Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 10 Topic Guide
CH 10 Topic Guide
Uploaded by
Jenn ShimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 10 Topic Guide
CH 10 Topic Guide
Uploaded by
Jenn ShimCopyright:
Available Formats
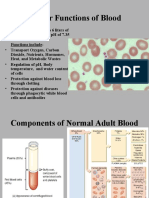
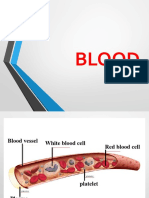
Ch 10: Blood Composition of Blood, Functions of Blood plasma and its proteins: o Makes up 55% of blood volume o Has
s proteins + globulins formed elements o Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells) Structure: Disc shaped and slightly thicker on perimeter Hemoglobin: Carries O2 + CO2. Has iron Hematocrit: Proportion of total blood volume that are RBC (36%-50%) o Leukocytes Diapedesis: WBC moving in and out of blood vessels Chemotaxis: Can respond to chemicals released by damaged tissues Neutrophils: Most common; phagocytic Eosinophils: Kills parasites, overact during allergies Basophils: Release histamine for inflammation Lymphocytes: B-Cells, T-Cells, Nk Cells B: produce antibodies to attack antigens T: Coordinates immune response; destroys Nk: Detects and destroy abnormal tissue cells Monocytes: fights chronic infections o Platelets: stick to collagen fibers; fibrinogen fibrin that traps RBC Blood Formation (Hematopoeisis) Occurs in Red bone marrow Hemostasis (blood clotting) Platelets stick to collagen fibers to form platelet plug Blood vessel narrows Fibrinogen forms fibrin mesh that traps RBCs Blood Groups/ Blood typing Blood types: o O- universal donor o AB-universal recipients Rh factors: If mom is Rh- but child is Rh+, it can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn Disorders/Diseases anemia and sickle cell anemia: hemoglobin shape is different, causes low # of RBC Leukemia: cancerous leukocytes Hemophilia: sex-linked; uncontrollable bleeding
You might also like
- BIOEN 345: Blood Vessel Biology and PathologiesDocument35 pagesBIOEN 345: Blood Vessel Biology and PathologiesasdfghjklNo ratings yet
- L32: Blood Cells: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesL32: Blood Cells: Learning Objectives李超然No ratings yet
- Seeley's Ess9e.chapt11 - Lecture.aDocument43 pagesSeeley's Ess9e.chapt11 - Lecture.aJhara100% (2)
- Blood Summary NotesDocument4 pagesBlood Summary NotesLaura FernandezNo ratings yet
- Major Functions of Blood: - The Body Contains 4 To 6 Liters ofDocument26 pagesMajor Functions of Blood: - The Body Contains 4 To 6 Liters ofDrSikander AdilNo ratings yet
- Composition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesComposition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning Objectivesmarinak_6No ratings yet
- BloodDocument49 pagesBloodDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition and Functions: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument41 pagesBlood Composition and Functions: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPADocument49 pagesHematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPASantoz ArieNo ratings yet
- Ch18 BloodDocument31 pagesCh18 BloodNoah DominoNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells and The Hematopoetic SystemDocument53 pagesBlood Cells and The Hematopoetic SystemMeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: - The Science Dealing With The FormationDocument104 pagesHematology: - The Science Dealing With The FormationYamSomandarNo ratings yet
- Hematologi 1Document57 pagesHematologi 1Till JannahNo ratings yet
- Heamatology Chapter 1Document38 pagesHeamatology Chapter 1Taima'a AlamaratNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPADocument49 pagesHematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPAImamAbdyNo ratings yet
- L15 - Blood - CMDocument32 pagesL15 - Blood - CMAleandra LettNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument4 pagesBloodFreakazoid is coolNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document35 pagesBlood Part 1Keziah TampusNo ratings yet
- CVS BloodDocument39 pagesCVS BloodMohan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells and CoagulationDocument26 pagesBlood Cells and CoagulationHoàngBảoLongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - BloodDocument5 pagesChapter 19 - Bloodtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Jigjiga University: For Medicine StudentsDocument80 pagesJigjiga University: For Medicine StudentsKamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument17 pagesBlood ComponentsJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: BloodDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System: BloodKoh Yen SinNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument27 pagesBloodJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Blood DiseasesDocument10 pagesBlood DiseasesDaniel HikaNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument24 pagesBLOODWenzy Razzie cruzNo ratings yet
- Blood: Group 1Document25 pagesBlood: Group 1Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Blood ReviewDocument13 pagesBlood ReviewDeleted AccountNo ratings yet
- Composition and Function of Blood: DR - Mohammed AlotaibiDocument22 pagesComposition and Function of Blood: DR - Mohammed AlotaibiUmar ManshadNo ratings yet
- The Blood and Its ConstituentsDocument71 pagesThe Blood and Its ConstituentsElidadi KatoNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro RBCsDocument59 pages1 Intro RBCsDanz ShNo ratings yet
- - تفسیر آزمایشات روتینDocument116 pages- تفسیر آزمایشات روتینrajabisamira8No ratings yet
- HSCI 100 HSCI 100: Human Biology Human Biology Human Biology Human BiologyDocument23 pagesHSCI 100 HSCI 100: Human Biology Human Biology Human Biology Human BiologyRosa ChoNo ratings yet
- Blood HBDocument31 pagesBlood HBBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Blood RBC WBCDocument51 pagesLecture 2-Blood RBC WBCsamayaNo ratings yet
- ANAT - Unit 3 - Blood Composition NotesDocument28 pagesANAT - Unit 3 - Blood Composition NotesJaren Balbal0% (1)
- 2014 Curs Hematologie - Baza-1Document1,336 pages2014 Curs Hematologie - Baza-1Andreea RheaNo ratings yet
- Human BloodDocument40 pagesHuman Bloodjetes67387No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Blood Coagulation and Coagulation DisordersDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Blood Coagulation and Coagulation DisordersdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument33 pagesBasic Hematologyrifa0% (1)
- Med Surg Midterms OverviewDocument69 pagesMed Surg Midterms OverviewMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- 3 - 1050FA2022 - Blood and Heart - NOTES 1perpgDocument48 pages3 - 1050FA2022 - Blood and Heart - NOTES 1perpgtristanmiura9No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Blood and 18 Review AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 17 Blood and 18 Review Answersmamun0zNo ratings yet
- 4 Blood PhysiologyDocument79 pages4 Blood Physiologysefiw.amareNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsDocument8 pagesHaemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document29 pagesBlood Part 1raneem fakhouriNo ratings yet
- Cardio WhatsoeverDocument12 pagesCardio WhatsoeverFernando DisuNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument103 pagesBloodrizwanbas50% (2)
- While Task Lecture On O2 HemaDocument140 pagesWhile Task Lecture On O2 HemaRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- 1 BloodDocument77 pages1 BloodVisaNathan100% (1)
- Haematologic and Lymphoreticular DiseasesDocument130 pagesHaematologic and Lymphoreticular DiseasesAgochi CollinsNo ratings yet
- The Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationDocument14 pagesThe Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IJulliene DadoleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - HematologyDocument37 pagesLecture 17 - HematologyberhanuNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi Darah RutinDocument22 pagesInterpretasi Darah Rutinboy jendri huluNo ratings yet
- Formed Elements of BloodDocument48 pagesFormed Elements of BloodJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Blood: Cardiovascular SystemDocument75 pagesBlood: Cardiovascular SystemTina MinottNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportNo ratings yet