Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nozinan
Nozinan
Uploaded by
Ella MalupaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nozinan
Nozinan
Uploaded by
Ella MalupaCopyright:
Available Formats
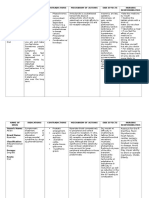
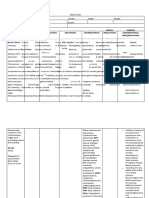
Drug
Mechanism of action
Form given orally as the maleate or by injection as the hydrochloride.
Indications and Contraindication Indications: Psychotic disturbances: Acute and chronic schizophrenias, senile psychoses, manic-depressive syndromes. can also be used to help manage confusion, dementia, behaviour problems and personality disorders. Contraindications: If the patient has any hypersensitivity to the drug if the patient is pregnant.
Adverse effects may cause severe orthostatic hypotension, sleepiness, weakness, dry mouth, low blood pressure (dizziness, feeling faint), rapid or irregular heartbeats, tremors, shaking, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), heat stroke, constipation.
Nursing considerations Increased risk of extrapyramidal effects with metoclopramide, acetylcholinesteras e inhibitors. If you receive a large initial dose, you will have to stay in bed. Avoid alcohol whilst taking levomepromazine. should be used with caution in the elderly as it may cause dizziness, fainting and/or lightheadedness. Try chewing sugar-free gum, sucking sugar-free sweets or pieces of ice.
it exerts its effects by LEVOMEPROMAZI blocking a variety of NE (nozenan) receptors, including adrenergic receptors, Anti-Psychotic drug dopamine receptors, class: phenothiazines histamine receptors, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, and serotonin receptors.
You might also like
- OB Medication SheetDocument9 pagesOB Medication SheetVanessa Garza100% (9)
- Morphine SulfateDocument2 pagesMorphine SulfateArianne Nicole PinuelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Zyprexa: Generic Name: OlanzapineDocument3 pagesZyprexa: Generic Name: Olanzapinenasir khanNo ratings yet
- Xanax Drug CardDocument3 pagesXanax Drug Cardnasir khanNo ratings yet
- What Is AmphetamineDocument15 pagesWhat Is AmphetamineIwant HotbabesNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine and Dextroamphetamine Uses, Side Effects & WarningsDocument7 pagesAmphetamine and Dextroamphetamine Uses, Side Effects & WarningspatgarettNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticDocument4 pagesAntiepilepticWan TokNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Indications Dosage Side / Adverse Effects Contraindication and Precaution Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of The Drug Indications Dosage Side / Adverse Effects Contraindication and Precaution Nursing ResponsibilitiesDrei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument3 pagesAnalgesicAnnaMaeVelosoNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Indication & DosageDocument18 pagesHaloperidol Indication & DosageRon Java FantillanNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineDocument2 pagesDrug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Dextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineDocument23 pagesDextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineSharry Fe OasayNo ratings yet
- Dextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineDocument23 pagesDextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineSharry Fe OasayNo ratings yet
- METFORMIN (Metformin Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Document1 pageMETFORMIN (Metformin Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Mary Chris Bacnis CabuangNo ratings yet
- Fluvoxamine MaleateDocument3 pagesFluvoxamine MaleateHilman Fitriaji Suganda PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPao HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument17 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsMJ Torralba100% (1)
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Tramadol HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDrug Study Tramadol HydrochlorideSEAN PATRICK SILADANNo ratings yet
- METFORMIN (Metformin Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Document1 pageMETFORMIN (Metformin Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Rhandel John ResiduoNo ratings yet
- DisulfiramDocument3 pagesDisulfiramapi-3797941100% (1)
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NamePia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine Uses, Side Effects & WarningsDocument6 pagesAtomoxetine Uses, Side Effects & WarningspatgarettNo ratings yet
- Lyks - Part 7 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesLyks - Part 7 Drug StudyLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- CarisoprodolDocument2 pagesCarisoprodolapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drugs For EmergencyDocument25 pagesDrugs For EmergencyJunathan L. DelgadoNo ratings yet
- ImipramineDocument1 pageImipramineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study - Diazepammarengbib100% (1)
- CITANEW 5mg TABLETDocument2 pagesCITANEW 5mg TABLETHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- LorazepamDocument4 pagesLorazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Special Nursing Medications Indications Contradictions Side Effects Adverse Effects Precautions Considerations/ ImplementationsDocument35 pagesSpecial Nursing Medications Indications Contradictions Side Effects Adverse Effects Precautions Considerations/ ImplementationsJay Angelo CañadaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology & Therapeutics (PCG-406) : Lecture # 03 Discussion of Individual Antihistamines CetrizineDocument11 pagesPharmacology & Therapeutics (PCG-406) : Lecture # 03 Discussion of Individual Antihistamines Cetrizineقاسم علی شاہNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyHennah Reblando100% (3)
- Indications: SyrupDocument3 pagesIndications: SyrupAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlibenclamideDocument1 pageMetformin Glibenclamideorly villalonNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesAtomoxetine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Alprazolam Side Effects: Allergic Reaction To Alprazolam: Hives DifficultDocument13 pagesAlprazolam Side Effects: Allergic Reaction To Alprazolam: Hives Difficult'Prasada WedatamaNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument3 pagesAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- Pseudo EphedrineDocument3 pagesPseudo Ephedrineapi-37979410% (1)
- Dextroamphetamine SulfateDocument3 pagesDextroamphetamine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument7 pagesRich Text Editor FileDeassi Puji LestariNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Document5 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- METHYLPHENIDATE (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Document1 pageMETHYLPHENIDATE (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Catherine FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Opioid Use Disorders:: Therapeutic Manuals for Healing and RecuperationFrom EverandOpioid Use Disorders:: Therapeutic Manuals for Healing and RecuperationNo ratings yet