm
21. In which direction will be deflected? a. Toward the bottom of the page. b. Toward the top of the page. c. Into the page d. Out of the page. e. It is not going to be deflected.
[1/0]
Answer: Alternative a: Toward the bottom of the page.
First method: The electron will be attracted to the positive plate. Second method: The electric field in the region between the plates is uniform: It is toward the top of the page. Due to the fact that charge of electron is negative, the electric force on it will be in the opposite direction of the electric field. Therefore the electron will accelerate r r downward: F = e E .
22. The force experienced by the electron during the time it is moving between the plates is: a. 3.2 10 13 N Downward toward the bottom of the page. b. 3.2 10 13 N Toward the top of the page. c. 3.2 10 19 N Toward the top of the page. d. 3.2 10 19 N Downward toward the bottom of the page. e. The electron is not going to be deflected. Therefore, the total force on the electron is zero. Why? Show your calculations below. [2] Answer: Alternative a: 3.2 10 13 N Downward toward the bottom of the page. r r F = e E F = 1.6 10 19 2.0 10 6 = 3.2 10 13 N [1]
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
10/11
Solutions V1 Test Ch6FyANVC08 Test Ch 16-19 Electricity NV-College
23. The electron is replaced by a proton. Compared to the magnitude of the force on the electron, the magnitude of the force on the proton will be a. greater. b. the same. c. less. Why? Explain. [1]
[1]
Answer: Alternative b: The same.
The charge of a proton is + e = 1.6 10 19 C r r F = + e E F = 1.6 10 19 2.0 10 6 = 3.2 10 13 N Upward toward the top of the page.
24. The potential difference across the two plates is: a. V = 4.0 kV . b. V = 1.0 kV . c. V = 4.0 MV d. V = 4.0 V e. V = 4.0 mV Why? Show your calculations below. [1]
[1/0]
Answer: Alternative a: V = 4.0 kV
E=
V V = E d V = 2.0 10 6 2.0 10 3 = 4.0 103 V = 4.0 kV d
25. The power and voltage on the light bulb read 400 W 240V. We take it to the USA where the electricity used in a common house is 110 V . When it is connected to the power source [1] a. the light bulb will burn. b. It will work normally as a 400 W light bulb. c. It will work as a 100 W light bulb. d. It will work as a 800 W light bulb. e. It will not work at all. Why? Show your calculations below. [1]
Answer: Alternative c: It will work as a 100 W light bulb.
PUSA =
2 V 2 110 2 4 110 2 V 2 220 2 (2 110 ) = , PEU = = = = R R R R R R
Therefore: PUSA =
V 2 110 2 1 220 2 1 = = = PEU R R 4 R 4
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes.
11/11
You might also like
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- V1+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+Electricity+G LevelDocument14 pagesV1+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+Electricity+G LevelEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Suggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityDocument9 pagesSuggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Fybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionDocument6 pagesFybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Fybch20-21Nvc07 Vg/Mvg-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionDocument4 pagesFybch20-21Nvc07 Vg/Mvg-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Physics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Document7 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Fybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionDocument6 pagesFybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: Principles and Applications, Fifth EditionDocument45 pagesElectrical Engineering: Principles and Applications, Fifth EditionHammad A. Irshad33% (9)
- Physics B: Fybnvc07 Electricity and Magnetism: Warning! There Are More Than One Version of The TestDocument7 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc07 Electricity and Magnetism: Warning! There Are More Than One Version of The TestEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Physics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Test On Magnetism & Ac-Circuits CH 20-21Document6 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Test On Magnetism & Ac-Circuits CH 20-21Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Trial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)Document11 pagesTrial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)CHRISTOPHER EMMANUEL RAJ A/L VELLAN MoeNo ratings yet
- LawDocument30 pagesLawrogelio1234567100% (1)
- Physics (Theory) : General Instructions: All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument7 pagesPhysics (Theory) : General Instructions: All Questions Are CompulsoryJames RossNo ratings yet
- Exam4 - Solutions - S15 (1) .PdfvvipDocument7 pagesExam4 - Solutions - S15 (1) .PdfvvipSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Physics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Document6 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Problems 3Document11 pagesProblems 3ansat5.ansatNo ratings yet
- WWW Learncbse in Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 ElectricityDocument83 pagesWWW Learncbse in Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 ElectricityakritiNo ratings yet
- Sp2014 Exam1Document4 pagesSp2014 Exam1dreamachiever12No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Lyp 2016 Central Outside Delhi Set1Document25 pages12 Physics Lyp 2016 Central Outside Delhi Set1Subham DasNo ratings yet
- Fybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionDocument6 pagesFybch20-21Nvc07 G-Level Test On Magnetism and Magnetic InductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1Document12 pagesTrial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1annahiaz0% (1)
- CBSE Hots Physics XII 2009Document57 pagesCBSE Hots Physics XII 2009jagannivas100% (1)
- Electric Charges and Fields NCERT SolutionsDocument23 pagesElectric Charges and Fields NCERT SolutionsRaja KarmaNo ratings yet
- The E Field and Voltage-SolutionsDocument6 pagesThe E Field and Voltage-SolutionsRosalinaNo ratings yet
- Exam1 PHYS 193 Spring2014-M2Document12 pagesExam1 PHYS 193 Spring2014-M2alkingkingNo ratings yet
- Exam1 Phys 193 Fall 2014-m2Document12 pagesExam1 Phys 193 Fall 2014-m2alkingkingNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsDocument19 pagesH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Hot PhysicsDocument50 pagesPhysics 12 Hot PhysicsdhirendrasisodiaNo ratings yet
- 9702 w15 QP 12Document20 pages9702 w15 QP 12Hew Li YangNo ratings yet
