Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Design of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters
Chapter 8 Design of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters
Uploaded by
Tahmina L. ZebinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 Design of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters
Chapter 8 Design of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital Filters
Uploaded by
Tahmina L. ZebinCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 Design of infinite impulse response (IIR) digital filters. % % Program 8.1, p511.
m-file for the analog filter design % (Example 8.19) % program name: prog81.m % FN=1000/2; fc=300; % cut offf frequency N=5; % filter order [z, p, k]=buttap(N); % create an analog filter w=linspace(0, FN/fc, 1000); % plot the response of filter h=freqs(k*poly(z), poly(p), w); f=fc*w; plot(f, 20*log10(abs(h))), grid ylabel('Magnitude (dB)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ============================================= % % Program 8.2, p511. m-file for the % impulse invariant filter (Example % program name: prog82.m % Fs=1000; fc=300; WC=2*pi*fc; N=5; [b,a]=butter(N,WC,'s'); [z, p, k]=butter(N, WC, 's'); [bz, az]=impinvar(b,a,Fs); [h, f]=freqz(bz, az, 512,Fs); plot(f, 20*log10(abs(h))), grid xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude (dB)') design of the 8.19) % % % % % sampling frequency cutoff frequency cutoff frequency in radian filter order create an analog filter
% determine coeffs of IIR filter
============================================== % % Program 8.3, p512. m-file for the design of the BZT filter % (Example 8.19) % program name: prog83.m % Fs=1000; % sampling frequency FN=Fs/2; fc=300; % cutoff frequency N=5; [z, p, k]=butter(N, fc/FN); [h, f]=freqz(k*poly(z), poly(p), 512, Fs); plot(f, 20*log10(abs(h))), grid ylabel('Magnitude (dB)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)')
===================================================== % % m-file for Example 8B.1 (Program 8B.1, p564). % Program name: prog8b1.m % N=2; % Filter order Fs=1280; % Sampling frequency fc=150; % Cutoff frequency WC=2*pi*fc; % Cutoff frequency in radian % % Create an analogue filter % [b,a]=butter(N,WC,'s'); [z,p,k]=butter(N, WC, 's'); % % Convert analogue filter into Discrete IIR filter % [bz, az]=impinvar(b, a, Fs); %Determine coeffs of IIR filter subplot(2,1,1) % Plot magnitude freq. response [H, f]=freqz(bz, az, 512, Fs); plot(f, 20*log10(abs(H))) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response (dB)') subplot(2,1,2) % Plot pole-zero diagram zplane(bz, az) zz=roots(bz); % Determine poles and zeros pz=roots(az); ============================================================ % % m-file for Example 8B.2 (Program % Program name: prog8b2.m % N=2; Fs=1280; FN=Fs/2; fc=150; Fc=fc/FN; [b,a]=butter(N,Fc); filter. [z,p,k]=butter(N, Fc); subplot(2,1,1) [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) zplane(b, a) b a
8B.2, p566). % Filter order % Sampling frequency % Cutoff frequency % Normalized Cutoff frequency % Create and digitize analogue % Plot magnitude freq. response
% Plot pole-zero diagram
==========================================================
% m-file for Example 8B.3 (Program % Program name: prog8b3.m % Fs=2000; FN=Fs/2; fc1=200/FN; fc2=300/FN; [b,a]=butter(4,[fc1, fc2]); filter. [z,p,k]=butter(4, [fc1, fc2]); subplot(2,1,1) [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) zplane(b, a)
8B.3, p567) % Sampling frequency
% Create and digitize analogue % Plot magnitude freq. response
% Plot pole-zero diagram
========================================================= % % m-file for Example 8B.4 (Program 8B.4, p569) % Program name: prog8b4.m % Fs=8000; % Sampling frequency Ap=3; As=20; wp=500/4000; ws=2000/4000; [N, wc]=buttord(wp, ws, Ap, As); % Determine filter order [zz, pz, kz]=butter(N,500/4000); % Digitise filter [b, a]=butter(N, 500/4000); subplot(2,1,1) % Plot magnitude freq. response [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) % Plot pole-zero diagram zplane(b, a) ======================================================= % % m-file for Example 8B.5 (Program 8B.5, % Program name: prog8b5.m % Fs=8000; Ap=3; As=20; wp=2000/4000; ws=500/4000; [N, wc]=buttord(wp, ws, Ap, As); [zz, pz, kz]=butter(N,2000/4000, 'high'); [b, a]=butter(N, 2000/4000, 'high'); subplot(2,1,1) response [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') p571) % Sampling frequency
% Determine filter order % Digitise filter % Plot magnitude freq.
ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) zplane(b, a)
% Plot pole-zero diagram
==================================================== % % m-file for Example 8B.6 (Program 8B.6, p572) % Program name: prog8b6.m % Band pass filter % Fs=1000; % Sampling frequency Ap=3; As=20; Wp=[200/500, 300/500]; % Band edge frequencies Ws=[50/500, 450/500]; [N, Wc]=buttord(Wp, Ws, Ap, As); % Determine filter order [zz, pz, kz]=butter(N,Wp); % Digitise filter [b, a]=butter(N, Wp); subplot(2,1,1) % Plot magnitude freq. response [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) % Plot pole-zero diagram zplane(b, a) ======================================================= % % % %
m-file for Example 8B.7 (Program 8B.7, p574) Program name: prog8b7.m Band stop filter % Sampling frequency
% Fs=1000; Ap=3; As=20; Wp=[50/500, 450/500]; Ws=[200/500, 300/500]; [N, Wc]=buttord(Wp, Ws, Ap, As); [zz, pz, kz]=butter(N,Ws, 'stop'); [b, a]=butter(N, Ws, 'stop'); subplot(2,1,1) [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, abs(H)) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response ') subplot(2,1,2) zplane(b, a)
% Band edge frequencies % Determine filter order % Digitise filter % Plot magnitude freq. response
% Plot pole-zero diagram
============================================================
% % m-file for the design Example 8B.8 (Program 8B.8, p576) % Program Name: prog8b8.m % Ap=0.25; As=45; Fs=100000; Wp=[20500/50000, 23500/50000]; % Band edge frequencies Ws=[19000/50000, 25000/50000]; [N,Wc]=ellipord(Wp, Ws, Ap, As); order [b, a]=ellip(N, Ap, As, Wc); coeffs [z, p, k]=ellip(N, Ap, As,Wc); zeros sos=zp2sos(z, p,k); order sections subplot(2,1,1) response [H, f]=freqz(b, a, 512, Fs); plot(f, 20*log10(abs(H))) xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ylabel('Magnitude Response (dB)') subplot(2,1,2) diagram zplane(b, a) % % % % % Determine filter Determine filter Determine poles and Convert to second Plot magnitude freq.
Plot pole-zero
============================================================ function IIRBZT %Design program for IIR filters with Butterworth, Chebyshev, Inverse %Chebyshev or Elliptic Characteristic using bilinear transformation %output arguments: %n - estimated minimun filter order. %Wn - cutoff frequencies. %b,a - coefficients of digital filter %ftype - 'low' for lowpass filter % 'high' for highpass filter % 'bandpass' for bandpass filter % 'stop' for bandstop filter %ctype - 1 for Butterworth filter % 2 for Chebyshev filter % 3 for Inverse Chebyshev filter % 4 for Elliptic filter %steps of designing a digital filter implied in the called functions: % step 1: estimate the minimum order of the filter from specifications % step 2: get analog, pre-warped frequencies % step 3: convert to low-pass prototype estimate % step 4: Get n-th order analog lowpass prototype with desired filter characters % step 5: Transform to lowpass, bandpass, highpass, or bandstop of desired Wn % step 6: Use Bilinear transformation to find discrete equivalent:
clear all; format; Fs = 100000; %sampling frequency(Hz). Wp = [20500 23500]/(Fs/2); %passband edge frequency normalised by Fs/2. Ws = [19000 25000]/(Fs/2); %stopband edge frewquency normalised by Fs/2. Rp = 0.25; %passband attenuation in dB. Rs = 45; %stopband attenuation in dB ctype = 4; %character of filter ftype = 'bandpass'; %type of filter if ctype==1 [n,Wn]=buttord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs); [b,a]=butter(n,Wn,ftype); elseif ctype==2 [n,Wn]=cheb1ord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs); [b,a]=cheby1(n,Rp,Wn,ftype); elseif ctype==3 [n,Wn]=cheb2ord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs); [b,a]=cheby2(n,Rs,Wn,ftype); elseif ctype==4 [n,Wn]=ellipord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs); [b,a]=ellip(n,Rp,Rs,Wn,ftype); end %Output the result disp('Numerator coefficients (in descending powers of z):'); disp(b); disp('Denominator coefficients (in descending powers of z):'); disp(a); freqz(b,a,1024,Fs); ======================================================= function Impinv %Impulse invariance method of anolog-to-digital filter conversion %a,b -- s-plane coefficients %az,bz -- digital filter coefficients clear all; b = 1; a = [1.84496 1.920675 1]; [bz,az]=impinvar(b,a) Inv. freqz(bz,az,1024);
