Professional Documents
Culture Documents
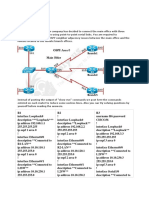
Lab 6
Uploaded by
Narayan MundhraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 6
Uploaded by
Narayan MundhraCopyright:
Available Formats
7.
The list of decision steps BGP goes through is:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j.
Largest WEIGHT Largest LOCAL_PREF Locally originated path Shortest AS_PATH Lowest origin type Lowest Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) External (eBGP) over internal (iBGP) path Lowest IGP metric over the BGP next hop. Multipath Determination. BGP router to prefer a current best path, if it has one, over a newer route with equal attributes
8. If your AS passes traffic from another AS to a third AS, BGP should not advertise a route before all routers in your AS learn about the route via IGP. BGP waits until IGP propagates the route within the AS and then advertises it to external peers. A BGP router with synchronization enabled does not install iBGP learned routes into its routing table if it is not able to validate those routes in its IGP. Issue the no synchronization command under router bgp in order to disable synchronization. This prevents BGP from validating iBGP routes in IGP. Refer to BGP Case Studies: Synchronization for a more detailed explanation. 9. IBGP is formed between Neighbors within the same AS whereas EBGP is formed between neighbors in different AS. A route learnt from an IBGP peer will not be advertised back to another IBGP by default. AS path is not prepended to the route when advertised to an IBGP peer. Attributes like local preference are sent to the IBGP peers but not to an EBGP peer. Under normal circumstances EBGP route is always preferred over an IBGP route (exception are if u configure BGP deterministic-med & BGP always-compare-med).
10. The three well-known mandatory paths attributes are:
ORIGIN: The ORIGIN attribute is generated by the speaker that originates the associated routing information. AS_PATH: This attribute identifies the autonomous systems through which routing information. NEXT_HOP: that defines the IP address of the router that SHOULD be used as the next hop. *Mar 7 03:32:11.715: BGP: Applying map to find origin for 200.1.4.3/32 *Mar 7 03:32:15.035: BGP: 20.2.4.7 rcv message type 4, length (excl. header) 0 *Mar 7 03:32:16.691: BGP: 20.2.4.7 send message type 4, length (incl. header) 1 9 *Mar 7 03:32:39.899: BGP: 20.2.4.1 rcv message type 4, length (excl. header) 0 *Mar 7 03:32:43.691: BGP: 20.2.4.1 send message type 4, length (incl. header) 1 9 *Mar 7 03:32:58.691: BGP: 20.2.4.2 send message type 4, length (incl. header) 1 9 *Mar 7 03:32:58.699: BGP: 20.2.4.2 rcv message type 4, length (excl. header) 0
You might also like
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Lan Switching and SecurityDocument13 pagesLan Switching and SecuritybikkerNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 6 PPT VLSM CIDRDocument34 pagesCCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 6 PPT VLSM CIDRAaron Christopher C. Garcia100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsFrom EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CCNA Routing Interview Question and Answer Will Help Your To Crack Interview EasilyDocument7 pagesCCNA Routing Interview Question and Answer Will Help Your To Crack Interview EasilySel Espinosa BallesterosNo ratings yet
- BGP Tutorial: Learn Basics of Border Gateway ProtocolDocument4 pagesBGP Tutorial: Learn Basics of Border Gateway Protocolokotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- Ccna New Lab Manual by Esp TeamDocument173 pagesCcna New Lab Manual by Esp TeamTamirat koreNo ratings yet
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Network Types: Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)Document10 pagesNetwork Types: Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)sans mahe1No ratings yet
- SDWAN TrainingDocument12 pagesSDWAN TrainingAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Cisco - I AS MPLS PDFDocument70 pagesCisco - I AS MPLS PDFRK JainNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocument2 pagesCisco Router Configuration CommandsHarun Ugur YelikliNo ratings yet
- SPEDGEDocument2 pagesSPEDGEliebofreakNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS XR Routing Configuration Guide For The Cisco CRS RouterDocument644 pagesCisco IOS XR Routing Configuration Guide For The Cisco CRS RouterChristopher Pepito0% (1)
