Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Slides 1
Uploaded by
Dipesh PatelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Slides 1
Uploaded by
Dipesh PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
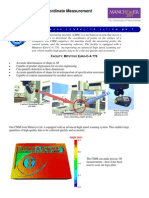
Slides 1-2 Introduction and Working A 'coordinate measuring machine' (CMM) is a device for measuring the physical geometrical
characteristics of an object. This machine may be manually controlled by an operator or it may be computer controlled. Measurements are defined by a probe attached to the third moving axis of this machine. Probes may be mechanical, optical, laser, or white light, among others. The typical CMM is composed of three axes, an X, Y and Z. These axes are orthogonal to each other in a typical three dimensional coordinate system. Each axis has a scale system that indicates the location of that axis. The machine will read the input from the probe, as directed by the operator or programmer. The machine then uses the X,Y,Z coordinates of each of these points to determine size and position. A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is also a device used in manufacturing and assembly processes to test a part or assembly against the design intent. By precisely recording the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the target, points are generated which can then be analyzed via regression algorithms for the construction of features. These points are collected by using a probe that is positioned manually by an operator or automatically via Direct Computer Control (DCC).
Slides 3-4 Applications of CMM
1.5.1 Inspection
Part-to-CAD analysis First article inspection Supplier quality inspection Conformity assessment of 3D models against original parts/ production tooling Conformity assessment of manufactured parts against originals Alignment Tooling certification Multi-shot measurement (up to 30 points/sec.) When use optical CMM 3D scanner, allows full free-form inspection and generates high density color maps.
1.5.2 Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering of geometrical entities (spheres, cylinders, planes)
When use optical CMM 3D scanner, allows faster and more accurate reverse engineering of mixed parts (geometrical and free-form).
1.5.3 Industries
Aerospace Automotive/Transport Equipment Production Consumer Products Education Metallurgy and Metal Processing Machine Tool Production Forming, Moulding, Manufacturing, Casting and Assembling [18]
You might also like
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument13 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineAjay G RNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument7 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineDivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)Document31 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)nurul ainiNo ratings yet
- CMM guide - Coordinate measuring machines explainedDocument6 pagesCMM guide - Coordinate measuring machines explainedMuhamad HafizNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesMetrology and Quality Assurance Lab: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAliNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument37 pagesCMMSachin AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 1) Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument12 pages1) Coordinate Measuring MachineBintang PaningitNo ratings yet
- Presentation On CMMDocument17 pagesPresentation On CMMSonu Sharma100% (1)
- Coordinate Measuring Machine-6840Document7 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machine-6840Deepak MisraNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument5 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)Document67 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)nurul aini0% (1)
- AccuracyDocument56 pagesAccuracyAnonymous KTlSqEBNo ratings yet
- Measuring Characteristics of Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument4 pagesMeasuring Characteristics of Coordinate Measuring MachineMuhammad JahanzaibNo ratings yet
- BY Parth Gajjar (007) Parth Panchal (003) Approved by C.P. Vithlani V.C. PatelDocument11 pagesBY Parth Gajjar (007) Parth Panchal (003) Approved by C.P. Vithlani V.C. PatelRing MasterNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring Machine: NavyatejDocument5 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machine: NavyatejNavya Tej MNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument15 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Measuring Machine: Metereology & Machining LabDocument4 pagesCo-Ordinate Measuring Machine: Metereology & Machining LabSumit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) : Prepared by Meiyalagan R KDocument10 pagesCo-Ordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) : Prepared by Meiyalagan R KVishnuNo ratings yet
- CMM Machine Measures Geometric PartsDocument34 pagesCMM Machine Measures Geometric PartsShanti Lal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Rohini 44437910254Document11 pagesRohini 44437910254mooventhanp13No ratings yet
- CMM Inspection ModuleDocument93 pagesCMM Inspection Modulejaskaran singhNo ratings yet
- CMM and CAIDocument6 pagesCMM and CAIdrkbala007No ratings yet
- Main Parts of CMMDocument9 pagesMain Parts of CMMRamprakashSundaram100% (1)
- CMM LectDocument15 pagesCMM LectAmin Ali AminNo ratings yet
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) GuideDocument18 pagesCMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) GuideDeepak ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Measuring Machines & It's Applications: Introduction ToDocument65 pagesCo-Ordinate Measuring Machines & It's Applications: Introduction Toshiva dNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Coordinate Measuring MachinesDocument6 pages10.2 Coordinate Measuring MachinesVenkateshYadavCivarlaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument13 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineAditya RajendraNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument26 pagesCMMSanjeev kumar Verma100% (1)
- ME8501 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - IIIDocument69 pagesME8501 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - IIIarunpdcNo ratings yet
- Re Lab Exp 6& 7Document15 pagesRe Lab Exp 6& 7pranja07No ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument2 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machineanu09306No ratings yet
- 18-MCE-49 Lab Session 04Document4 pages18-MCE-49 Lab Session 04Waqar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Machine VisionDocument4 pagesMachine Visionharim_meNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: 1.1 CantileverDocument6 pagesObjectives:: 1.1 CantileverramaNo ratings yet
- CMM MQCDocument36 pagesCMM MQCThanigaivel ANo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document13 pagesAssignment No.1Muhammad WaleedNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC: My Current Final Year ProjectDocument2 pagesCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC: My Current Final Year Projectmd_rehan_2No ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument20 pagesCoordinate Measuring Machinerajamanickam sNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 Advances in MetrologyDocument45 pagesUNIT-5 Advances in MetrologySURESH KUMAR APNo ratings yet
- 04 Data Acquisition Contact 2019 09 12Document53 pages04 Data Acquisition Contact 2019 09 12TimNo ratings yet
- Micro ProjectDocument19 pagesMicro Projectmamatarane0207No ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument34 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineSiddu KaragarNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Measuring MachineDocument20 pagesCoordinate Measuring MachineDevadattNo ratings yet
- Ch15-Inspection in FMSDocument25 pagesCh15-Inspection in FMSyogesh jadhavNo ratings yet
- CMMDocument4 pagesCMMSuvin PsNo ratings yet
- Micro ProjectDocument19 pagesMicro Projectmamatarane0207No ratings yet
- Measure Complex Shapes With Co-ordinate Measuring MachinesDocument4 pagesMeasure Complex Shapes With Co-ordinate Measuring MachinessathiaNo ratings yet
- CMM Basics and TypesDocument8 pagesCMM Basics and Typesகுமார் வே.வெங்கடேஷ்100% (1)
- CMM PresentationDocument22 pagesCMM PresentationVipin PachouriNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering: Submitted ToDocument24 pagesReverse Engineering: Submitted Tovarun.119100% (1)
- Module IV: Computer-Aided and Laser Metrology TechniquesDocument9 pagesModule IV: Computer-Aided and Laser Metrology TechniquesShiba SahuNo ratings yet
- 8th International Quality Conference May 2014Document6 pages8th International Quality Conference May 2014Dragana RajicNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet MetrodologyDocument2 pagesLab Sheet MetrodologyAmeer RifqyNo ratings yet
- Theoretical method to increase the speed of continuous mapping in a three-dimensional laser scanning system using servomotors controlFrom EverandTheoretical method to increase the speed of continuous mapping in a three-dimensional laser scanning system using servomotors controlNo ratings yet
- CMMS Unleashed: Harnessing the Power of Technology for Efficient Maintenance Management: Cryotos CMMS, #1From EverandCMMS Unleashed: Harnessing the Power of Technology for Efficient Maintenance Management: Cryotos CMMS, #1No ratings yet