Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blunt End: Molecular Biology DNA Fragment DNA Molecule
Uploaded by
Careless WhisperrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blunt End: Molecular Biology DNA Fragment DNA Molecule
Uploaded by
Careless WhisperrCopyright:
Available Formats
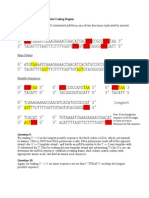
Blunt end
(molecular biology) The end of a DNA fragment resulting from the breaking of DNA molecule in which there are no unpaired bases, hence, both strands are of the same length. In molecular biology, a blunt end may result from the breaking of double-stranded DNA; however, there are no overhangs or unpaired bases. An example of a blunt end: 5'-CTGATCTGACTGATGCGTATGCTAGT-3' 3'-GACTAGACTGACTACGCATACGATCA-5'
Sticky end
(molecular biology) A fragment of DNA (often produced by a staggered cut on the DNA using restriction enzymes) in which the terminal portion has a stretch of unpaired nucleotides, and the strands are not of the same length. The ends of the DNA are sticky because it can easily match up with a complementary overhang. For example, these two sticky ends can be joined together since they can form complementary base pairs in the overhang region: 5'-ATCTGACT ______+ GATGCGTATGCT-3' 3'-TAGACTGACTACG________CATACGA-5'
You might also like
- DNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookDocument81 pagesDNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookithilaminNo ratings yet
- Restriction EndonucleasesDocument12 pagesRestriction EndonucleasesShiv Kumar100% (1)
- Restriction Enzymes ActivityDocument7 pagesRestriction Enzymes ActivityDoree GlantzNo ratings yet
- Restriction Enzymes: Restriction Enzymes Is An Enzyme That Cuts Double Stranded or SingleDocument3 pagesRestriction Enzymes: Restriction Enzymes Is An Enzyme That Cuts Double Stranded or SingleArafat MiahNo ratings yet
- Restriction EnzymeDocument6 pagesRestriction EnzymeFelix SimsungNo ratings yet
- Hareem T. Maune Et Al - Self-Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes Into Two-Dimensional Geometries Using DNA Origami TemplatesDocument6 pagesHareem T. Maune Et Al - Self-Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes Into Two-Dimensional Geometries Using DNA Origami TemplatesCogsmsNo ratings yet
- CYTOGENETICS Worksheet 2 Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCYTOGENETICS Worksheet 2 Central DogmaMalaika Villanueva TingsonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document8 pagesAssignment 3Samson FungNo ratings yet
- Restriction EnzymeDocument4 pagesRestriction Enzymesingh16No ratings yet
- SAGE Is Sequence Sampling Technique in Which Very Short Sequence Tags Are Joined Into Long ConcatamersDocument1 pageSAGE Is Sequence Sampling Technique in Which Very Short Sequence Tags Are Joined Into Long ConcatamersSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology - Molecular Cloning: 08. - 12. November 2021Document21 pagesMolecular Biology - Molecular Cloning: 08. - 12. November 2021SafooraShirvaniNo ratings yet
- Intro REDocument5 pagesIntro REespada_fourNo ratings yet
- Chapter CD: Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesChapter CD: Molecular BiologyZoher PainterNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma ArtifactDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma Artifactapi-654411219No ratings yet
- Restriction EnzymesDocument9 pagesRestriction EnzymesskmfscNo ratings yet
- Multidimensional Function Optimization Based On Dna ComputingDocument8 pagesMultidimensional Function Optimization Based On Dna ComputingnalytoolsNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyDocument61 pagesGlossary of Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyTitaree SuksawadNo ratings yet
- Csir Net NotesDocument63 pagesCsir Net Notesssjusvinder75% (4)
- Basic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureDocument36 pagesBasic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureLutfil HadiNo ratings yet
- Basic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureDocument36 pagesBasic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureLutfil HadiNo ratings yet
- A Molecular Biology GlossaryDocument24 pagesA Molecular Biology GlossaryNabaneeta MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lulu Qian and Erik Winfree - A Simple DNA Gate Motif For Synthesizing Large-Scale CircuitsDocument17 pagesLulu Qian and Erik Winfree - A Simple DNA Gate Motif For Synthesizing Large-Scale CircuitsCogsmsNo ratings yet
- Basa RNADocument4 pagesBasa RNAIch RamNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems HourlyDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Hourlyjls tjhNo ratings yet
- 340Document17 pages340alem010100% (1)
- LOCSON Midterm OutputDocument1 pageLOCSON Midterm OutputMelaine Grace Gemoranion GeopanoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Workbook UpdateDocument36 pagesGenetics Workbook UpdateLauren WinnettNo ratings yet
- Mutations WorksheetDocument5 pagesMutations Worksheetapi-32772460No ratings yet
- Point Mutations: Silent Mutation: Although A Change in The DNA Sequence Occurs, ThisDocument3 pagesPoint Mutations: Silent Mutation: Although A Change in The DNA Sequence Occurs, ThisHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Linker, AdaptorsDocument25 pagesLinker, AdaptorsShanmugapriya100% (1)
- Lab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021Document11 pagesLab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021thesoccerprince.10No ratings yet
- DNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNADocument16 pagesDNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNAmohamedtnsNo ratings yet
- STR IntroductionDocument6 pagesSTR Introductionwan diendNo ratings yet
- Primer Design: (In This Case The Word Primer Means An Oligonucleotide)Document19 pagesPrimer Design: (In This Case The Word Primer Means An Oligonucleotide)kundansagarNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Deals With Problems of Heredity and VariationDocument37 pagesGenetics: Deals With Problems of Heredity and VariationjdazuelosNo ratings yet
- Guide To Electropherogram v3Document12 pagesGuide To Electropherogram v3varveroonNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing:: Sanger Method (Dideoxynucleotide Chain Termination)Document4 pagesDNA Sequencing:: Sanger Method (Dideoxynucleotide Chain Termination)Nitu ThulasidharanNo ratings yet
- 2859 764 4 61932GeneticEngineeringDocument40 pages2859 764 4 61932GeneticEngineeringAman HoodaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsDocument11 pagesLecture 4: Detecting Mutations and Mutation Consequences Learning GoalsAngelica SmithNo ratings yet
- Genomes and Their EvolutionDocument23 pagesGenomes and Their Evolutionprehealthhelp100% (2)
- Restriction - Endonucleases For Gene Manipulation - Unit 1 (Portion)Document17 pagesRestriction - Endonucleases For Gene Manipulation - Unit 1 (Portion)akshayaNo ratings yet
- 1.2,3 DNA SequencingDocument64 pages1.2,3 DNA SequencingMansiNo ratings yet
- SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats)Document2 pagesSSR (Simple Sequence Repeats)raghavmayank886No ratings yet
- cDNA, cDNA Library and CloningDocument70 pagescDNA, cDNA Library and CloningDerick SemNo ratings yet
- BioDocument4 pagesBioChloe TanNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Molecular Biology (COMPLETE)Document51 pagesTechniques in Molecular Biology (COMPLETE)Endik Deni NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Nanoscale Coulomb Blockade Memory and Logic DevicesDocument5 pagesNanoscale Coulomb Blockade Memory and Logic Deviceslogan302No ratings yet
- N - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeDocument5 pagesN - HS-LS1-1 Protein Synthesis PracticeMa Anna Cris LumongsudNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Fragment AssemblyDocument40 pagesLecture 5 Fragment AssemblyAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- Questions 9, 10, and 11Document2 pagesQuestions 9, 10, and 11JeffenNo ratings yet
- Network Coding, Algebraic Coding, and Network Error CorrectionDocument5 pagesNetwork Coding, Algebraic Coding, and Network Error CorrectionSaissi NadiaNo ratings yet
- Computing With DNANov28th2009Document100 pagesComputing With DNANov28th2009Sunny3141No ratings yet
- Designer Genes: Practice-Biotechnology: Dna Composition ProblemsDocument22 pagesDesigner Genes: Practice-Biotechnology: Dna Composition ProblemsGiovanni TorresNo ratings yet
- Nucl. Acids Res.-2006-Fouché-6044-50Document7 pagesNucl. Acids Res.-2006-Fouché-6044-50Bich-Thao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Exercise 10 - The Tools of DNA TechnologyDocument7 pagesGenetics Lab Exercise 10 - The Tools of DNA Technologybry uyNo ratings yet
- Seq ShotgunDocument4 pagesSeq ShotgunRohith MirapakayalaNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Sequencing and Sequence Assembly: Methodologies and AlgorithmsFrom EverandNext Generation Sequencing and Sequence Assembly: Methodologies and AlgorithmsNo ratings yet