Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAC Layer Functions for Wireless LAN Reliability
Uploaded by
Fatima M QuadriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MAC Layer Functions for Wireless LAN Reliability
Uploaded by
Fatima M QuadriCopyright:
Available Formats
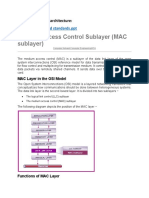
Medium Access Control
MAC
layer covers three functional areas
reliable data delivery access control security
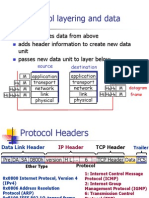
LAN Protocol Architecture
Reliable Data Delivery
802.11 physical / MAC layers unreliable
noise, interference, and other propagation effects result in loss of frames even with error-correction codes, frames may not successfully be received
can be dealt with at a higher layer, e.g. TCP more efficient to deal with errors at MAC level 802.11 includes frame exchange protocol
station receiving frame returns acknowledgment (ACK) frame exchange treated as atomic unit if no ACK within short period of time, retransmit
Four Frame Exchange
can use four-frame exchange for better reliability
source issues a Request to Send (RTS) frame to dest destination responds with Clear to Send (CTS) after receiving CTS, source transmits data destination responds with ACK
RTS alerts all stations within range of source that exchange is under way CTS alerts all stations within range of destination other stations dont transmit to avoid collision RTS/CTS exchange is required function of MAC but may be disabled
Media Access Control
Distributed Coordination Function
DCF
sublayer uses CSMA
if station has frame to send it listens to medium if medium idle, station may transmit else waits until current transmission complete
no
collision detection since on wireless network DCF includes delays that act as a priority scheme
Point Coordination Function (PCF)
alternative access method implemented on top of DCF polling by centralized polling master (point coordinator) uses PIFS when issuing polls point coordinator polls in round-robin to stations configured for polling
You might also like
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- WifiDocument29 pagesWifiSreedevi BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN StandardDocument33 pagesIEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN StandardCarlos León AraujoNo ratings yet
- WLANDocument40 pagesWLANusitggsipuNo ratings yet
- MC IIb IEEE802 11Document60 pagesMC IIb IEEE802 11Abdul AzeemNo ratings yet
- Network Protocols and Security LayersDocument16 pagesNetwork Protocols and Security LayersŹéý ÑêbNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN StandardDocument33 pagesIEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN StandardSatish NaiduNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Backoff Scheme in CSMA/CA For IEEE 802.11: Wen-Kuang Kuo and C.-C. Jay KuoDocument5 pagesEnhanced Backoff Scheme in CSMA/CA For IEEE 802.11: Wen-Kuang Kuo and C.-C. Jay KuoKawthar HedNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer Communications: LAN SystemsDocument38 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer Communications: LAN SystemsLê Đắc Nhường (Dac-Nhuong Le)No ratings yet
- Multiple-Access Protocols: Done By: Sana'a Al-Qaralleh Presented To: Dr. Ibrahim Al-QatawnehDocument40 pagesMultiple-Access Protocols: Done By: Sana'a Al-Qaralleh Presented To: Dr. Ibrahim Al-QatawnehMhmd NeamatNo ratings yet
- Chapter6MAC LayerDocument35 pagesChapter6MAC LayerMd NehalNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Contention Window For Quality of Service in IEEE 802.11 NetworksDocument5 pagesDynamic Contention Window For Quality of Service in IEEE 802.11 NetworksLiyang ChangNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Switching Concepts Explained in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesEthernet Switching Concepts Explained in 40 Charactersatilio2No ratings yet
- Flow ControlDocument51 pagesFlow ControlAsharab JunaidNo ratings yet
- Protocol Layering and DataDocument20 pagesProtocol Layering and DataAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 on Wireless LANs and PANs StandardsDocument49 pagesLecture 4 on Wireless LANs and PANs StandardsManoj Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument12 pagesUnit 3 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.insoetshashitomarNo ratings yet
- Lan Standards and ArchitectureDocument34 pagesLan Standards and ArchitectureNawal K SahNo ratings yet
- Cisco Module 5Document51 pagesCisco Module 5kwinlimNo ratings yet
- Lec 2. Computer NetworksDocument42 pagesLec 2. Computer NetworksHayam UmarNo ratings yet
- Introducing To NetworkingDocument5 pagesIntroducing To Networkinggheorghe_tiberiu96No ratings yet
- Protocol Layering and DataDocument19 pagesProtocol Layering and DataAleena KanwalNo ratings yet
- Lapd Vs Lapdm (Technical)Document4 pagesLapd Vs Lapdm (Technical)cp56441No ratings yet