%get z-plane coefficients using impulse
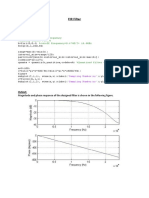
======================================================= % % Program name - prob825.m (problem 8.25(1), p553) % Comparison of magnitude and phase responses of an analogue % and equivalent BZT and impulse invariant discrete-time filters % and pole-zero diagrams (elliptic low pass filter) % Fs=10000; FN=Fs/2; fp=1000; fs=3000; wp=fp*2*pi; ws=fs*2*pi; Ap=1; As=60; %
% Calculate filter coefficients and frequency responses [N, wc]=ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As,'s'); % analog filter [B, A]=ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 's'); [bBZT, aBZT]=bilinear(B,A,Fs); % BZT filter [bIIT,aIIT]=impinvar(B,A,Fs); % Impulse invariance filter % % Compute frequency response [Ha, wa]=freqs(B,A); [HBZT, fBZT]=freqz(bBZT, aBZT, 512, Fs); [HIIT, fIIT]=freqz(bIIT, aIIT, 512, Fs); % % Plot magnitude frequency responses % figure(1); % Plot analogue magnitude response plot(wa/(2*pi), 20*log10(abs(Ha))) hold on figure (1); plot(fBZT, 20*log10(abs(HBZT)), 'r:') % Plot BZT magnitude response hold on figure (1); plot(fIIT, 20*log10(abs(HIIT)), 'g:') % Plot Impinv magnitude response legend('Analog', 'BZT', 'Imp Invar'); axis([0 10000 -120 0]) ylabel('Magnitude (dB)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') title('Filter magnitude responses') hold off; % % Plot phase responses % figure(2); plot(wa/(2*pi), angle(Ha)*180/pi) % Plot analogue phase response hold on figure (2); plot(fBZT, angle(HBZT)*180/pi, 'r:') % Plot BZT phase response hold on figure(2); plot(fIIT, angle(HIIT)*180/pi, 'g.') %ImpInvar phase response legend('Analog', 'BZT','Imp Invar'); axis([0 10000 -360 360]) ylabel('Phase (Degrees)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') title('Filter Phase Responses') hold off % % Plot pole-zero diagrams % figure (3); zplane(bBZT, aBZT) title('Pole-zero diagram - BZT filter') figure (4); zplane(bIIT, aIIT) xmin=-1; xmax=1; ymin=-1; ymax=1; % Scale the z-plane for the Impulse Inva. axis([xmin xmax ymin ymax]) title('Pole-zero diagram - impulse invariance filter')
===================================================== % % Program name - prob8261a.m (modified problem 8.26(1), p553) % Comparison of characteristic features of discrete-time Butterworth, % Chebyshev 1,Chebyshev 2 and elliptic lowpass filters. % Fs=8000; fp=500/4000; fs=2000/5000; Ap=0.1; As=60; % % Calculate filter coefficients [N1, wc1]=buttord(fp, fs, Ap, As); % filter order [N2, wc2]=cheb1ord(fp, fs, Ap, As); [N3, wc3]=cheb2ord(fp, fs, Ap, As); [N4, wc4]=ellipord(fp, fs, Ap, As); [b1, a1]=butter(4, fp); % Butterworth filter [b2, a2]=cheby1(4, Ap, fp); [b3, a3]=cheby2(4, As, fs); [b4, a4]=ellip(4, Ap, As, fp); % % Calculate frequency responses % [H1, f1]=freqz(b1, a1, 512, Fs); [H2, f2]=freqz(b2, a2, 512, Fs); [H3, f3]=freqz(b3, a3, 512, Fs); [H4, f4]=freqz(b4, a4, 512, Fs); % % Plot magnitude frequency responses % figure (1); plot(f1, 20*log10(abs(H1)), 'r:') % Plot Butterworth magnitude response hold on figure (1); plot(f2, 20*log10(abs(H2)), 'b--') % Plot Cheby1 magnitude response hold on figure (1); plot(f3, 20*log10(abs(H3)), 'g-.') % Plot Cheby2 magnitude response hold on figure (1); plot(f4, 20*log10(abs(H4)), 'k-') % Plot elliptic magnitude response hold on legend('Butworth', 'Cheby1', 'Cheby2', 'Ellip'); axis([0 4000 -100 10]) ylabel('Magnitude (dB)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') title('Filter magnitude responses') hold off; % % Plot phase responses % figure (2); plot(f1, angle(H1)*180/pi, 'r:') % Plot BZT phase response hold on figure (2); plot(f2, angle(H2)*180/pi, 'b--') % Plot Cheby 1 phase response hold on figure (2); plot(f3, angle(H3)*180/pi, 'g-.') % Plot Cheby 2 phase response
hold on figure (2); plot(f4, angle(H4)*180/pi, 'k-') % Plot elliptic phase response hold on figure(2); legend('Butter', 'Cheby1','Cheby2', 'Ellip'); axis([0 4000 -360 360]) ylabel('Phase (Degrees)') xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') title('Filter Phase Responses') hold off % % Plot pole-zero diagrams % figure (3); zplane(b1, a1) title('Pole-zero diagram - Butterworth filter') figure (4); zplane(b2, a2) title('Pole-zero diagram - Chebyshev 1 filter') figure (5); zplane(b3, a3) title('Pole-zero diagram - Chebyshev 2 filter') figure (6); zplane(b4, a4) title('Pole-zero diagram - Elliptic filter') N1 N2 N3 N4 ==========================================================
You might also like
- Filter Design Using MatlabDocument4 pagesFilter Design Using MatlabHafid ScooteristNo ratings yet
- Sigs 3Document2 pagesSigs 3api-26142417No ratings yet
- CQ 09 September 1946Document68 pagesCQ 09 September 1946Сергей БезразличныйNo ratings yet
- FS-T6 With R6B Manual 20130520 (Update)Document24 pagesFS-T6 With R6B Manual 20130520 (Update)NeilNo ratings yet
- RC602-GEF Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageRC602-GEF Datasheet PDFmauroelectroNo ratings yet
- Matlab Practice DSP LabDocument10 pagesMatlab Practice DSP LabPrudhvi MunagalaNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology Lahore: TheoryDocument11 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology Lahore: TheoryEngr Umer CheemaNo ratings yet
- To Design and Implement An IIR Filter For Given SpecificationsDocument9 pagesTo Design and Implement An IIR Filter For Given Specifications4NM19EC157 SHARANYA R SHETTYNo ratings yet
- WindowsDocument39 pagesWindowsSaurabhMoharirNo ratings yet
- Appropriate Parameters and Use Mat Lab Programming Hamming Window Hanning Window Rectangular Window Triangular WindowDocument9 pagesAppropriate Parameters and Use Mat Lab Programming Hamming Window Hanning Window Rectangular Window Triangular WindowGeremu TilahunNo ratings yet
- WC Lab ProgramDocument9 pagesWC Lab ProgramManojLaraNo ratings yet
- FIR Filter Design MatlabDocument9 pagesFIR Filter Design Matlabrajendra4343No ratings yet
- Linear ConvolutionDocument17 pagesLinear ConvolutionRahul DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- MATLABDocument6 pagesMATLABAmar DizdarNo ratings yet
- 'Var' 'S' 'Analogbutterworthlpf ': X TF (B, A, ,) Disp X (n1, d1) Bilinear (B, A,10) y TF (n1, d1, T) Disp yDocument2 pages'Var' 'S' 'Analogbutterworthlpf ': X TF (B, A, ,) Disp X (n1, d1) Bilinear (B, A,10) y TF (n1, d1, T) Disp yudaya57No ratings yet
- Function: 'Datain - Dat' 'R' '%G %G'Document35 pagesFunction: 'Datain - Dat' 'R' '%G %G'Haroon HussainNo ratings yet
- Designing FilterDocument16 pagesDesigning FiltercameenNo ratings yet
- FIR IIR Filter0413062226Document8 pagesFIR IIR Filter0413062226Abu RaihanNo ratings yet
- 22bec0389 VL2023240505431 Ast04Document7 pages22bec0389 VL2023240505431 Ast04mpkvarun69No ratings yet
- nu3MATLAB CodesDocument73 pagesnu3MATLAB CodesbotametunosegaNo ratings yet
- DSP ManualDocument84 pagesDSP ManualBala913100% (1)
- (EE3101) Laboratory 2 ReportDocument14 pages(EE3101) Laboratory 2 Report94747No ratings yet
- To Design and Implement An FIR Filter For Given SpecificationsDocument8 pagesTo Design and Implement An FIR Filter For Given Specifications4NM19EC157 SHARANYA R SHETTYNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5: Analog Filter DesignDocument7 pagesChapter-5: Analog Filter DesignAlexis RolandoNo ratings yet