- 350-401 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopics - WithdiscussionsDocument1,021 pages350-401 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopics - WithdiscussionsOrly, Jr. PalomarNo ratings yet
- CCNP Enterprise Workbook - Lab Topology Diagrams - Lab Startup BGP NeighborshipDocument2 pagesCCNP Enterprise Workbook - Lab Topology Diagrams - Lab Startup BGP NeighborshipNyinyi LwinNo ratings yet
- IEWB-RS Advanced Technologies Labs RIPDocument45 pagesIEWB-RS Advanced Technologies Labs RIPJoffre Ramiro Pesantez VerdezotoNo ratings yet
- CCNP R&S Overview PresentationDocument19 pagesCCNP R&S Overview PresentationsafaNo ratings yet
- 5 - IsIS For ISPs (Cisco Training)Document40 pages5 - IsIS For ISPs (Cisco Training)Nhơn KiệmNo ratings yet
- ENCOR - Chapter - 3 - Advanced STP TuningDocument34 pagesENCOR - Chapter - 3 - Advanced STP TuningwondeNo ratings yet
- How To Implement Cisco Unified SRST and MGCP Fallback - Cisco Support CommunityDocument3 pagesHow To Implement Cisco Unified SRST and MGCP Fallback - Cisco Support CommunityRamakrishnan PisharodyNo ratings yet
- CCIE RoutingampampampSwitching Advance Workbook5 V2 (Technology Focused)Document223 pagesCCIE RoutingampampampSwitching Advance Workbook5 V2 (Technology Focused)César Arévalo LealNo ratings yet
- CCIE R&S LAB h2+ UpdatedDocument67 pagesCCIE R&S LAB h2+ UpdatedOmarNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Case Study: Bank of POLONA: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksDocument50 pagesTroubleshooting Case Study: Bank of POLONA: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksAustin SpillerNo ratings yet
- Devnet 2000Document36 pagesDevnet 2000Kaung Kyaw KhantNo ratings yet
- Cisco TAC Entry Training - 12 - Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) PDFDocument54 pagesCisco TAC Entry Training - 12 - Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) PDFFerasHamdanNo ratings yet
- Doc6 Mpls VPNDocument59 pagesDoc6 Mpls VPNUmair Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- Shortnote LabDocument22 pagesShortnote LabSamiNo ratings yet
- CCIE Troubleshooting TipsDocument4 pagesCCIE Troubleshooting Tipshem777No ratings yet
- EROU01 Routing BasicsDocument37 pagesEROU01 Routing BasicsztanjimNo ratings yet
- OSPF Deep Dive: Juniper Router Lab Guide0x800000047680x22 0x5c4c0x800000037680x22 0x5c4c0x800000027680x22 0x2e480x800000027680x22 0x2e480x800000027680x22 0x2e480x8000000a8010x22 0x2e480x800000037680Document149 pagesOSPF Deep Dive: Juniper Router Lab Guide0x800000047680x22 0x5c4c0x800000037680x22 0x5c4c0x800000027680x22 0x2e480x800000027680x22 0x2e480x800000027680x22 0x2e480x8000000a8010x22 0x2e480x800000037680hem777No ratings yet
- Best Cisco ACI Data Center DCCOR Labs 300-630 DCACIA 300-620 350-601 Advance Training - DCLessonsDocument7 pagesBest Cisco ACI Data Center DCCOR Labs 300-630 DCACIA 300-620 350-601 Advance Training - DCLessonsravi kantNo ratings yet
- ENCOR - Chapter - 1 - Packet ForwardingDocument57 pagesENCOR - Chapter - 1 - Packet ForwardingwondeNo ratings yet
- PDF CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual (2nd Edition) (Lab Companion) Free Download and Read OnlineDocument6 pagesPDF CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual (2nd Edition) (Lab Companion) Free Download and Read OnlinefaraxxxNo ratings yet
- MQC MLS QOS Conversion Tool: Interface SpeedDocument13 pagesMQC MLS QOS Conversion Tool: Interface Speedmarly95670No ratings yet
- Ccna 200-125 LabsDocument53 pagesCcna 200-125 LabsMaidet J. Baino100% (1)
- MPLS Layer 2 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SDocument674 pagesMPLS Layer 2 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SChristopher PepitoNo ratings yet
- Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 300-615 Exam Name: Troubleshooting Cisco Data CenterDocument44 pagesVendor: Cisco Exam Code: 300-615 Exam Name: Troubleshooting Cisco Data CenterGopi Chowdary50% (2)
- Cisco (DMVPN) NHRP Phase 1-2-3Document9 pagesCisco (DMVPN) NHRP Phase 1-2-3Gayloard FockerNo ratings yet
- Quick Configs - CCIE Notes PDFDocument215 pagesQuick Configs - CCIE Notes PDFNoah AzpiriNo ratings yet
- CCIE R&S Q and ADocument88 pagesCCIE R&S Q and Asujeet_hat100% (1)
- BGP Route SelectionDocument45 pagesBGP Route SelectionTarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cisco 350-401 : Practice Test QuestionsDocument101 pagesCisco 350-401 : Practice Test QuestionsJaume Tarafa BetancourthNo ratings yet
- Devnet Exam GuideDocument14 pagesDevnet Exam Guidehenx582No ratings yet
- MPLS VPN TroubleshootingDocument58 pagesMPLS VPN Troubleshootinghem777No ratings yet
