Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generic Name
Uploaded by
Jhennyvie Dueñas ArcoirezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Generic Name
Uploaded by
Jhennyvie Dueñas ArcoirezCopyright:
Available Formats
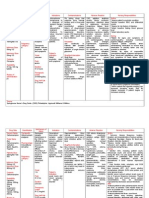
Generic name: chlorpromazine Brand name: Laractyl CLASSIFI-CATION: Antipsychotics ACTION: Block dopamine receptors in the brain; also
alter dopamine release and turnover. Prevention of seizures INDICATION / USES: Acute and chronic psychoses, particularly when accompanied by increased psychomotor activity. Nausea and vomiting. Also used in the treatment of intractable hiccups. COMMON ADVERSE EFFECTS: CNS: neuroleptic malignant syndrome, sedation, extrapyramidal reactions, tardive dyskinesia CV: hypotension (increased with IM, IV) EENT: blurred vision, dry eyes, lens opacities GI: constipation, dry mouth, anorexia, hepatitis, ileus GU: urinary retention Hematologic: agranulocytosis, leukopenia Skin: photosensitivity, pigment changes, rashes CONTRA-INDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity. Cross-sensitivity may exist among phenothiazines. Should not be used in narrow-angle glaucoma. Should not be used in patients who have CNS depression. NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Assess mental status prior to and periodically during therapy. Monitor BP and pulse prior to and frequently during the period of dosage adjustment. May cause QT interval changes on ECG. Observe patient carefully when administering medication, to ensure that medication is actually taken and not hoarded.
Monitor I&O ratios and daily eight. Assess patient for signs and symptoms of dehydration. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (fever, respiratory distress, tachycardia, seizures, diaphoresis, hypertension or hypotension, pallor, tiredness, severe muscle stiffness, loss of bladder control. Report symptoms immediately. May also cause leukocytosis, elevated liver function tests, elevated CPK. Advise patient to take medication as directed. Take missed doses as soon as remembered, witih remaining doses evenly spaced through out the day. May require several weeks to obtain desired effects. Do not increase dose or discontinue medication without consulting health care professional. Abrupt withdrawal may cause dizziness, nausea, vomiting, GI upset, trembling, or uncontrolled movements of mouth, tongue or jaw
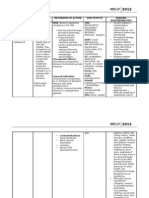
Carbamazepine
Epazin Anticonvulsant
MECHANISM OF ACTION In addition to anticonvulsant effects, carbamazepine has anticholinergic, antineuralgic, antidiuretic, muscle relaxant, antimanic, antidepressive, and antiarrhythmic properties; may depress activity in the nucleus ventralis of the thalamus or decrease synaptic transmission or decrease summation of temporal stimulation leading to neural discharge by limiting influx of sodium ions across cell membrane or other unknown mechanisms; stimulates the release of ADH and potentiates its action in promoting reabsorption of water; chemically related to tricyclic antidepressants
Common Side Effects:
Clumsiness or unsteadiness; dizziness (mild); drowsiness (mild); lightheadedness; nausea or vomiting (mild)
You might also like
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Nursing Care GuideDocument3 pagesOlanzapine Nursing Care GuideBarbara Detaro100% (2)
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- HaldolDocument6 pagesHaldolJon ChuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsSarah Carretero0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMariCris CaronanNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument2 pagesHaloperidolMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug Info SheetDocument2 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Info SheetCham ChamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Clinical Manifestations Patient N.R.MDocument6 pagesDrug Study Clinical Manifestations Patient N.R.MRiva Tiara Tabieros AranasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Contraindication /indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageDrug Action Contraindication /indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument3 pagesHALOPERIDOLSonny Dizon PareñasNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument3 pagesHTTPChon 앙드레 BalanayNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin medication guideDocument15 pagesGabapentin medication guideTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Clonidine Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesClonidine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Fluphenazine Drug Study!Document3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study!EmJay Balansag100% (3)
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsnurse_nurseNo ratings yet
- CLOZAPINE ForscribdDocument4 pagesCLOZAPINE ForscribdMaria Rhodora PetajenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Document5 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDDocument25 pagesDoctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- CNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageDocument4 pagesCNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageYanna N. CuakiNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyKate Chavez100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- Drug Study 2019Document14 pagesDrug Study 2019Aubrey Unique Evangelista100% (1)
- Prepared By: Manisha Thapa Leeza ShresthaDocument12 pagesPrepared By: Manisha Thapa Leeza ShresthaManjesh Mishra XettriNo ratings yet
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- Clonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688875% (4)
- Olanzapine C Loza Pine, Drug StudyDocument7 pagesOlanzapine C Loza Pine, Drug StudyAubrey MacNo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugDocument25 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugANI SAMNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument5 pagesAtropine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Dept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKDocument62 pagesDept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKAnonymous zZrGTONhNo ratings yet
- Centrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRDocument4 pagesCentrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Drug StudySanny L Asim Jr.No ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument1 pageOlanzapineKallie ChartrandNo ratings yet
- Availability: Psychopharmacology Chlorpromazine HydrochlorideDocument10 pagesAvailability: Psychopharmacology Chlorpromazine HydrochlorideWendz Palma-TudaNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol for Psychosis, Anxiety, SeizuresDocument2 pagesHaloperidol for Psychosis, Anxiety, SeizuresDe Chavez Levy RoyNo ratings yet
- GENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONDocument3 pagesGENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- Abilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsDocument6 pagesAbilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Amlo Cloni PregaDocument4 pagesAmlo Cloni PregaKym Karla PatrizyahNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Drugs Psych WardDocument4 pagesDrugs Psych WardIris CaberteNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineDocument2 pagesDrug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Non-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugDocument27 pagesNon-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and UsesDocument11 pagesDrug Study Effects and UsesVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet