Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration Respiratory System
Uploaded by
sawsan NajajrehOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration Respiratory System
Uploaded by
sawsan NajajrehCopyright:
Available Formats
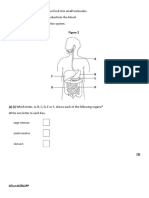
Respiration &respiratory system
Lung ventilation: The flow of air in and out of the alveoli is called ventilation and has two stages: inspiration (or inhalation) and expiration (or exhalation )
Expiration (Exhaling) with resistance: The abdominal muscles contract, pushing the diaphragm upwards The internal intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs downward This gives a larger and faster expiration More CO2 is expulsed
Inspiration (Inhaling) with resistance: The diaphragm contracts and flattens downwards The external intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs up and out The volume of the thorax increases More air is delivered deeper into the lungs The lung and alveoli volume increases More oxygen is absorbed
Lung volumes The lung can be divided into four different compartments which are illustrated below . These are: ( )1Total lung capacity (TLC) which is the amount of air in the lungs after a deep breath in. ( )2The residual volume (RV), which is the amount of air left in the lungs after maximal expiration (a deep breath out). ()3The vital capacity (VC) which is the amount of gas expired when going from total lung capacity to residual volume. ( )4The functional residual capacity (FRC) which is the amount of gas within the lungs at end expiration .
Boher effect
Inspired oxygen 160 mmHg Alveolar oxygen ~ 120 mmHg Oxygen in the blood~ 100 mmHg Oxygen at tissue level~ 4-20 mmHg
CO2 + H2O <> H2CO3 H2CO3 <> H+ + HCO3
Hb4(O2)4 + CO2 + H+ = Hb4CO2(H+) + 4O2
Respiration in fish
Respiration in birds
You might also like
- Unit Test-I, First Term 2018: Maavashu School L.Maavah/ Rep - of MaldivesDocument7 pagesUnit Test-I, First Term 2018: Maavashu School L.Maavah/ Rep - of MaldivesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- c1 RespirationDocument4 pagesc1 Respirationnor85anNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Final Term 2019-2020Document2 pagesUsman Public School System: Final Term 2019-2020muneeza dueveshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document2 pagesLesson 3.1Evangelia GkNo ratings yet
- Bio 20 - Unit C - Unit PlanDocument21 pagesBio 20 - Unit C - Unit Planapi-199149636No ratings yet
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Transportation WorksheetDocument4 pagesRespiration and Transportation WorksheetAarjav JainNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- Yr 7 Acids&alkaliDocument33 pagesYr 7 Acids&alkaliYumni AminNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- Respiration QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiration QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Document12 pagesPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument9 pagesGas Exchange in HumanscherylrachelNo ratings yet
- H. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration LabDocument4 pagesH. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration LaberikabeltranNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon CycleRyan NegadNo ratings yet
- Revision-Forces and Motion-Grade 9Document12 pagesRevision-Forces and Motion-Grade 9Nour A100% (1)
- G8 Enzymes & Body Systems Progress Test SY 2017 - 18Document5 pagesG8 Enzymes & Body Systems Progress Test SY 2017 - 18pixelhoboNo ratings yet
- The Heart LA WorksheetDocument4 pagesThe Heart LA Worksheeteas grade04No ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 pagesSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Digestive System-1Document3 pagesDigestive System-1elinandreaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaNo ratings yet
- (42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section ADocument15 pages(42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section AGie KieNo ratings yet
- Science Acids and Alkalis Test, Corrected WorkDocument3 pagesScience Acids and Alkalis Test, Corrected WorktanhaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science AssessmentDocument10 pagesCambridge Science AssessmentdiptiNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 19 Organisms and Their Environment - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 19 Organisms and Their Environment - CAIE Biology IGCSESara AbdelfattahNo ratings yet
- Snells Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesSnells Law Worksheetbshashi9No ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerDocument6 pagesRespiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell AssessmentDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Cell AssessmentJennifer DequinaNo ratings yet
- 9a Mark SchemesDocument6 pages9a Mark Schemesobomar2010No ratings yet
- Science Prep.2Document64 pagesScience Prep.2Mayar DahyNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 22: RespirationDocument67 pages% Chapter 22: RespirationTiko Li100% (1)
- IGCSE Digestion - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesIGCSE Digestion - Print - Quizizzjv peridoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 4Document66 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 4Minh MeoNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic ModelDocument16 pagesDalton's Atomic ModelHadeel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- Class10 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkDocument38 pagesClass10 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkAndy Rei KouNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Yr09 t2 2018Document12 pagesChemistry Yr09 t2 2018imanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- The Transport System in HumansDocument8 pagesThe Transport System in HumansazuraNo ratings yet
- Rajarshi Shahu JR Science College, Latur Screening Test - 2019 Syllabus: Physics 1 Motion 2Document7 pagesRajarshi Shahu JR Science College, Latur Screening Test - 2019 Syllabus: Physics 1 Motion 2Dr. Laxman RautNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Summary NotesNoraNo ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document12 pagesHuman Nutrition - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Zhi En LeeNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument5 pagesRespiratoryKrisdiansah PurnawidjajaNo ratings yet
- Respiration ExperimentDocument5 pagesRespiration ExperimentAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Using The Words Given. Trachea Bronchus Lungs: Learning Objective: Human Breathing MechanismDocument3 pagesUsing The Words Given. Trachea Bronchus Lungs: Learning Objective: Human Breathing MechanismMp GopalNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 1 Grade 12 BioDocument8 pagesUnit Test 1 Grade 12 BioSarah KwanNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Hematocrits: Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument4 pagesInterpreting Hematocrits: Critical Thinking Questionsapi-400575655No ratings yet
- HSBDocument12 pagesHSBjemima MillsNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 7.1 The Respiratory Structures and Breathing Mechanisms in Humans and AnimalsDocument9 pagesWORKSHEET 7.1 The Respiratory Structures and Breathing Mechanisms in Humans and AnimalsGhanapathi RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Net Ionic EquationsDocument3 pagesPractice Problems On Net Ionic EquationsZainabNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument1 pageRespirationShamaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Things CellsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things CellsFrances FlynnNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Worksheet-R06answersDocument3 pagesCell Respiration Worksheet-R06answersAllison KhooNo ratings yet
- Question Paper of Law of Conservation of Mass - Class 9Document3 pagesQuestion Paper of Law of Conservation of Mass - Class 9suranjana26No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Document79 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Phillip TranNo ratings yet
- Revision 2023Document10 pagesRevision 2023Zain AliNo ratings yet
- Taste BudDocument10 pagesTaste Budsawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument59 pagesMuscular Systemsawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument61 pagesNervous Tissuesawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument62 pagesConnective Tissuesawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissuesDocument17 pagesAdipose Tissuessawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument45 pagesEpithelial Tissuessawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument23 pagesKidneysawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Hearing and Ear StructureDocument38 pagesHearing and Ear Structuresawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument20 pagesEye and Visionsawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet
- Excretory System1Document78 pagesExcretory System1sawsan NajajrehNo ratings yet