Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp 2
Uploaded by
Rohan MehtaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp 2
Uploaded by
Rohan MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
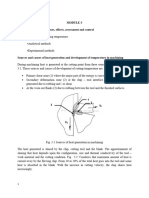
EXPERIMENT: 1
To measure the tool-chip interface temperature in drilling operation, under various cutting speeds and to plot temperature v/s speed curve for given tool-work piece material. (1) Drilling machine (small) (2) Drill chuck sleeve. (3) HSS drill. (12.5) (4) Calorimeter setup (5) Work piece. (6) Tachometer. (7) Measuring flask (8) 2.5 cm3 M.S. work piece (9) Vernier calliper
The temperature generated in the region of tool point during cutting control the rate tool wear, the practical cutting speed and the metal removal rate. Almost all the work done in deforming the material to form the chip and to move the freshly cut work surface over the tool is converted into heat. The total heat generated can be given by equation: Q= Where, Q = amount of heat generated in cutting F*V = Work done in cutting E = Mechanical equipment of heat
Heat balance in metal cutting can be expressed by the quation: Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 Where, Q = total heat generated Q1 = amount of heat carried away in the chip Q2 = amount of heat carried away in the chip Q3 = amount of heat passing into the work piece Q4 = amount of heat radiated to the surrounding air
OBESRVATION TABLE L =length of stroke N = Ram speed V = cutting velocity
SR.NO 1 2 3 4
RACK ANGLE
AVERAGE LENGTH OF CHIP (cm)
LENGTH OF WORK PIECE (cm)
SHEAR PLANE ANGLE
CALCULATIONS:
Here = rack angle = shear plane angle Therefore = ________ GRAPH: Rack angle VS shear plane angle ............................. [ANS]
CONCLUSION:
QUESTIONS: Q 1: What is the effect of variations of shear plane angle on force, power consumption, Chip thickness ratio? Q 2: What is the importance of measurement of shear plane angle? Q 3: Explain the method for measurement of shear plane angle?
You might also like
- Thermal Modeling of Metal Cutting ProcessDocument38 pagesThermal Modeling of Metal Cutting ProcessEl Mehdi MakaveliNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Technique For The Measurement of Temperature Fields For The Orthogonal Cutting in High Speed MachiningDocument9 pagesAn Experimental Technique For The Measurement of Temperature Fields For The Orthogonal Cutting in High Speed MachiningTEJ SAKPALNo ratings yet
- Thermal Loading in Cutting Tools: 2.1 Heat Generation in The Contact SurfacesDocument15 pagesThermal Loading in Cutting Tools: 2.1 Heat Generation in The Contact SurfacesJaimeFeijooNo ratings yet
- 11 Cutting Temperature - Causes, Effects, AssessmentDocument14 pages11 Cutting Temperature - Causes, Effects, AssessmentPRASAD326100% (3)
- Steady State Temperature Distribution of Cast Resin Dry Type Transformer Based On New Thermal Model Using Finite Element MethodDocument5 pagesSteady State Temperature Distribution of Cast Resin Dry Type Transformer Based On New Thermal Model Using Finite Element MethodAnonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Micro Steam Turbine Using Catia and AnsysDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Micro Steam Turbine Using Catia and AnsysInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of Moving Heat Source Shape For Arc Welding Process of High Deposition RateDocument4 pagesCritical Analysis of Moving Heat Source Shape For Arc Welding Process of High Deposition RatechethanNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2016-17 4628 RM001 Mee303 ElaDocument57 pagesFallsem2016-17 4628 RM001 Mee303 ElamansurNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Technique For The Measurement of Temperature Fields For The Orthogonal Cutting in High Speed MachiningDocument8 pagesAn Experimental Technique For The Measurement of Temperature Fields For The Orthogonal Cutting in High Speed Machiningkuba DefaruNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Temperature Loss of Hot Metal During Hot Rolling Process at Steel PlantDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Temperature Loss of Hot Metal During Hot Rolling Process at Steel PlantIJMERNo ratings yet
- Cutting Temperature - Causes - Effects - Estimation (Assessment) & ControlDocument14 pagesCutting Temperature - Causes - Effects - Estimation (Assessment) & ControlvelladuraiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Science: "Heat Generation & Cutting Tool Temperature"Document25 pagesManufacturing Science: "Heat Generation & Cutting Tool Temperature"mnizam48100% (2)
- A Digital Rykalin Function For Welding: SandiaDocument22 pagesA Digital Rykalin Function For Welding: Sandiabuecherwurm123No ratings yet
- 08Document10 pages08Mohammed EndrisNo ratings yet
- White LDocument29 pagesWhite LAnupam AlokNo ratings yet
- Source of HeatDocument9 pagesSource of HeatSreekumar RajendrababuNo ratings yet
- Air Cooling Effect of Fins in MotorcycleDocument7 pagesAir Cooling Effect of Fins in Motorcyclestorage spaceNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling of Circular Saws: K KT KTTDocument8 pagesHeating and Cooling of Circular Saws: K KT KTTte2makanza5279No ratings yet
- Experiment No: Date Heat Transfer From Pin FinDocument4 pagesExperiment No: Date Heat Transfer From Pin FinBharat ThakorNo ratings yet
- The Temperature Rise:: Lecture Nineteen - 2Document6 pagesThe Temperature Rise:: Lecture Nineteen - 2balsamNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document4 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- Design and Experimental Analysis of PipeDocument7 pagesDesign and Experimental Analysis of PipeMustafa VatanseverNo ratings yet