- DSE 03 - Digital Signal Processing - Practical 08 (Sudipta Majumder) - MergedDocument6 pagesDSE 03 - Digital Signal Processing - Practical 08 (Sudipta Majumder) - MergedBoot BoxNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing in Matlab (Present)Document39 pagesSignal Processing in Matlab (Present)epc_kiranNo ratings yet
- IIR Filter Design: %LPF Analog Design To Dgital Design (Butter) %initiaizing The InputsDocument21 pagesIIR Filter Design: %LPF Analog Design To Dgital Design (Butter) %initiaizing The InputsGanesha KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Lab: Discrete Time Systems: DownsamplingDocument9 pagesDigital Signal Processing Lab: Discrete Time Systems: DownsamplingMian Safyan KhanNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX F - Matlab Code Used To Determine Extrapolation FactorDocument12 pagesAPPENDIX F - Matlab Code Used To Determine Extrapolation FactorMartina Marinković PlehatiNo ratings yet
- IIR Filter DesignDocument7 pagesIIR Filter DesignjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Filtros Analogicos Con MatlabDocument10 pagesFiltros Analogicos Con MatlabacajahuaringaNo ratings yet
- Solutions of MatlabDocument14 pagesSolutions of MatlabRaviKiranNo ratings yet
- DSP8 (1) WatermarkDocument16 pagesDSP8 (1) Watermarkraneraji123No ratings yet
- Lab 10 ENTC 4347 Iir Filters: K N y A K N X B N yDocument6 pagesLab 10 ENTC 4347 Iir Filters: K N y A K N X B N ysageson_m-1No ratings yet
- MATLAB Lab Project - Mtech IIsemDocument61 pagesMATLAB Lab Project - Mtech IIsemSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 12: Butterworth Digital LPF: If ElseDocument4 pagesEXPERIMENT 12: Butterworth Digital LPF: If ElseappuamreddyNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Program Using MatlabDocument11 pagesPower Flow Program Using MatlabSafnas KariapperNo ratings yet
- Muncion Matlab 2015 FreqzDocument9 pagesMuncion Matlab 2015 FreqzlitronixNo ratings yet
- Write A Mat Lab Program To Perform Linear and Circular Convolution of The Discrete Time Sequences XDocument26 pagesWrite A Mat Lab Program To Perform Linear and Circular Convolution of The Discrete Time Sequences XD Geetha Durai50% (2)
- Numerical Mathematics With MATLABDocument66 pagesNumerical Mathematics With MATLABReza Abazari87% (15)
- Program To Design Butterworth Low Pass Filter For Given SpecificationDocument4 pagesProgram To Design Butterworth Low Pass Filter For Given SpecificationVishnu RaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document16 pagesExperiment 8raneraji123No ratings yet
- CchelpDocument119 pagesCchelpLaco tangara JhuniorNo ratings yet
- ECE 351 Filtering Example - v3Document3 pagesECE 351 Filtering Example - v3Mj EchaviaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Iterasi MATLABDocument10 pagesKumpulan Iterasi MATLABZia SilverNo ratings yet
- FspecialDocument7 pagesFspecialAhmad BasNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document7 pagesExp 1abdo abdokNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument30 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingSundram InvinsibleNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab 9-10 Filters NewDocument4 pagesDSP Lab 9-10 Filters NewM AneesNo ratings yet
- (Ice)Document4 pages(Ice)rockerautheyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ProblemsDocument21 pagesChapter 8 Problemskhrid3100% (2)
- Simulated Analysis In: Sine-Wave MatlabDocument9 pagesSimulated Analysis In: Sine-Wave MatlabAshwin DuttNo ratings yet
- % 100 Samples / SignalDocument14 pages% 100 Samples / Signalmujeeb__gsmNo ratings yet
- Matlab Script FileDocument8 pagesMatlab Script Filetvr123No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Z-Transform and Its Applications in Signal ProcessingDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Z-Transform and Its Applications in Signal ProcessingTommy ManNo ratings yet
