Professional Documents
Culture Documents
This Is Image of Novel Prize 2011
This Is Image of Novel Prize 2011
Uploaded by
jeorajaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
This Is Image of Novel Prize 2011
This Is Image of Novel Prize 2011
Uploaded by
jeorajaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2011
1
Innate immunity rapid halts infection no memory
2
Adaptive immunity slower clears infection memory
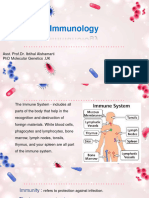
The immune system
Infection of the human body by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi triggers the immune response. It occurs in a two-step process: innate immunity halts the infection, and adaptive immunity subsequently clears it.
T lymphocytes Microorganism
TLR
Dendritic cell
Components of microorganisms bind to Toll-like receptors located on many cells in the body. This activates innate immunity, which leads to inflammation and to the destruction of invading microorganisms.
Innate immunity
2 Adaptive immunity
Dendritic cells activate T lymphocytes, which initiates adaptive immunity. A cascade of immune reactions follows, with formation of antibodies and killer cells.
2011 The Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine The Nobel Prize and the Nobel Prize medal design mark are registered trademarks of the Nobel Foundation
Illustration: Mattias Karln
You might also like
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 pagesZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument15 pagesImmunologyAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- W8 Immunology and ImmunizationDocument9 pagesW8 Immunology and ImmunizationJamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708 21406740150 - 885398426264138 - 2308855381410239775 - n.pdf4. Infectious Inflammatory and ImmuDocument180 pagesvt59.2708 21406740150 - 885398426264138 - 2308855381410239775 - n.pdf4. Infectious Inflammatory and ImmuswsnkkcgbhNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument24 pagesInfectionGarzota PrincessjhoannaNo ratings yet
- ImunologiDocument4 pagesImunologiDhiya NabilaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Immunology Have Led To A Better Understanding of The Human Immune System and The MechaDocument2 pagesRecent Advances in Immunology Have Led To A Better Understanding of The Human Immune System and The MechaAzhara Rizki GitaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- L 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDDocument15 pagesL 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Mportant Functions of Innate ImmunityDocument1 pageMportant Functions of Innate ImmunitygyanNo ratings yet
- 47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense SystemsDocument20 pages47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemArun Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- LE3219 - Leather Microbiology Infection and ImmunityDocument21 pagesLE3219 - Leather Microbiology Infection and ImmunityAnik AlamNo ratings yet
- Microbial Fungal and Parasitic ImmunityDocument31 pagesMicrobial Fungal and Parasitic ImmunityM Saeed MohmandNo ratings yet
- Pdfimmunesystem JannatiAulahDocument30 pagesPdfimmunesystem JannatiAulahnanaNo ratings yet
- Overview of InflammationDocument6 pagesOverview of InflammationNauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- 4 Immune DisordersDocument11 pages4 Immune DisorderscedonuliNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology 2017 - AmaDocument122 pagesBasic Immunology 2017 - AmaEka RizkyanaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Defenses Against Disease - Week8 - DrNyembe - 2022Document26 pages10 - Defenses Against Disease - Week8 - DrNyembe - 2022Muke MpilwenhleNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Inflammatory MediatorsDocument28 pagesInflammation and Inflammatory Mediatorsla.instagramawaNo ratings yet
- 13i Immunologic DisordersDocument73 pages13i Immunologic DisordersDjayNo ratings yet
- Chap 16 Part 3 Antigen-Antibody ComplexesDocument6 pagesChap 16 Part 3 Antigen-Antibody ComplexesclrssNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument65 pagesDiseases of The Immune Systemanon_62816775No ratings yet
- HDP 301: Lecture #2: Immune Pathology PainDocument51 pagesHDP 301: Lecture #2: Immune Pathology PainLinda NguyenNo ratings yet
