Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IMCI
Uploaded by
xtinemarie_d4977Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IMCI
Uploaded by
xtinemarie_d4977Copyright:
Available Formats
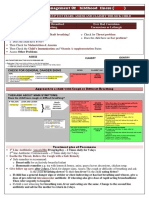
Table 1: IMCI classification table for COUGH OR DIFFICULT
BREATHING
SIGNS CLASSIFY AS Severe pneumonia IDENTIFY TREATMENT (Urgent pre-referral treatments are in bold print.) General danger signs: The child is not able to drink or breastfeed The child vomits everything The child had convulsions The child is lethargic or unconscious. Criteria for fast breathing 2 months to 12 months old: 50 breaths or more per minute 12 months to 5 years old: 40 breaths or more per minute Give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic Refer URGENTLY to hospital.
Any general danger sign or Chest wall indrawing or Stridor in calm child Fast breathing
Non-severe pneumonia
No signs of pneumonia
No pneumonia: cough or cold
Give an appropriate oral antibiotic for 5 days Soothe the throat and relieve the cough with a safe remedy Advise mother when to return immediately Follow-up in 2 days If coughing more than 30 days, refer for assessment Soothe the throat and relieve the cough with a safe remedy Advise mother when to return immediately Follow-up in 5 days if not improving.
SIGNS
Table 2: IMCI classification table for EAR PROBLEM CLASSIFY AS IDENTIFY TREATMENT (Urgent pre-referral treatments are in bold print.) Mastoiditis Give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic. Give first dose of paracetamol for pain. Refer URGENTLY to hospital. Give an oral antibiotic for 5 days Give paracetamol for pain Dry the ear by wicking Follow-up in 5 days Dry the ear by wicking Follow-up in 5 days
Tender swelling behind
Pus is seen draining from the ear and discharge is reported for less than 14 days, or Ear pain Pus is seen draining from the ear and discharge is reported for 14 days or more No ear pain and No pus seen draining from the ear
Acute ear infection
Chronic ear infection No ear infection
No additional treatment
Table 3: IMCI classification for POSSIBLE BACTERIAL INFECTION SIGNS CLASSIFY IDENTIFY TREATMENT (Urgent pre-referral treatments are in bold print.) AS Convulsions, or Fast breathing, or Severe chest indrawing or Nasal flaring, or Grunting, or Bulging fontanelle, or Pus draining from ear, or Umbilical redness extending to the skin, or Fever (37.5 C* or above or feels hot) or low body temperature (less than 35.5C* or feels cold), or Many or severe skin pustules, or Lethargic or unconscious or Less than normal movement Red umbilicus or draining pus, or Skin pustules Possible serious bacterial infection Give first dose of intramuscular antibiotics Treat to prevent low blood sugar Advise mother how to keep the infant warm on the way to hospital Refer URGENTLY to hospital
Local bacterial infection
Give an appropriate oral antibiotic for 5 days Teach the mother to treat local infections at home Advise mother to give home care for the young infant Follow-up in 2 days
* These thresholds are based on axillary temperature. The thresholds for rectal temperature readings are approximately 0.5 C higher.
You might also like
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessesDocument12 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessesRaul Suzara100% (1)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Flip ChartDocument78 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness Flip ChartkjtomananNo ratings yet
- IMCI Job-Aid Users' Manual: Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci) : Age 0 To 2 MonthsDocument1 pageIMCI Job-Aid Users' Manual: Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci) : Age 0 To 2 MonthsCOMDIS-HSDNo ratings yet
- Case Management of Ari at PHC LevelDocument29 pagesCase Management of Ari at PHC Levelapi-3823785No ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Chilhood IllnessesDocument12 pagesIntegrated Management of Chilhood Illnessescorpuzdarryl3No ratings yet
- IMCIDocument42 pagesIMCIMichael Anthony ErmitaNo ratings yet
- IMCI Guideline-2023 HeshamElsayedDocument57 pagesIMCI Guideline-2023 HeshamElsayedMalak Rageh100% (2)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Document102 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Jasmin Jacob100% (2)
- Acute Respiratory InfectionsDocument26 pagesAcute Respiratory InfectionsSuneel SagareNo ratings yet
- Cough, Pediatric: What Are The Causes?Document2 pagesCough, Pediatric: What Are The Causes?astarimediantoNo ratings yet
- IMCI Technical UpdatesDocument3 pagesIMCI Technical Updatesmikaela_pascuaNo ratings yet
- IMCI NewDocument81 pagesIMCI NewBianca de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- IMCIDocument112 pagesIMCIJohann Dexter Malimban GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management On Childhood Illnesses 0101Document132 pagesIntegrated Management On Childhood Illnesses 0101James Felix Gallano Gales100% (1)