- PJST13 1 48Document15 pagesPJST13 1 48Jeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Cylindrical Pin With Trapezoidal Fin Heat Sink Using ANSYS Fluent 14.0Document8 pagesCFD Analysis of Cylindrical Pin With Trapezoidal Fin Heat Sink Using ANSYS Fluent 14.0Nithin GowdaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Heat Transfer From Finned SurfacesDocument5 pagesExperiment 2: Heat Transfer From Finned SurfacesAlexNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument8 pagesPresentationShreyash ChhatralaNo ratings yet
- Heat Has Critical Influences On Machining. To Some Extent, It Can Increase Tool Wear andDocument8 pagesHeat Has Critical Influences On Machining. To Some Extent, It Can Increase Tool Wear andPassmore DubeNo ratings yet
- 4.1.3 Step-by-Step CalculationDocument11 pages4.1.3 Step-by-Step Calculationmohamed nizal100% (1)
- Effect of Inclination of Impinging Jets On Flow and Heat Transfer CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEffect of Inclination of Impinging Jets On Flow and Heat Transfer CharacteristicsInternational Journal of Science and Engineering InvestigationsNo ratings yet
- J Ijthermalsci 2016 01 013Document17 pagesJ Ijthermalsci 2016 01 013jayNo ratings yet
- Mech311 Midterm 2009, 2011 and 2012Document9 pagesMech311 Midterm 2009, 2011 and 2012Parvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- ME 320 Lab 4Document17 pagesME 320 Lab 4Ajay KrishNo ratings yet
- Forming, Cross Wedge Rolling and Stepped ShaftDocument4 pagesForming, Cross Wedge Rolling and Stepped ShaftMrLanternNo ratings yet
- HT302 C3bDocument17 pagesHT302 C3bAnuj BhawsarNo ratings yet
- ENS6134-Equation Sheet For Final ExaminationDocument4 pagesENS6134-Equation Sheet For Final ExaminationDhaval PatelNo ratings yet
- Issn: 2349-3860Document18 pagesIssn: 2349-3860Pat TejNo ratings yet
- Nilesh PPT TrainingDocument16 pagesNilesh PPT TrainingsureshNo ratings yet
- Final Doc Report Simulation and ModellingDocument31 pagesFinal Doc Report Simulation and ModellingObright OlekuNo ratings yet
- Casting Forming & Casting, Forming &: Welding WeldingDocument25 pagesCasting Forming & Casting, Forming &: Welding WeldingWen LiNo ratings yet
- Cold Forming and Heat Treatment Requirement of Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubes.Document5 pagesCold Forming and Heat Treatment Requirement of Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubes.R kumarNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine LabDocument19 pagesHeat Engine LabAbul Lais NalbandNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Cutting Temperature During MachiningDocument15 pagesMeasurement of Cutting Temperature During MachiningivanNo ratings yet
- Deform Friction Stir WeldingDocument6 pagesDeform Friction Stir Weldingramkumar121100% (1)
- Pimm HSM 2012 BoyerDocument6 pagesPimm HSM 2012 BoyerTeguh Dwi WidodoNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection Heat Transfer in A Vertical Concentric AnnulusDocument11 pagesNatural Convection Heat Transfer in A Vertical Concentric Annulusmuhammad asmaeelNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Program Effect Fin Spacing Heat TransferDocument3 pagesMATLAB Program Effect Fin Spacing Heat TransferAkshat RastogiNo ratings yet
- Ijesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologyDocument12 pagesIjesrt: International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research TechnologyasfsfsafsafasNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument12 pagesChapter Threeحسنين محمد عبدالرضا فليحNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling of Friction Stir Welding in Aluminum AlloysDocument10 pagesFinite Element Modeling of Friction Stir Welding in Aluminum AlloysIlman FauzaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Jet Air Cooling Relating With Reynolds Number and Nusselt NumberDocument10 pagesMultiple Jet Air Cooling Relating With Reynolds Number and Nusselt NumberTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Transient Temperature Distribution in A Steel Rod Subjected To Friction WeldingDocument11 pagesTransient Temperature Distribution in A Steel Rod Subjected To Friction WeldingMuhammad Fatka FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat Transfer Lab Analysis of Cylinder, Sphere MaterialsDocument15 pagesTransient Heat Transfer Lab Analysis of Cylinder, Sphere MaterialsShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- 1.) Matlab Program To Study The Effect of Variation of Length of Fin On Overall Effectiveness & Total Heat TransferDocument3 pages1.) Matlab Program To Study The Effect of Variation of Length of Fin On Overall Effectiveness & Total Heat TransferAkshat RastogiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab ManualDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer Lab ManualRachit_Goyal25_10No ratings yet
- S 7 - Heat Transfer LabDocument30 pagesS 7 - Heat Transfer LabKiran Madhavan100% (2)
- Analysis of Transient Thermal Stresses in A Delayed Coke Drum - PDFXDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Transient Thermal Stresses in A Delayed Coke Drum - PDFXShivangi ThakkerNo ratings yet
- NEWDocument15 pagesNEWRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Operations Research: Edited by Xiang-Sun Zhang De-Gang Liu Ling-Yun WuDocument10 pagesLecture Notes in Operations Research: Edited by Xiang-Sun Zhang De-Gang Liu Ling-Yun WuRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: ConvolutionDocument2 pagesExperiment 3: ConvolutionRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Reducing DC Energy Consumption With Wet Side EconomizersDocument12 pagesReducing DC Energy Consumption With Wet Side EconomizersRohan MehtaNo ratings yet