- UP Physics Exam on Electricity ConceptsDocument13 pagesUP Physics Exam on Electricity ConceptsMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument34 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsRamadhuraiNo ratings yet
- 1.determine The Value of The Voltage Measured by The Meter: SSC JE Electrical Important MCQ Part 30Document10 pages1.determine The Value of The Voltage Measured by The Meter: SSC JE Electrical Important MCQ Part 30Pankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedDocument48 pagesElectrostatics and Current Electricity Concepts ExplainedMin NimNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument51 pagesCircuit Analysishola0987No ratings yet
- 10 ElectricityDocument22 pages10 Electricity이다연No ratings yet
- Doon International School City Campus Dalanwala, DehradunDocument5 pagesDoon International School City Campus Dalanwala, DehradunRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Document12 pagesG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Obj Sub NDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Obj Sub NMisbah sabirNo ratings yet
- Phy 12 (Ncert)Document10 pagesPhy 12 (Ncert)Aravind BhomboreNo ratings yet
- University of the Philippines College of Science Physics 72 Final ExamDocument16 pagesUniversity of the Philippines College of Science Physics 72 Final ExamAthena LealNo ratings yet
- Recit 4 PDFDocument4 pagesRecit 4 PDFEloiNo ratings yet
- 04 Electric Field Part 2Document6 pages04 Electric Field Part 2kayla888No ratings yet
- Electricity GuideDocument62 pagesElectricity GuideJatin PathakNo ratings yet
- 11 12 H2 Prelim P1Document20 pages11 12 H2 Prelim P1Vincent WackyNo ratings yet
- Term Test: PC1432 - Physics IIEDocument9 pagesTerm Test: PC1432 - Physics IIEZhang PinzhengNo ratings yet
- Physics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19 & CH 20Document9 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19 & CH 20Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Physics 72 Final Exam Set A Draft 3 (With Feeling Answer Key)Document12 pagesPhysics 72 Final Exam Set A Draft 3 (With Feeling Answer Key)Ronaldyn DabuNo ratings yet
- Current of Electricity Tutorial 2011 SolutionDocument10 pagesCurrent of Electricity Tutorial 2011 SolutionbandagecookieNo ratings yet
- Exam1 PHYS 193 Summer2015Document8 pagesExam1 PHYS 193 Summer2015alkingkingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NumericalDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Numericalhecef67380No ratings yet
- Thread 3-1 (Electeic Potential+electric Current)Document11 pagesThread 3-1 (Electeic Potential+electric Current)srian551No ratings yet
- Assignment 6 - Electricity-ProblemsDocument4 pagesAssignment 6 - Electricity-ProblemsAlan Chen0% (1)
- Phys102 Final Exam Key ConceptsDocument15 pagesPhys102 Final Exam Key ConceptsammuNo ratings yet
- EV101 Electrical Principles Mesh Analysis & Circuit ProblemsDocument5 pagesEV101 Electrical Principles Mesh Analysis & Circuit ProblemsGy LiawNo ratings yet
- COMPETENCY BASED QUESTIONSDocument17 pagesCOMPETENCY BASED QUESTIONSLochana T SNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 11 Physics - Chapter 10 ElectrostaticsDocument24 pagesMaharashtra Board Solutions Class 11 Physics - Chapter 10 ElectrostaticsManveer SingNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document27 pagesCH 1HariNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument7 pagesOutlineEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Warning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsDocument12 pagesWarning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLDocument6 pagesMathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument192 pagesInequalitiesEpic Win100% (2)
- The Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsDocument18 pagesThe Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- New 18Document5 pagesNew 18Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Ram RecDocument8 pagesRam RecEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Syntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument7 pagesSyntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- RomeDocument7 pagesRomeEpic WinNo ratings yet
- ElemDocument101 pagesElemEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Nelson BibDocument5 pagesNelson BibEpic WinNo ratings yet
- IstDocument34 pagesIstEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinNo ratings yet
- HopeDocument4 pagesHopeEpic WinNo ratings yet
- FogDocument5 pagesFogEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Hilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityDocument27 pagesHilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityEpic WinNo ratings yet
- FaithDocument8 pagesFaithceceph354No ratings yet
- WeinerDocument6 pagesWeinerEpic WinNo ratings yet
- EDocument9 pagesEEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Zhang TDocument4 pagesZhang TEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Internal Set TheoryDocument26 pagesInternal Set TheoryEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Edward NelsonDocument1 pageEdward NelsonEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WoolfDocument9 pagesWoolfEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Zhang QDocument15 pagesZhang QEpic WinNo ratings yet
- J-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationDocument9 pagesJ-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionDocument17 pagesProbability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- J. P. MayDocument17 pagesJ. P. MayEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WalijiDocument6 pagesWalijiEpic WinNo ratings yet
- VParticipantsDocument1 pageVParticipantsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- WaddleDocument10 pagesWaddleEpic WinNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (50)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Waves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastFrom EverandWaves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsFrom EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of Nature: A Little Book on ThermodynamicsFrom EverandThree Laws of Nature: A Little Book on ThermodynamicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Machinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeFrom EverandMachinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Introduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsFrom EverandIntroduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Basic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansFrom EverandBasic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansJohn SangerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)