Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIS FunctionalApplication
MIS FunctionalApplication
Uploaded by
lukkysreeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIS FunctionalApplication
MIS FunctionalApplication
Uploaded by
lukkysreeCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS)
Management information system (MIS)
An MIS provides managers with information and support for effective decision making, and provides feedback on daily operations Output, or reports, are usually generated through accumulation of transaction processing data Each MIS is an integrated collection of subsystems, which are typically organized along functional lines within an organization
Sources of Management Information
Schematic
Employees Corporate databases of internal data Databases of external data Corporate intranet Decision support systems Executive support systems
Business transactions
Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions
Management information systems
Application databases
Drill-down reports Exception reports Demand reports
Expert systems
Operational databases
Key-indicator reports
Input and error list
Scheduled reports
Outputs of a Management Information System
Scheduled reports
Produced periodically, or on a schedule (daily, weekly, monthly)
Key-indicator report
Summarizes the previous days critical activities Typically available at the beginning of each day
Demand report
Gives certain information at a managers request
Exception report
Automatically produced when a situation is unusual or requires management action
Scheduled Report Example
Daily Sales Detail Report
Prepared: 08/10/xx Order # P12453 P12453 P12453 P12455 P12456 Customer ID C89321 C89321 C03214 C52313 C34123 Sales Rep ID CAR CAR GWA SAK JMW Ship Date 08/12/96 08/12/96 08/13/96 08/12/96 08J/13/96 Quantity 144 288 12 24 144 Item # P1234 P3214 P4902 P4012 P3214 Amount $3,214 $5,660 $1,224 $2,448 $720
Key Indicator Report Example
Daily Sales Key Indicator Report This Month Total Orders Month to Date Forecasted Sales for the Month $1,808 $2,406 Last Month $1,694 $2,224 Last Year $1,014 $2,608
Demand Report Example
Daily Sales by Sales Rep Summary Report Prepared: 08/10/xx Sales Rep ID CAR GWA Amount $42,345 $38,950
SAK
JWN
$22,100
$12,350
Exception Report Example
Daily Sales Exception Report ORDERS OVER $10,000 Prepared: 08/10/xx
Order # P12453 P12453 P12453 Customer ID C89321 C89321 C03214 Sales Rep ID CAR CAR GWA Ship Date 08/12/96 08/12/96 08/13/96 Quantity 144 288 12 Item # P1234 P3214 P4902 Amount $13,214 $15,660 $11,224
Outputs of a Management Information System
Earnings by Quarter (Millions) Actual Forecast $11.8 $10.7 $14.5 $13.3 Variance 6.8% 0.9% -1.4% -3.0%
Drill Down Reports Provide detailed data about a situation.
2ND Qtr 1999 1st Qtr 1999 4th Qtr 1998 3rd Qtr 1998
$12.6 $10.8 $14.3 $12.8
Characteristics of a Management Information System
Provides reports with fixed and standard formats
Hard-copy and soft-copy reports
Uses internal data stored in the computer system End users can develop custom reports Requires formal requests from users
Management Information Systems for Competitive Advantage
Provides support to managers as they work to achieve corporate goals Enables managers to compare results to established company goals and identify problem areas and opportunities for improvement
MIS and Web Technology
Data may be made available from management information systems on a companys intranet Employees can use browsers and their PC to gain access to the data
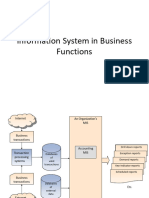
Functional Aspects
MIS is an integrated collection of functional information systems, each supporting particular functional areas.
Schematic
Internet
An Organizations MIS Financial MIS
Business transactions
Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions
Accounting MIS
Drill down reports
Exception reports Demand reports
Marketing MIS
Key-indicator reports Scheduled reports
Business transactions
Databases of external data
Human Resources MIS Etc.
Etc.
Extranet
Figure 9.3
Financial MIS
Provides financial information to all financial managers within an organization.
Schematic
Databases of internal data
Databases of external data
Financial DSS
Business transactions Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions for each TPS
Financial MIS
Financial applications databases
Business transactions Operational databases
Financial statements Uses and management of funds Financial statistics for control
Financial ES
Internet or Extranet
Business transactions
Customers, Suppliers
Figure 9.3
Inputs to the Financial Information System
Strategic plan or corporate policies
Contains major financial objectives and often projects financial needs.