- DSP ProgramDocument118 pagesDSP ProgramSandeep Banerjee100% (1)
- 121ec0896 IshanBal DSPDocument24 pages121ec0896 IshanBal DSPHilbertNo ratings yet
- Compte Rendu: Electronique Numerique: Réalise ParDocument4 pagesCompte Rendu: Electronique Numerique: Réalise ParChrif ÀyOùbNo ratings yet
- All Matlab Code For Problem 4Document14 pagesAll Matlab Code For Problem 4habteNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Group 38Document23 pagesMini Project Group 38VijayNo ratings yet
- Discrete Wavelet Transform: A Signal Processing ApproachFrom EverandDiscrete Wavelet Transform: A Signal Processing ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Per Unit System 2016Document18 pagesPer Unit System 2016Jalu PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Delay 1.0K Millis 2.3K Micros 1.0K Delaymicroseconds 359 Analogwrite 274 Tone 1.4K Notone 76 Servo Library 1.6KDocument11 pagesDelay 1.0K Millis 2.3K Micros 1.0K Delaymicroseconds 359 Analogwrite 274 Tone 1.4K Notone 76 Servo Library 1.6KOthmane Bouzarzar100% (1)
- Test and Measurement Cat2019 Cat en 5213-7590-42 v0800 120dpiDocument286 pagesTest and Measurement Cat2019 Cat en 5213-7590-42 v0800 120dpicarlosmandopinto100% (1)
- Intelligent Interface: (IIM-2000 FN-2000 PANEL MOUNT)Document2 pagesIntelligent Interface: (IIM-2000 FN-2000 PANEL MOUNT)ejhagunNo ratings yet
- Electrolux Induction - Single Zone - 603522 - English UKDocument2 pagesElectrolux Induction - Single Zone - 603522 - English UKChee Wen ZhiNo ratings yet
- AVC Fan AVC. Asia Vital Components Co.,Ltd.Document138 pagesAVC Fan AVC. Asia Vital Components Co.,Ltd.Steven ChowNo ratings yet
- DSP Processor & Architecture-2Document2 pagesDSP Processor & Architecture-2junaid Sheikh0% (1)
- Commscope UTP Cat6Document3 pagesCommscope UTP Cat6SJCR MISNo ratings yet
- Ref 1 AR-1209Document60 pagesRef 1 AR-1209Bruno Hercílio de Andrade CatãoNo ratings yet
- Clocked Synchronous State MachinesDocument2 pagesClocked Synchronous State MachinesMahesh AbnaveNo ratings yet
- DFC and CFCDocument2 pagesDFC and CFCSaumyadip GhoshNo ratings yet
- GearmotorsDocument11 pagesGearmotorsEkhlas MamdouhNo ratings yet
- (SJ341DCA01-00E) 1.0 X3-Booster MailDocument32 pages(SJ341DCA01-00E) 1.0 X3-Booster MailÁlvarez LuisNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFDocument8 pagesMultiplexing FDM TDM and TCM PDFQuang Nghĩa VõNo ratings yet
- SF-C21 Safety Control UnitDocument4 pagesSF-C21 Safety Control UnitSancudo SancudonNo ratings yet
- EM InductionDocument20 pagesEM InductionSakib Ex-rccNo ratings yet
- Internship 1Document19 pagesInternship 1UnknownNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Manufracture of TurbogeneratorDocument25 pagesPresentation On Manufracture of TurbogeneratorXvasdfr DfgNo ratings yet
- MINI PROJECT 2.arduino PDFDocument21 pagesMINI PROJECT 2.arduino PDFSonam NetalkarNo ratings yet
- NTB02 057Document3 pagesNTB02 057PMNo ratings yet
- E-OLSS: Electronic ControlDocument12 pagesE-OLSS: Electronic ControlSamidiNo ratings yet
- SR So 8500199288 De110 SN Ecl03434 Ri Avr Regulator PT Perdana Abadi Perkasa - Bintang Anugrah SejahteraDocument11 pagesSR So 8500199288 De110 SN Ecl03434 Ri Avr Regulator PT Perdana Abadi Perkasa - Bintang Anugrah SejahteraTeguh Prabowo CenaNo ratings yet
- EMFT, TL & Waveguides and AWPDocument4 pagesEMFT, TL & Waveguides and AWPpawansvsuNo ratings yet
- CW3Document5 pagesCW3phutd09No ratings yet
- AT2003Document7 pagesAT2003williamsarenas75No ratings yet
- Hobart 90CU420 ManualDocument49 pagesHobart 90CU420 Manualhb Corp100% (1)
- Radiation Effects On Space Electronics and Mitigation TechniquesDocument20 pagesRadiation Effects On Space Electronics and Mitigation TechniquessujithgcolabNo ratings yet