Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Treatment
Heat Treatment
Uploaded by
Ezebunwo NwoforOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Treatment
Heat Treatment
Uploaded by
Ezebunwo NwoforCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Treatment
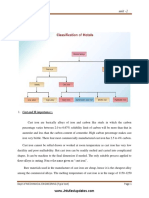
Type of heat treatment Normalizing Objective To change an irregular and coarse grain structure into a uniform one with fine lamellar ferrite-perlite structure. After diffusion annealing, after welding, after casting. If the steel is embrittled due to aging To increase the thoughness or yield strength To reduce the internal stresses without essential influence to other properties. After welding, after casting To make the grains coarser so that the smearing effect and cutting forces are small resulting in easier machineability. For milling, turning To convert the lamellar cementite into globular cementite and hence to obtain a suitable structure for further operations. For milling, cold deformation To compensate the local differences of the chemical composition To restore the original material properties after cold deformation for further cold deformation. To increase the strength and wear resistance. To obtaion the ideal combination of strength and toughness To incease the hardness of the surface by means of dip hardening, flame hardening and induction hardening. ncraesing the surface hardness by diffusing carbon into the surface. ncraesing the surface hardness by diffusing nitrogen into the surface. Hardening of the surface by aplying the cementation and nitriding at the same time.
Stress relief annealing Coarse graing annealing Soft annealing Diffusion annealing Recrystallization Hardening Quenching and tempering Surface layer hardening Cementation Nitrogen hardening Carbonitriding
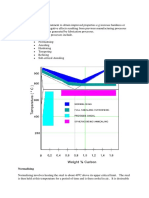
diffusion annealing
coarse grain annealing
Temperature (C)
normalizing hardening quenching and tempering
soft annealing
stress relief annealing recrystallisation annealing
C content (%)
temperature
normalizing
hardening A3 A1 air cooling
quenching
time
diffusion annealing upto 50 h
temperature
coarse grain annealing 1-2 h A3 A1 air cooling
air cooling
time
You might also like
- Heat Treatment Process: By: Jagdish PampaniaDocument67 pagesHeat Treatment Process: By: Jagdish PampaniabassamNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment: ME 318 Manufacturing TechniquesDocument12 pagesHeat Treatment: ME 318 Manufacturing Techniquesmayur_mechNo ratings yet
- Course: Materials TechnologyDocument60 pagesCourse: Materials TechnologyelvisNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument56 pagesStainless SteeljalindrepNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6: Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys - Importance Heat Treatment Processes NormalisingDocument47 pagesLecture-6: Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys - Importance Heat Treatment Processes NormalisingSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- TTT DiagramsDocument4 pagesTTT DiagramsEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment LectureDocument58 pagesHeat Treatment LectureKeith Tanaka Magaka100% (1)
- Jephthah Efekiruo: ISO 9001:2015 - Quality Management System (QMS)Document1 pageJephthah Efekiruo: ISO 9001:2015 - Quality Management System (QMS)Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Hsla SteelDocument22 pagesHsla SteelriteshbarmanNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment: Prepared by Approved byDocument20 pagesHeat Treatment: Prepared by Approved byBhanu Pratap ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsDocument24 pagesUnit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Cast IronDocument27 pagesCast IronSanthoshsharma Devaraju100% (1)
- Heat Treatment GC - 08Document54 pagesHeat Treatment GC - 08kr_abhijeet72356587No ratings yet
- A Snail Business Plan and Feasibility Study (1000snails)Document16 pagesA Snail Business Plan and Feasibility Study (1000snails)Ezebunwo Nwofor100% (2)
- Normalizing Process For SteelsDocument3 pagesNormalizing Process For Steelsduazo2009No ratings yet
- Bulk Deformation Processes: RollingDocument17 pagesBulk Deformation Processes: RollingEthan DanielsNo ratings yet
- Weldability of High Strength Low Alloy SteelDocument34 pagesWeldability of High Strength Low Alloy SteelGanesan Veerasamy100% (1)
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- WPS & PQR Training PDFDocument316 pagesWPS & PQR Training PDFamini_mohiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Heat TreatmentsDocument34 pagesPresentation On Heat TreatmentsVinothkumarNo ratings yet
- Tech Gudeline - HEAT TREATMENTDocument15 pagesTech Gudeline - HEAT TREATMENTggi internationalNo ratings yet
- Introduction HotandColdProcessDocument16 pagesIntroduction HotandColdProcessRahul BajpaiNo ratings yet
- MSM R19 - Unit-2Document28 pagesMSM R19 - Unit-2Madheswaran DharmapuriNo ratings yet
- Iml213 (2 Föy)Document65 pagesIml213 (2 Föy)HilalAldemirNo ratings yet
- HeattreatmentprocessesDocument16 pagesHeattreatmentprocessesEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of SteelDocument3 pagesHeat Treatment of SteelKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Heat TreatmentDocument6 pagesObjectives of Heat TreatmentAdaitaChowdhury100% (1)
- Mt14 ReviewerDocument16 pagesMt14 ReviewerMichelle TuballaNo ratings yet
- CIVE 6338 CH 1Document35 pagesCIVE 6338 CH 1satyaNo ratings yet
- 0710 Bodycote PDFDocument13 pages0710 Bodycote PDFRuchira Chanda InduNo ratings yet
- aLLOY STEEL 15 For Name 205Document40 pagesaLLOY STEEL 15 For Name 205Sakib RafeeNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Processes in Gear Design: Prepared By:-Kartik Thakkar WebsiteDocument16 pagesHeat Treatment Processes in Gear Design: Prepared By:-Kartik Thakkar WebsiteHerdi PriyoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 37Document4 pagesLecture 37Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Em Heat TreatmentDocument42 pagesEm Heat TreatmentIdk 1No ratings yet
- Case Hardening Heat TreatmentDocument15 pagesCase Hardening Heat Treatmentmohit1990dodwalNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatments of SteelsDocument7 pagesHeat Treatments of SteelsBianca MihalacheNo ratings yet
- 5 SteelDocument57 pages5 SteelsndNo ratings yet
- High Temperature & Low Temperature Thermo-Mechanical ProcessesDocument24 pagesHigh Temperature & Low Temperature Thermo-Mechanical Processesnaseema shaikNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Jominy End-Quench Test - 2015-05-07 - Industrial HeatingDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Jominy End-Quench Test - 2015-05-07 - Industrial HeatingfaqhrulNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformation Processes in Metal WorkingDocument83 pagesBulk Deformation Processes in Metal WorkingMr-Mk MughalNo ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument31 pagesHeat TreatmentJackNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-Kartik ThakkarDocument16 pagesPrepared By:-Kartik ThakkarMANGESHNo ratings yet
- Material Science NotesDocument2 pagesMaterial Science NotesRam ChandraNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron: Alloys of Iron and Carbon With More Than 2.11% Carbon Are Called Cast IronsDocument24 pagesCast Iron: Alloys of Iron and Carbon With More Than 2.11% Carbon Are Called Cast IronsArun Bongale100% (1)
- Brake Disc Rotor Manufacturing ProcessesDocument3 pagesBrake Disc Rotor Manufacturing Processessumukha nadigNo ratings yet
- 4 HardenabilityDocument107 pages4 HardenabilityKrishnananda AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Case HardeningDocument2 pagesCase HardeningdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- ME3302 - Lecture-10 - Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening-2Document76 pagesME3302 - Lecture-10 - Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening-2Jesh KeerawellaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Ferrous and Non Ferrous MetalsDocument68 pagesUNIT 3 Ferrous and Non Ferrous MetalsAmutha PSGRKCWNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Steel: ObjectDocument10 pagesHeat Treatment Steel: ObjectKetut Rizki FirmandanuNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon SteelDocument12 pagesHeat Treatment of Plain Carbon Steelweda walata heduwaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document76 pagesUnit 3Thor OdinsonNo ratings yet
- Etals Nternational Imited: Thermal-Mechanical Surface HardeningDocument1 pageEtals Nternational Imited: Thermal-Mechanical Surface HardeningSSMNo ratings yet
- Note CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document40 pagesNote CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_ryeNo ratings yet
- Resumen MaterialesDocument20 pagesResumen MaterialesLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Heat Treating BasicsDocument36 pagesHeat Treating BasicsSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument23 pagesLiterature ReviewRISHAVNo ratings yet
- Aerospace MaterialsDocument28 pagesAerospace MaterialsSebastian M. PajaroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Plain Carbon Steels - 2013Document45 pagesLecture 9 - Plain Carbon Steels - 2013ArunNo ratings yet
- 1435551458629-Overview of HT PDFDocument74 pages1435551458629-Overview of HT PDFakashNo ratings yet
- High Alloy White Cast IronDocument1 pageHigh Alloy White Cast IronPRASHANTHNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Carbon SteelDocument23 pagesHeat Treatment of Carbon SteelArielle Joyce de JesusNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - 1 Flame HardeningDocument11 pagesTerm Paper - 1 Flame HardeningSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Gas Certificate PDFDocument3 pagesGas Certificate PDFEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Educational Credential Assessment For Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship CanadaDocument2 pagesEducational Credential Assessment For Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship CanadaEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- To: MSC Structural Integrity (Asset Reliability Management) : Programme Specification For Postgraduate Programme LeadingDocument6 pagesTo: MSC Structural Integrity (Asset Reliability Management) : Programme Specification For Postgraduate Programme LeadingEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Qualifications Explained Factsheet PDFDocument2 pagesQualifications Explained Factsheet PDFEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Welding Oven Calibration Certificate PDFDocument4 pagesWelding Oven Calibration Certificate PDFEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd Gives Me The Best Choice When It Comes To Material Sourcing!!Document1 pageScribd Gives Me The Best Choice When It Comes To Material Sourcing!!Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- I Just Discovered Some New Stuff at Scribd!!Document1 pageI Just Discovered Some New Stuff at Scribd!!Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Marking On 16T D-Ring: Y09A0Document2 pagesMarking On 16T D-Ring: Y09A0Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Cross Sectional AreaDocument2 pagesCross Sectional AreaEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument1 pageRich Text Editor FileEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd "My Best Educational Resource Center"Document1 pageScribd "My Best Educational Resource Center"Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd Remains The Best SiteDocument1 pageScribd Remains The Best SiteEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd Remains My First Port of Call When I Need MaterialsDocument1 pageScribd Remains My First Port of Call When I Need MaterialsEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- God Is LoveDocument1 pageGod Is LoveEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- I Just Downloaded Iso 6947 From Sribd Very Good Huh!!!Document1 pageI Just Downloaded Iso 6947 From Sribd Very Good Huh!!!Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Just Downloaded The Books I NeededDocument1 pageJust Downloaded The Books I NeededEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Basic Assumptions of Evolutionary: TheoryDocument160 pagesBasic Assumptions of Evolutionary: TheoryEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- I Just Got The Latest Welding Books From ScribdDocument1 pageI Just Got The Latest Welding Books From ScribdEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- This Remains My Number 1 Site11Document1 pageThis Remains My Number 1 Site11Ezebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd The Best Site in Terms of KnowledgeDocument1 pageScribd The Best Site in Terms of KnowledgeEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet
- Scribd Gave Me The Best Cwi Book. Thanks Guys I Really AppreciateDocument1 pageScribd Gave Me The Best Cwi Book. Thanks Guys I Really AppreciateEzebunwo NwoforNo ratings yet