Transaction processing system (TPS)
Important financial information collected from almost every TPS - payroll, inventory control, order processing, accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger. External sources Annual reports and financial statements of competitors and general news items.
Financial MIS Subsystems and Outputs
Financial subsystems
Profit/loss and cost systems Auditing Internal auditing External auditing Uses and management of funds
Manufacturing MIS
Schematic
Databases of internal data
Databases of external data
Manufacturing DSS
Business transactions Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions for each TPS
Manufacturing MIS
Manufacturing applications databases
Business transactions Operational databases
Quality control reports Process control reports
Internet or Extranet
JIT reports MRP reports Production schedule CAD output
Manufacturing ES
Business transactions
Customers, Suppliers
Figure 9.6
Inputs to the Manufacturing MIS
Strategic plan or corporate policies. The TPS:
Order processing Inventory data Receiving and inspecting data Personnel data Production process
External sources
Manufacturing MIS Subsystems and Outputs
Design and engineering Master production scheduling Inventory control Manufacturing resource planning Just-in-time inventory and manufacturing Process control Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) Quality control and testing
Marketing MIS
Supports managerial activities in product development, distribution, pricing decisions, and promotional effectiveness
Schematic
Databases of internal data
Databases of external data
Manufacturing DSS
Business transactions
Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions for each TPS
Marketing MIS
Marketing applications databases
Sales by customer Sales by salesperson
Operational databases
Sales by product Pricing report Total service calls Customer satisfaction
Manufacturing ES
Figure 9.9
Inputs to Marketing MIS
Strategic plan and corporate policies The TPS External sources:
The competition The market
Marketing MIS Subsystems and Outputs
Marketing research Product development Promotion and advertising Product pricing
Human Resource MIS
Concerned with all of the activities related to employees and potential employees of the organization
Databases of internal data
Databases of external data
Manufacturing DSS
Business transactions
Transaction processing systems
Databases of valid transactions for each TPS
Human Resource MIS
Human resource applications databases
Benefit reports Salary surveys
Operational databases
Scheduling reports Training test scores Job applicant profiles Needs and planning reports
Manufacturing ES
Figure 9.12
Inputs to the Human Resource MIS
Strategic plan or corporate policies The TPS:
Payroll data Order processing data Personnel data
External sources
Human Resource MIS Subsystems and Outputs
Human resource planning Personnel selection and recruiting Training and skills inventory Scheduling and job placement Wage and salary administration
Other MISs
Accounting MISs
Provides aggregated information on accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, and other applications. Enables managers to pair pre-drawn maps or map outlines with tabular data to describe aspects of a particular geographic region.
Geographic information systems (GISs)
You might also like
- Crane LoadingsDocument2 pagesCrane Loadingsmoseslugtu632470% (10)
- Inclusive Education in The Philippines: Study Guide For Module No. 1 (Las 2)Document9 pagesInclusive Education in The Philippines: Study Guide For Module No. 1 (Las 2)Maia GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Mis of Axis BankDocument29 pagesMis of Axis BankPratosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Jeff Butler's Presentation PDFDocument27 pagesJeff Butler's Presentation PDFYustina Lita SariNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Diagnostic TestDocument47 pagesTOEFL Diagnostic TestLilian G. Romero L.No ratings yet
- MIS HR Finance MarkettingDocument32 pagesMIS HR Finance MarkettingA Sailesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemsDocument33 pagesManagement Information SystemsAkshay kumarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Management Information SystemsDocument32 pagesCharacteristics of Management Information SystemsArif NasimNo ratings yet
- Mah Mba PPT03Document13 pagesMah Mba PPT03Mohamed MandourNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SystemDocument57 pagesTypes of Information SystemNavdeep Bhangu100% (4)
- Computer Applications in Management: Lecture PPT - MBA (I) R.Faculty Tushar Pradhan NIS Academy-Vadodara CentreDocument35 pagesComputer Applications in Management: Lecture PPT - MBA (I) R.Faculty Tushar Pradhan NIS Academy-Vadodara Centreanup_nair201093No ratings yet