- HCIE-Routing & Switching V3.0 Mock ExamDocument4 pagesHCIE-Routing & Switching V3.0 Mock ExamToffe Gokale Michel100% (1)
- Cisco SD Wan and UmbrellaDocument3 pagesCisco SD Wan and UmbrellabuendiaisauroNo ratings yet
- Static NAT On Cisco IOSDocument6 pagesStatic NAT On Cisco IOSThọ Lương ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Cisco 350 401Document189 pagesCisco 350 401Mario Cisneros IIINo ratings yet
- Routing Lab Jncis SPDocument3 pagesRouting Lab Jncis SPLeni Fery JNo ratings yet
- PassLeader 200-125 Exam DumpsDocument5 pagesPassLeader 200-125 Exam DumpsklguuNo ratings yet
- CCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st EditionDocument531 pagesCCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st Editionmansoorali_af100% (2)
- Yasser Auda CCIEv5 WorkbookDocument26 pagesYasser Auda CCIEv5 WorkbookphamvanhaNo ratings yet
- ACI Automation & Scripting - DCLessonsDocument11 pagesACI Automation & Scripting - DCLessonsravi kantNo ratings yet
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)Document18 pagesLink Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)Wewe SlmNo ratings yet
- Advance VPLS Technology Atachements OptionsDocument62 pagesAdvance VPLS Technology Atachements Optionsandresfcl83No ratings yet
- CCNP SwitchDocument78 pagesCCNP Switchshalem123No ratings yet
- 5 продвинутых технологий Cisco, которые нужно знатьDocument50 pages5 продвинутых технологий Cisco, которые нужно знатьAnonymous OQhJsHNo ratings yet
- Ccna Sec 1.2 ExasDocument27 pagesCcna Sec 1.2 Exasesquirla300No ratings yet
- JSEC 12.a-R LGDDocument208 pagesJSEC 12.a-R LGDTucsi2000No ratings yet
- Comba Nms v2.0 Qu 1-1-0Document93 pagesComba Nms v2.0 Qu 1-1-0EdivaldoVianaNo ratings yet
- Diglit A s2 s1 A3 Windows 10 Study GuideDocument4 pagesDiglit A s2 s1 A3 Windows 10 Study Guideapi-377090598No ratings yet
- Sensor NetworksDocument21 pagesSensor NetworksmuheNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument25 pagesGprsYuvraj TjNo ratings yet
- (Junos) How To Mount A USB Drive On The EX - SRXDocument3 pages(Junos) How To Mount A USB Drive On The EX - SRXLi KangNo ratings yet
- ConfigDocument37 pagesConfigJennifer TaylorNo ratings yet
- Nemo FSR1 3.01 User ManualDocument45 pagesNemo FSR1 3.01 User ManualReNz GonzalesNo ratings yet
- VCL TP Teleprotection Equipment Easy To Use GUI Guide: Valiant Communications Limited - 2018 1Document58 pagesVCL TP Teleprotection Equipment Easy To Use GUI Guide: Valiant Communications Limited - 2018 1PlamenNo ratings yet
- 08 OCI DatabaseDocument30 pages08 OCI DatabaseBreno RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Miss Call Issue V2 0Document8 pagesAnalysis of Miss Call Issue V2 0Armaghan AhmadNo ratings yet
- IT8510E/TE/G: Embedded ControllerDocument284 pagesIT8510E/TE/G: Embedded ControllerАлександр ВласенкоNo ratings yet
- ThinkCentre Edge 71zDocument4 pagesThinkCentre Edge 71zDirland MultasimNo ratings yet
- GOT2000 - UserManual Monitor - SH 081196 I PDFDocument614 pagesGOT2000 - UserManual Monitor - SH 081196 I PDFFanny Achmad Hindrarta KusumaNo ratings yet
- An Internet Service ProviderDocument23 pagesAn Internet Service ProviderGlocer BartolabaNo ratings yet
- IBM VIO Server VIO-Server-Genera: Image DescriptionDocument39 pagesIBM VIO Server VIO-Server-Genera: Image DescriptionAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- IO Summary For IBMS Service PDFDocument348 pagesIO Summary For IBMS Service PDFpratimNo ratings yet
- Project #3 Hotel System NetworkDocument2 pagesProject #3 Hotel System Networkznabugrmay20adiNo ratings yet
- Cs1111-Computer Networks and Distributed SystemsDocument16 pagesCs1111-Computer Networks and Distributed SystemsMedishetty YeshvanthNo ratings yet
- Specification: Short Message Service Centre External Machine InterfaceDocument68 pagesSpecification: Short Message Service Centre External Machine InterfacesanbivNo ratings yet
- Telefire TSA-1000 Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesTelefire TSA-1000 Brochure PDFJoseph BoshehNo ratings yet
- MIMO Systems and Spatial Diversity.: Dshutin@tugraz - atDocument36 pagesMIMO Systems and Spatial Diversity.: Dshutin@tugraz - atnaranjitoNo ratings yet
- FTTH DesignguideDocument52 pagesFTTH Designguideanadigupta100% (1)
- SG 244688Document304 pagesSG 244688api-3697260100% (2)
- XBT Xk800eDocument84 pagesXBT Xk800efakhriNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Layer Protocols and ConceptsDocument3 pagesMobile Network Layer Protocols and ConceptsPragya Chakshoo100% (1)
- Installation of Ns 2.34Document3 pagesInstallation of Ns 2.34Muhammad FuadNo ratings yet