Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 - First-Order Circuits Source-Free RC Circuit: DT DV C I DT Di L V
Uploaded by
atifk_67Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 - First-Order Circuits Source-Free RC Circuit: DT DV C I DT Di L V
Uploaded by
atifk_67Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 First-Order Circuits
In Chapters 1-5, when we apply KVL or KCL: v = Ri In Chapter 7,
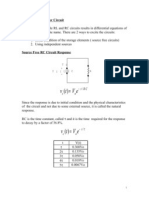
Source-Free RC Circuit
Given: R & C, vC(0) = Vo Find: v(t) and i(t)
di dv vL = L L ; iC = C C dt dt
Differential eqns.
First-Order Circuit: One energy storage element (C or L) 1st order diff eq Energy dissipation element/s (R) Excitation (source of energy) Energy initially stored in L or C source-free Vs or Is
Example 1. Given: vC(0) = 15 V Find: vC, vx and ix
Natural Response: behavior w/o external sources decay
exponential
Smaller time constant
faster decay
Example 2. Given: Switch closed for a long time, and opened at t=0. Find: vC, for t>0.
Source-Free RL Circuit
Given: R & L, iL(0) = Io Find: i(t)
Example 3. Given: i(0) = 10 A Find: i(t), and ix(t)
Example 4. Given: Switch open for a long time, and I is closed at t=0. Find: i(t), io(t) and vo(t) for t>0.
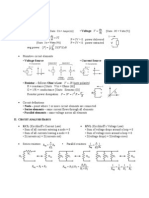
Singularity Functions
either discontinuous, or have discontinuous derivatives. useful in switching Unit Step Function:
Example:
Unit Impulse Function:
(t ) =
t<0 0, du (t ) = undefined, t = 0 dt 0, t >0
An applied or resulting shock A very short duration pulse.
Unit Ramp Function:
Step Response of an RC Circuit
-excitation is a step function Given: v(0) = Vo; Switch closed at t=0.
r (t ) = u (t ) dt
0, t 0 r (t ) = = t u (t ) t, t > 0
V , v(t ) = o t / V + (Vo V )e
t<0 t>0
Complete Response = Natural Response + Forced Response
Example 5. Given: Switch has been at position A for a long time, and moves to B at t=0. Find: v(t) for t>0.
Complete Response = Steady-state Response + Transient Response
3 Parameters: 1. Vo Initial voltage from I.C. no jump condition for vc 2. V - steady-state response at steady state, C becomes an open circuit 3. Time constant
Step Response of RL Circuits
Given: i(0) = Io; Switch closed at t=0.
Example 6. Given: Switch has been closed for a long time, and opens at t=0. Find: vL(t) for t>0.
Ex. 7. Find i(t) for t >0.
First-Order Circuits with Op Amps
Method 1: Set up and solve ODE. Method 2: Find RTH as seen by C or L replace with test V or I.
Example: Given: R1 = 20k, Rf = 80k, C=5F, and v(0)=3 V Find: vo(t)
Method 2: Find vo(0+):
Method 1: See Lab #4 Op Amp differentiator
Find RTH:
You might also like
- RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesRL RC CircuitDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhDocument40 pagesLecture 01 - Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits - MLinhTran Quoc PhongNo ratings yet
- Circuitry Ch07 First-Order CircuitsDocument50 pagesCircuitry Ch07 First-Order CircuitsGeorge VargheeseNo ratings yet
- Lec7 FirstOrder 01 PDFDocument60 pagesLec7 FirstOrder 01 PDFPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: First-Order CircuitsDocument22 pagesCircuit Theory: First-Order Circuitsmalek992No ratings yet
- First-Order Circuit ADocument42 pagesFirst-Order Circuit ARay Ann RamonNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document54 pagesCH 7toalomari0No ratings yet
- Ch.1 DC CircuitsDocument40 pagesCh.1 DC Circuitsaattish100% (1)
- Topic 5 1st OrderDocument3 pagesTopic 5 1st OrderUmakandan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- CH7Document34 pagesCH7Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Ch7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument34 pagesCh7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsFakrul HanifNo ratings yet
- ES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseDocument39 pagesES-1 Natural and Forced ResponseGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- Solving Differential Equation Using Operational AmplifierDocument15 pagesSolving Differential Equation Using Operational AmplifierPalash DubeyNo ratings yet
- Circuit Types: DC CircuitsDocument6 pagesCircuit Types: DC Circuitsprasad4funNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Upto 12th MayDocument39 pagesChapter 7 Upto 12th Maycb.en.u4ece22010No ratings yet
- ECS203 2014 CH 10 U4Document23 pagesECS203 2014 CH 10 U4luzmancia0204No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - DC Transient AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 5 - DC Transient AnalysisMohamed Awad100% (1)