- IMCIDocument35 pagesIMCIharutoshippuden0No ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument43 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessMark LugtuNo ratings yet
- Roll. 66 J 133 Batch PSM AssignmentDocument3 pagesRoll. 66 J 133 Batch PSM AssignmentMishaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument148 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessMichael CrisologoNo ratings yet
- Ari Workshop.2Document40 pagesAri Workshop.2drusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- IMCI - ContentDocument13 pagesIMCI - ContentMarianne Daphne GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Common Cold HDocument2 pagesCommon Cold Hnaheed jalilNo ratings yet
- Control of Acute Respiratory Infections 2Document6 pagesControl of Acute Respiratory Infections 2إحسان ماجد محمدNo ratings yet
- Approach To Fever and AntibioticsDocument13 pagesApproach To Fever and Antibioticsasraf amirullahNo ratings yet
- Imci Technical Update S:: CoughingDocument6 pagesImci Technical Update S:: CoughingKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Child Health, Nutrition & SafetyDocument30 pagesChild Health, Nutrition & Safetyleela kumaresan100% (1)
- XXX Pneumonia Information LeafletDocument2 pagesXXX Pneumonia Information LeafletPuti Cendik HaryadiNo ratings yet
- IMCI Nov 2009Document141 pagesIMCI Nov 2009togononkaye100% (1)
- IMNCI - 6th SemDocument32 pagesIMNCI - 6th SemAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument6 pagesFebrile SeizuresKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Ear Infections Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsDocument4 pagesEar Infections Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsbehrangNo ratings yet
- IMCI NewDocument151 pagesIMCI NewDiana Lane CunananNo ratings yet
- 9 - IMCI - 2mos To 5 YearsDocument62 pages9 - IMCI - 2mos To 5 YearsCARMENCITA PACISNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) Programs in Children U5YDocument16 pagesAcute Respiratory Infection (ARI) Programs in Children U5YsamiNo ratings yet
- IMCI UpdatedDocument5 pagesIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PDFDocument3 pagesPneumonia PDFSari RamadhanNo ratings yet
- IMCI StrategyDocument7 pagesIMCI StrategyAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument21 pagesTonsillitisKavy AkhsanulNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument161 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessDobby AsahiNo ratings yet
- IMCI Revised For CHN 1 NEW 1st Sem 2022Document82 pagesIMCI Revised For CHN 1 NEW 1st Sem 2022Aech Euie100% (1)
- IMNCI Integrated Management of Newborn and Childhood IllnessDocument11 pagesIMNCI Integrated Management of Newborn and Childhood IllnessPriyaNo ratings yet
- Common ProblemsDocument8 pagesCommon ProblemsSunshine Sucabit BongsiwNo ratings yet
- PSM 5 ImnciDocument52 pagesPSM 5 ImnciAnagha M NairNo ratings yet
- Measles: SynonymsDocument5 pagesMeasles: SynonymsAelora JullienneNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument195 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illnesskarendelarosa06277100% (1)
- Common Child InfectionsDocument5 pagesCommon Child InfectionsAnonymous L3W8LlpMPWNo ratings yet
- Common DiseasesDocument15 pagesCommon DiseasesKoyal HowtarNo ratings yet
- Strep A - NHSDocument1 pageStrep A - NHSAndreea Mădălina TanasăNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Caring For A Sick ChildDocument20 pagesLesson 4 Caring For A Sick ChildJoanne Kyle BumagatNo ratings yet
- Infections in Ear Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsDocument4 pagesInfections in Ear Are Very Common in Children. Children Are More Prone To Ear InfectionsbehrangNo ratings yet
- ARI Control ProgrammeDocument13 pagesARI Control ProgrammeArun George50% (8)
- Classification: A. No Pneumonia: Cough or Cold B. PneumoniaDocument2 pagesClassification: A. No Pneumonia: Cough or Cold B. PneumoniaSheryl Nishmae Bernardo SantosNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument21 pagesFebrile SeizuresIrfan FauziNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Alina CommunityDocument29 pagesPresentation of Alina CommunitySmita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Common Childhood Illness Week 12Document76 pagesCommon Childhood Illness Week 12Hydra Olivar - PantilganNo ratings yet
- IMCIDocument116 pagesIMCIPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHIN0% (1)
- This Document and The Information Thereon Is The Property of PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing)Document14 pagesThis Document and The Information Thereon Is The Property of PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing)Mark Raymunstine TamposNo ratings yet
- Caridad C. Lintao, RN., Man School of Nursing Emilio Aguinaldo College - CaviteDocument32 pagesCaridad C. Lintao, RN., Man School of Nursing Emilio Aguinaldo College - CaviteImmanuel Capurcos Duabe JavilagNo ratings yet
- Week 9 CHNDocument4 pagesWeek 9 CHNZxiayieee JeonNo ratings yet