- Mis Case Study: Killicks Kulkarni CombineDocument30 pagesMis Case Study: Killicks Kulkarni Combinezeet_98No ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Ravenshaw Management Centre, CuttackDocument29 pagesManagement Information Systems: Ravenshaw Management Centre, CuttackRaj MaanaNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Lesson 2Document34 pagesManagement Information Systems: Lesson 2ankush2148265No ratings yet
- Management Information System Overview & Characteristics: Prof. Arun Mishra Mobile: 9893686820Document22 pagesManagement Information System Overview & Characteristics: Prof. Arun Mishra Mobile: 9893686820Arun MishraNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems by DR S Sena Senior Lecturer Business StudiesDocument32 pagesManagement Information Systems by DR S Sena Senior Lecturer Business StudiesTawanda MahereNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and OrganizationsDocument33 pagesManagement Information Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and OrganizationsSoumya Jyoti BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Lec-8 MISDocument33 pagesLec-8 MISKomal BanikNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: CA Naveen AgarwalDocument28 pagesManagement Information Systems: CA Naveen Agarwalsiddhi2112No ratings yet
- Financial and Production Information Systems: Department of Computer ScienceDocument28 pagesFinancial and Production Information Systems: Department of Computer Sciencelakha9637No ratings yet
- Final MisDocument33 pagesFinal MisDnyaneshwar DaundNo ratings yet
- MIS Functional AspectsDocument27 pagesMIS Functional Aspectssimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- Functional Systems 1Document30 pagesFunctional Systems 1Vinetha J MNo ratings yet
- Mis BF IiDocument22 pagesMis BF IiaastikpanditaNo ratings yet
- MIS Functional AspectsDocument30 pagesMIS Functional AspectsAmin Abdullah Khan100% (1)
- DSS & Mis 01 - MisDocument9 pagesDSS & Mis 01 - MisSoumya Jyoti BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Categories of Is: Based On Support Provided, LevelsDocument71 pagesCategories of Is: Based On Support Provided, Levelsarchana_sree13No ratings yet
- MIS BBA 6th Sem UNIT 1-2-3Document167 pagesMIS BBA 6th Sem UNIT 1-2-3thakurrohit22614No ratings yet
- MIS UNIT 5aDocument23 pagesMIS UNIT 5aVaibhav ShrotriNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 and 3 MIS in PerspectiveDocument46 pagesUnit 2 and 3 MIS in PerspectiveMukong LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Mis 4Document17 pagesMis 4Manish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: To Know Information Systems &Document25 pagesLearning Objectives: To Know Information Systems &Kanbiro OrkaidoNo ratings yet
- Information Flow in DepartmentsDocument2 pagesInformation Flow in DepartmentsAli QasmiNo ratings yet
- Mis of Axis BankDocument29 pagesMis of Axis Bankabhay_iipmNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Decision Support and Expert Systems: Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-WingDocument24 pagesModule 2: Decision Support and Expert Systems: Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-WingPavithra AnandhNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Why Do People Need Information?Document70 pagesInformation Systems: Why Do People Need Information?Eswarlal B KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organizational Systems: UNIT-2Document50 pagesIntroduction To Organizational Systems: UNIT-2nandini swamiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support and Expert SystemsDocument23 pagesDecision Support and Expert SystemsMahmoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mis Application in FinanceDocument13 pagesMis Application in Financereotoms123No ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Dominic K. LouisDocument44 pagesManagement Information Systems: Dominic K. LouisBaffoe AaronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1Sangam AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SystemsDocument29 pagesTypes of Information SystemsrajavikramarkaNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument48 pagesManagement Information SystemRachit Puri100% (89)
- Mis ProjectDocument2 pagesMis Projectsocial sgNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MisDocument25 pagesIntroduction To MisKeith D'souzaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Chapter 1Document41 pagesAccounting Information System Chapter 1AngelieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - The Information System An Accountant's PerspectiveHads LunaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument8 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveHads LunaNo ratings yet
