Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Building Behavior
Uploaded by
Taqi ZaidiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Building Behavior
Uploaded by
Taqi ZaidiCopyright:
Available Formats
BUILDING BEHAVIOR
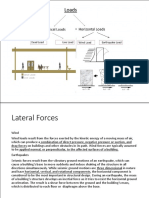
The seismic motions of the ground do not damage a building by impact, as does a wreckers ball, or by externally applied pressure such as wind, but by internally generated inertial forces caused by the vibration of the building mass. An increase in mass has two undesirable effects on the earthquake design. First, it results in an increase in the force, and second, it can cause buckling or crushing of columns and walls when the mass pushes down on a member bent or moved out of plumb by the lateral forces. This effect is known as the P effect and the greater the vertical forces, the greater the movement due to P. tall buildings respond to seismic motion differently than low-rise buildings. The magnitude of inertia forces induced in an earthquake depends on the building mass, ground acceleration, the nature of the foundation, and the dynamic characteristics of the structure.
INFLUENCE OF SOIL
The intensity of ground motion reduces with the distance from the epicenter of the earthquake. The reduction, called attenuation. As a building vibrates due to ground motion, its acceleration will be amplified if the fundamental period of the building coincides with the period of vibrations being transmitted through the soil. This amplified response is called resonance. An obvious design strategy is to ensure that buildings have a natural period different from that of the expected ground vibration to prevent amplification.
DAMPING
Buildings do not resonate with the purity of a tuning fork because they are damped; the extent of damping depends upon the construction materials, the type of connections, and the influence of nonstructural elements on the stiffness characteristics of the building.
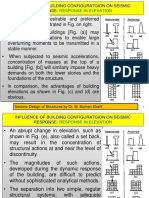
BUILDING MOTIONS AND DEFLECTIONS
Lateral deflections that occur during earthquakes should be limited to prevent distress in structural members and architectural components.
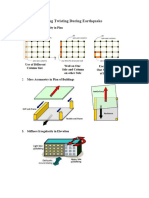
BUILDING DRIFT AND SEPARATION
Drift is generally defined as the lateral displacement of one floor relative to the floor below. Drift control is necessary to limit damage to interior partitions, elevator and stair enclosures, glass, and cladding systems.
You might also like
- Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDocument17 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Structuresteju_13No ratings yet
- Lateral Forces: Wind Loads and Earthquake EffectsDocument14 pagesLateral Forces: Wind Loads and Earthquake Effectsalamin r.aNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistent Building ConstructionDocument10 pagesEarthquake Resistent Building ConstructionSrinivas Gowda MNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Effects On BuildingsDocument15 pagesEarthquake Effects On BuildingsRian WibisonoNo ratings yet
- G19' (T4)Document3 pagesG19' (T4)Punku BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Design Concepts of SubstructuresDocument8 pagesDesign Concepts of Substructuresmohith reddyNo ratings yet
- Twisting of Building - DuctilityDocument3 pagesTwisting of Building - DuctilityGenreson De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument9 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresAbhinav RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Seminar Project 2nd Part Earthquake Resisting BuildingDocument31 pagesSeminar Project 2nd Part Earthquake Resisting BuildinganimeshranjandhnNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Building: Iqra Javed 3 ADocument16 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building: Iqra Javed 3 AIqRa JaVedNo ratings yet
- Assignment High RiseDocument18 pagesAssignment High Risemanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Earthquake ResistentDocument15 pagesEarthquake ResistentShadIngNo ratings yet
- Presentation on EarthquakesDocument39 pagesPresentation on EarthquakesRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Mitigation and Management Rajat PalDocument10 pagesDisaster Mitigation and Management Rajat PalRajat PalNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Building Construction MethodsDocument1 pageEarthquake Resistant Building Construction MethodsGenver HoraNo ratings yet
- Design of Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument25 pagesDesign of Earthquake Resistant StructuresVinod Kumar A100% (2)
- Pressure Effects Buildings BlastsDocument19 pagesPressure Effects Buildings BlastsHarishkumarv551995No ratings yet
- Joomla PDFDocument2 pagesJoomla PDFਤਨ੍ਹਾ ਰਾਜੀਵ ਮਾਯੂਸNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Conceptual Design of Earthquake Resistant BuildingsDocument11 pagesAssignment On Conceptual Design of Earthquake Resistant BuildingsShaijal KmNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant BuildingDocument30 pagesEarthquake Resistant BuildingArsatNo ratings yet