- Ethernet: Understanding the Fundamental Networking TechnologyDocument39 pagesEthernet: Understanding the Fundamental Networking TechnologyMario_LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer (Ethernet)Document37 pagesData Link Layer (Ethernet)Yash TamakuwalaNo ratings yet
- OSI Model ExplainedDocument43 pagesOSI Model ExplainedAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Basic Switch Concept and ConfigurationDocument50 pagesChapter-2: Basic Switch Concept and Configurationdeepank singhNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802 LAN Protocol ArchitectureDocument27 pagesIEEE 802 LAN Protocol ArchitectureMallikarjuna Naik100% (1)
- IEEE 802.11 ProtocolDocument24 pagesIEEE 802.11 Protocol김성수No ratings yet
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasDocument42 pagesCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudNo ratings yet
- 802.11 Wireless Data Link Layer MAC Protocols - DCF, PCF, CSMA/CADocument20 pages802.11 Wireless Data Link Layer MAC Protocols - DCF, PCF, CSMA/CAVenkat ram ReddyNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks (LAN)Document50 pagesLocal Area Networks (LAN)Battala Vamshi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Qos Provided by The Ieee 802.11 Wireless Lan To Advanced Data Applications: A Simulation AnalysisDocument18 pagesQos Provided by The Ieee 802.11 Wireless Lan To Advanced Data Applications: A Simulation AnalysisAndré GamaNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and Wimax: by T. Sridhar, FlextronicsDocument8 pagesWi-Fi, Bluetooth and Wimax: by T. Sridhar, FlextronicsmakayaboNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control and ProtocolsDocument61 pagesData Link Control and ProtocolsusitggsipuNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer Communications: - Local Area NetworkDocument55 pagesData and Computer Communications: - Local Area NetworkPria JayaNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Fundamentals: Introduction to Ethernet MACDocument28 pagesEthernet Fundamentals: Introduction to Ethernet MACKlokanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Wireless LANs Part 2 - 16x9Document34 pagesChapter 4 - Wireless LANs Part 2 - 16x9alomarianas52No ratings yet
- Lec 7Document14 pagesLec 7bayav.nimetollaNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument61 pagesData and Computer CommunicationsShah Amran NayanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 CNDocument35 pagesUNIT 2 CNmsk.official321No ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument3 pagesPhysical LayershivaprasadmvitNo ratings yet
- MODULE 8 - Ethenet SwitchingDocument4 pagesMODULE 8 - Ethenet SwitchingGrecu GianiNo ratings yet
- Introducing SOFT MAC: Ghassan M. Abdalla, Mosa Ali Abu-Rgheff and Sidi-Mohammed SenouciDocument10 pagesIntroducing SOFT MAC: Ghassan M. Abdalla, Mosa Ali Abu-Rgheff and Sidi-Mohammed SenouciUbiquitous Computing and Communication JournalNo ratings yet
- Application Application Transport Transport Internet Network Link Data Link PhysicalDocument18 pagesApplication Application Transport Transport Internet Network Link Data Link Physical934859348No ratings yet
- WSN Unit-3Document89 pagesWSN Unit-3mr8566No ratings yet
- CN - CHPT 5Document7 pagesCN - CHPT 5Deepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- The IEEE 802.11 MAC - by Laselva DDocument17 pagesThe IEEE 802.11 MAC - by Laselva DtuanbaronxNo ratings yet
- Ce3716 Computer Networks 5Document21 pagesCe3716 Computer Networks 5jake dossryNo ratings yet
- Why CSMA/CD cannot be used in wireless LANDocument17 pagesWhy CSMA/CD cannot be used in wireless LAN054 Jaiganesh MNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer Communications: - Local Area NetworkDocument60 pagesData and Computer Communications: - Local Area NetworkpusXingNo ratings yet
- MTech ACN Unit2-Lecture2Document62 pagesMTech ACN Unit2-Lecture2Tarun RaghuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-5Document54 pagesChapter 4-5MehariNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11 MAC: An Introduction to Key ConceptsDocument27 pagesIEEE 802.11 MAC: An Introduction to Key ConceptsNovIta ApsariDewiNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of MAC For QoS in IEEEDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of MAC For QoS in IEEEChaitanya Tilak PathaNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'sDocument21 pagesNetwork Devices: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC'sAzhar SkNo ratings yet
- C CCC PPDocument20 pagesC CCC PPSwtz Zraonics100% (1)
- Guide to Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) Topology, Standards, and ConfigurationDocument47 pagesGuide to Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) Topology, Standards, and ConfigurationAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bi An Chi 1996Document5 pagesBi An Chi 1996Rajesh ECNo ratings yet