- Lect 31Document6 pagesLect 31filmon dissanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Management Information SystemsDocument71 pagesStructure of Management Information SystemsKochappen Ipe KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Information SystemsDocument58 pages01 - Introduction To Information SystemsTrina Mae OcampoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Information SystemsDocument15 pagesBasics of Information SystemsUtkarsh GhagareNo ratings yet
- COMP2 - X Reviewer Prelims PDFDocument161 pagesCOMP2 - X Reviewer Prelims PDFcynangelaNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Management: The Range and Roles of IS in OrganisationsDocument44 pagesInformation Systems Management: The Range and Roles of IS in OrganisationsKatherine ZMNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MIS: Transactions and Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument56 pagesIntroduction To MIS: Transactions and Enterprise Resource Planningabi12No ratings yet
- The Data Warehouse Toolkit: The Complete Guide to Dimensional ModelingFrom EverandThe Data Warehouse Toolkit: The Complete Guide to Dimensional ModelingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Agile Procurement: Volume II: Designing and Implementing a Digital TransformationFrom EverandAgile Procurement: Volume II: Designing and Implementing a Digital TransformationNo ratings yet
- Data Processing, Hosting & Related Service Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandData Processing, Hosting & Related Service Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study (Compatibility Mode)Document35 pagesFeasibility Study (Compatibility Mode)Deep ShahNo ratings yet
- What Is The Relevance of Mechanics To Electrical Engineering?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Relevance of Mechanics To Electrical Engineering?Jerome EstradaNo ratings yet
- 010 ASSIGNMENT - Auditor's Report - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovDocument2 pages010 ASSIGNMENT - Auditor's Report - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovMarilou Panisales0% (1)
- The Religion of The Ancient Celts - 9781605061979Document345 pagesThe Religion of The Ancient Celts - 9781605061979null10100% (2)
- PRIMARY vs. SECONDARY SOURCESDocument2 pagesPRIMARY vs. SECONDARY SOURCESShannise Dayne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Blocki 2007Document5 pagesBlocki 2007Abdellah LAHDILINo ratings yet
- Neuro BrandingDocument41 pagesNeuro BrandingZia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Task ManagementDocument11 pagesTask Managementnaveedskhan100% (1)
- Module NoDocument2 pagesModule NoCristia FayeNo ratings yet
- Anorectal Malformations in A Tertiary Pediatric Surgery Center Fromromania 20 Years of Experience 1584 9341-12-2 3Document5 pagesAnorectal Malformations in A Tertiary Pediatric Surgery Center Fromromania 20 Years of Experience 1584 9341-12-2 3Jeff LapianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacutical IndustryDocument59 pagesPharmacutical Industrysunil188patel_983482No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - System PlanningDocument40 pagesChapter 2 - System PlanningJia Ming100% (1)
- TS BRANDING ResearchDocument11 pagesTS BRANDING ResearchPARITOSH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 English Unit PlanDocument8 pagesAssignment 3 English Unit Planapi-626567329No ratings yet
- Final Jury Instructions Seditious Conspiracy Oath KeepersDocument51 pagesFinal Jury Instructions Seditious Conspiracy Oath KeepersDaily KosNo ratings yet
- Possible Worlds in Narrative SpaceDocument19 pagesPossible Worlds in Narrative SpaceMariia Mandrikova100% (1)
- Unit 6 Short Test 2A: GrammarDocument1 pageUnit 6 Short Test 2A: GrammarGordanaNo ratings yet
- SAIMC-2019 Keystage-3 Individual Final.x17381Document7 pagesSAIMC-2019 Keystage-3 Individual Final.x17381Darma YasaNo ratings yet
- Vu Re Lecture 16Document28 pagesVu Re Lecture 16ubaid ullahNo ratings yet
- Trial MixDocument9 pagesTrial Mixfikri y nugrahaNo ratings yet
- An Excerpt From The Barbour Bible Reference CompanionDocument31 pagesAn Excerpt From The Barbour Bible Reference CompanionBarbour Books100% (2)
- Unruh 2Document7 pagesUnruh 2amanNo ratings yet
- Pol Part in Europe PDFDocument22 pagesPol Part in Europe PDFSheena PagoNo ratings yet
- Why Marketing Is The Best Career Option: By: Hajra HafeezDocument10 pagesWhy Marketing Is The Best Career Option: By: Hajra HafeezMohamed Masood NasirNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument3 pagesMidtermapi-272864612No ratings yet
- Karen Horney Quiz Theories of PersonalityDocument2 pagesKaren Horney Quiz Theories of Personalityzainab hanifNo ratings yet
- English 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish 10 Reviewerathea garciaNo ratings yet