- Setbacks and RedundancyDocument21 pagesSetbacks and RedundancyAyushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistent Building: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument20 pagesEarthquake Resistent Building: Submitted To: Submitted bypiyush ji srivastavNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering: Faculty of Civil Engineering and Building Services Vizitiu Roxana-Andreea Group: 3410Document7 pagesEarthquake Engineering: Faculty of Civil Engineering and Building Services Vizitiu Roxana-Andreea Group: 3410Roxana Andreea VizitiuNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Can Be Defined As What Happens When Two Blocks of The Earth Suddenly Slip Past One AnotherDocument3 pagesEarthquakes Can Be Defined As What Happens When Two Blocks of The Earth Suddenly Slip Past One AnotherNeerom BaldemoroNo ratings yet
- Influence of Building Configuratgion On Seismic ResponseDocument36 pagesInfluence of Building Configuratgion On Seismic ResponseAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Seminar On "Earthquake Resistant Building Construction": Submitted By:-Amir HussainDocument26 pagesSeminar On "Earthquake Resistant Building Construction": Submitted By:-Amir Hussainwajid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Direct Effects Caused by EarthquakesDocument20 pagesDirect Effects Caused by EarthquakesGerard VelicariaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Soils On Ground MotionDocument9 pagesEffects of Soils On Ground MotionMary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNo ratings yet
- Pandit Lakhmi Chand State University of Performing and Visual Arts, Rohtak Faculty of Urban Planning and ArchitectureDocument38 pagesPandit Lakhmi Chand State University of Performing and Visual Arts, Rohtak Faculty of Urban Planning and ArchitectureShubham Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- 2 Earthquake Engg Nat ReportDocument15 pages2 Earthquake Engg Nat ReportlenerNo ratings yet
- Study on a Structural Building Subjected to Earthquake ForcesDocument6 pagesStudy on a Structural Building Subjected to Earthquake Forcessandeep chauhanNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Resistant Building ConstructionDocument16 pagesCyclone Resistant Building Construction1DA16CV082Spoorthi L100% (3)
- Earthquake Resistant Building ArchitectureDocument28 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building Architecturesalmantop10% (1)
- Earthquake Resistant Building Design and Seismic Effects on StructuresDocument11 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building Design and Seismic Effects on Structuresgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- TN 30 Cladding Subject To EarthquakesDocument5 pagesTN 30 Cladding Subject To Earthquakesj.prolovic.savicNo ratings yet
- Gateway College of Architecture and Design: Lesson Plan - 3ADocument55 pagesGateway College of Architecture and Design: Lesson Plan - 3AChopra ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Field On Civil EngineeringDocument5 pagesField On Civil EngineeringCristian YumulNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Construction HandbookDocument17 pagesEarthquake Resistant Construction HandbookArifsalimNo ratings yet
- Effect of Earthquake and Wind Load On Residential by Using EtabsDocument61 pagesEffect of Earthquake and Wind Load On Residential by Using EtabsManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Earthquake TipsDocument33 pagesSeminar ON: Earthquake TipsRTNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Sustainability Factor: DuctilityDocument10 pagesEarthquake Sustainability Factor: DuctilitysidsinsNo ratings yet
- Failure of Foundation Due To Earth Quake-LiquefactionDocument19 pagesFailure of Foundation Due To Earth Quake-LiquefactionAlam Mohammad Parvez SaifiNo ratings yet
- Loads and Earthquake Effects on StructuresDocument2 pagesLoads and Earthquake Effects on StructuresAmanuel MintesnotNo ratings yet
- Structural Building Elements for Seismic ResistanceDocument5 pagesStructural Building Elements for Seismic ResistanceCE3263 Aniruddh ShingteNo ratings yet
- Ground Vibrations and Air Blasts: Causes, Effects and AbatementDocument21 pagesGround Vibrations and Air Blasts: Causes, Effects and AbatementDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tips To Design Earthquake Resistant Building - Jean-Rayner KuswadiDocument40 pagesTips To Design Earthquake Resistant Building - Jean-Rayner KuswadiMae Lingan-LasqueroNo ratings yet
- Fields of Civil EngineeringDocument34 pagesFields of Civil EngineeringLit WorksNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Building DesignDocument5 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building DesignSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Building StructuresDocument6 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building StructuresShubhayu DuttaNo ratings yet
- Failure of Foundation Due To EarthquakeDocument20 pagesFailure of Foundation Due To EarthquakeKuldeep Kumar83% (6)
- Lateral Loads on Structures ExplainedDocument5 pagesLateral Loads on Structures ExplainedPrince AJNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Principles & EffectsDocument10 pagesSeismic Design Principles & Effectsfaheem momdNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Design and FunctionsDocument20 pagesShear Wall Design and FunctionsKeyur VasavaNo ratings yet
- Análisis Dinámico 01Document14 pagesAnálisis Dinámico 01Andres FierroNo ratings yet
- Earthquake-Resistant Construction MethodsDocument2 pagesEarthquake-Resistant Construction MethodsAkmalNo ratings yet
- Factors Causing Failure of Heritage Buildings in EarthquakesDocument23 pagesFactors Causing Failure of Heritage Buildings in EarthquakesParay FirdousNo ratings yet
- Base Isolation and Seismic Consideration in Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument15 pagesBase Isolation and Seismic Consideration in Earthquake Resistant StructuresAuqib BhattNo ratings yet
- Earthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyFrom EverandEarthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Power of Positive EnergyDocument13 pagesThe Hidden Power of Positive Energypinuta100% (2)
- 8 ST1407-040Document9 pages8 ST1407-040HarshitaGRajuNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of A 19 Story Concrete Shear Wall BuildingDocument12 pagesPushover Analysis of A 19 Story Concrete Shear Wall BuildingNityananda Permadi TjokrodimurtiNo ratings yet
- Astm A615Document5 pagesAstm A615Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- 289 Sayings of Imam AliDocument30 pages289 Sayings of Imam AliTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Curvature Ductility Prediction of Reinforced High Strength Concrete Beam SectionsDocument10 pagesCurvature Ductility Prediction of Reinforced High Strength Concrete Beam SectionsTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Earthworks Chapter 07Document8 pagesEarthworks Chapter 07Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Assignment, Practical Ce-403Document5 pagesAssignment, Practical Ce-403Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Development of PortsDocument63 pagesDevelopment of PortsArif Samoon75% (4)
- ASTM D 2166-00 Standard Test Method For Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive SoilDocument6 pagesASTM D 2166-00 Standard Test Method For Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive SoilPablo Antonio Valcárcel Vargas100% (2)
- Terzaghi DerivationDocument3 pagesTerzaghi DerivationTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Fundamentals: Traverse ComputationsDocument60 pagesCoordinate Geometry Fundamentals: Traverse ComputationsTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Roads & BridgesDocument66 pagesRoads & BridgesvivekranjanjamNo ratings yet
- Assignment, Practical Ce-403Document5 pagesAssignment, Practical Ce-403Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- C1 Lab06 G34Document17 pagesC1 Lab06 G34Taqi Zaidi100% (1)
- Dimensional Consolidation TestDocument10 pagesDimensional Consolidation TestTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Dimension Assignments by Groups: Ce 405: Reinforced Concrete Design - Ii GROUP ASSIGNMENT (Due On Thursday 12 April 2012)Document5 pagesDimension Assignments by Groups: Ce 405: Reinforced Concrete Design - Ii GROUP ASSIGNMENT (Due On Thursday 12 April 2012)Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Precision Runway Marking DiagramDocument1 pagePrecision Runway Marking DiagramTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Plate Load TestDocument3 pagesPlate Load TestTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Runway and Taxiway MarkingDocument2 pagesRunway and Taxiway MarkingTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Design of Air Side AreaDocument10 pagesDesign of Air Side AreaTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Classiifcation 2Document1 pageClassiifcation 2Taqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesAircraft CharacteristicsTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- CLASSIIFCATIONDocument1 pageCLASSIIFCATIONTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Civil Airport Imaginary Surfaces: Surface Slope KeyDocument1 pageCivil Airport Imaginary Surfaces: Surface Slope KeyTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Distribution ConceptsDocument7 pagesHorizontal Distribution ConceptsTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- What Is Creep in RailDocument2 pagesWhat Is Creep in RailTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Design aids for reinforced concrete structuresDocument33 pagesDesign aids for reinforced concrete structuresTaqi ZaidiNo ratings yet