- Immunology (Final) Laden SalehDocument193 pagesImmunology (Final) Laden SalehLaden SalehNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologyChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Innate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inDocument2 pagesInnate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inSTEFFY MARY JOHNSON 2031844No ratings yet
- Pathology (Inflammation and Wound Healing)Document14 pagesPathology (Inflammation and Wound Healing)andrew100% (1)
- Immunity 3Document10 pagesImmunity 3Parth KulkarniNo ratings yet
- General Features of Immune System Immune System: DefinitionDocument17 pagesGeneral Features of Immune System Immune System: Definitionمحمد نعیم اقبالNo ratings yet
- 4'th Crew 1. Evya A (130210103043) 2. Ridlo Firmansyah (130210103078) 3. Zainatuh Arifa (130210103066) 4. Heni Lusiana (130210103044)Document47 pages4'th Crew 1. Evya A (130210103043) 2. Ridlo Firmansyah (130210103078) 3. Zainatuh Arifa (130210103066) 4. Heni Lusiana (130210103044)Heni LusianaNo ratings yet
- Immune System To Agent InfectionDocument70 pagesImmune System To Agent Infectionliza yunitaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Asst. Prof - Dr. Ibtihal Alshamarti PHD Molecular Genetics .UkDocument15 pagesImmunology: Asst. Prof - Dr. Ibtihal Alshamarti PHD Molecular Genetics .Uklmar696210No ratings yet
- Slide On Marine Fish DiseaseDocument47 pagesSlide On Marine Fish DiseaseNayan MallickNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Immune SystemDocument5 pagesTopic 4 - Immune SystemYara Jeah Ingay BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated & Humoral Immunity PathologyDocument65 pagesCell-Mediated & Humoral Immunity PathologyCrystal GamingNo ratings yet
- Prologue Syllabus 2008Document14 pagesPrologue Syllabus 2008Francisco Eriberto de LimaNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoNo ratings yet
- Kolawole Taiye Sodeeq PresentDocument13 pagesKolawole Taiye Sodeeq PresentAbubakarNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Overview (Moses Franklyn Dumbuya)Document69 pagesImmunology: Overview (Moses Franklyn Dumbuya)Moses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- L07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument10 pagesL07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune Systemhstest842No ratings yet
- 5 Immunological DisordersDocument22 pages5 Immunological DisordersPaula CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Sysmex SEED Haematology InflammatoryDocument7 pagesSysmex SEED Haematology InflammatoryTzeto Han CongNo ratings yet
- Immune System GlossaryDocument4 pagesImmune System GlossaryLorena Lévano BastoNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- 8 Immunity PDFDocument47 pages8 Immunity PDFSPARTANS ARENANo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Inflammatory and Immunologic FunctionDocument114 pagesDisturbances in Inflammatory and Immunologic Functionshenric16No ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument3 pagesMICROBIOLOGYbritishsam57No ratings yet
- Immunology Final PruductDocument22 pagesImmunology Final Pruductnikki_swift_1No ratings yet
- Immune ResponsesintissueDocument22 pagesImmune ResponsesintissueFahim AhmadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology: DR - Elamin Abu AlasDocument19 pagesClinical Immunology: DR - Elamin Abu AlasR Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Immunology Teaching Objectives:: I. Overview of The Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmunology Teaching Objectives:: I. Overview of The Immune SystemOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1Document8 pagesUnit 4.1Bloody MarieNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument12 pagesImmunityCATBILAR VlogNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural ImmunityDocument20 pagesDiseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural Immunitymano343No ratings yet
- Disease of Immune System - Siti Mirhalina 2Document25 pagesDisease of Immune System - Siti Mirhalina 2M.Satria PerdanapNo ratings yet
- Essentials IntroductionDocument4 pagesEssentials IntroductionAna CaterevNo ratings yet
- First Announcement WebDocument4 pagesFirst Announcement WebAna CaterevNo ratings yet
- Burn Care FacilitiesDocument25 pagesBurn Care FacilitiesAna CaterevNo ratings yet
- Burn TreatmentDocument2 pagesBurn TreatmentAna CaterevNo ratings yet