- KBTU Lecture9 10 Handout First TransientDocument2 pagesKBTU Lecture9 10 Handout First TransientdextergtsNo ratings yet
- Rland RCDocument33 pagesRland RCSyed Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- Svcma Course Material ModifiedDocument46 pagesSvcma Course Material Modifiedsai manoharNo ratings yet
- Application of Laplace TransformsDocument4 pagesApplication of Laplace TransformssthamizhselviNo ratings yet
- Report Source FreeDocument43 pagesReport Source FreeCliford AlbiaNo ratings yet
- G RC/RL Step-by-Step Procedure: TH Eq Eq THDocument2 pagesG RC/RL Step-by-Step Procedure: TH Eq Eq THDileep GNo ratings yet
- Module-Iii Syllabus:: Transient Behavior and Initial Conditions: Behavior of Circuit Elements Under SwitchingDocument32 pagesModule-Iii Syllabus:: Transient Behavior and Initial Conditions: Behavior of Circuit Elements Under Switchinglohith sNo ratings yet
- The Important (Dual) Relationships For Capacitors and Inductors AreDocument28 pagesThe Important (Dual) Relationships For Capacitors and Inductors AreRaja FahadNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of RC and RL Circuits: A First ExampleDocument6 pagesTransient Response of RC and RL Circuits: A First ExampleRasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Source Free CircuitDocument4 pagesSource Free CircuitAhnaf HasanNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesCircuit AnalysisoffnruninNo ratings yet
- Transient in RC and RL CircuitsDocument10 pagesTransient in RC and RL CircuitsHenok BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument21 pagesTime Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsMOHSINALI MOMINNo ratings yet
- First-Order Circuits: An Independent Source. Thus, The Elements of ADocument9 pagesFirst-Order Circuits: An Independent Source. Thus, The Elements of ABulatovic NemanjaNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1 The InductorDocument52 pages4.2.1 The InductorVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- EEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Document88 pagesEEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Mert YılmazNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Ii (Eee202)Document19 pagesFundamentals of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Ii (Eee202)ALABI ABIODUNNo ratings yet
- NT Tutorial 1Document10 pagesNT Tutorial 1Pushkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- DC Transient AnalysisDocument206 pagesDC Transient Analysisasanithanair35No ratings yet
- Source-Free RL and RC Circuit and Source-Free Series and Parallel RLC CircuitWORKSHEETDocument11 pagesSource-Free RL and RC Circuit and Source-Free Series and Parallel RLC CircuitWORKSHEETHarold RondillaNo ratings yet
- Unit4 KCVDocument52 pagesUnit4 KCVsanoopmkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3Gemechis AsfawNo ratings yet
- Melbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017Document34 pagesMelbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017RogerNo ratings yet
- 2018-I-Ing Quimica Differential Equation (List-05)Document3 pages2018-I-Ing Quimica Differential Equation (List-05)Bryan MuñozNo ratings yet
- First Order Differentiate PDFDocument21 pagesFirst Order Differentiate PDFDharamNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument56 pagesElectric Circuits Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsAlexander_Tir_91570% (1)
- Chapter 6 First Order Transient PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 6 First Order Transient PDFRindra RahmatullohNo ratings yet
- BEE1133: Circuit Analysis I: Chapter 4: First Order CircuitsDocument51 pagesBEE1133: Circuit Analysis I: Chapter 4: First Order CircuitsNatasha EmlynNo ratings yet
- Materi 5 RL2Document93 pagesMateri 5 RL2Christian KevinNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3: Free Response of Simple Systems: EG1110 Signals and SystemsDocument4 pagesExercise 3: Free Response of Simple Systems: EG1110 Signals and Systemssrinvas_107796724No ratings yet
- Techtutor Academy: Electrical Circuits Sheet-5 (First Order Circuits)Document10 pagesTechtutor Academy: Electrical Circuits Sheet-5 (First Order Circuits)Masum BillahNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Transient Circut Analysis Part 1Document16 pagesChapter-4 Transient Circut Analysis Part 1temesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Theory Tutorial #4 (Time Domain Analysis, Classical Approach: part-II) Bex/Bct/Bel Ii/IDocument2 pagesElectric Circuit Theory Tutorial #4 (Time Domain Analysis, Classical Approach: part-II) Bex/Bct/Bel Ii/IJcb NitinNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet