Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. Cfls
Uploaded by
Mayank SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. Cfls
Uploaded by
Mayank SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison Chart LED Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs.
CFLs
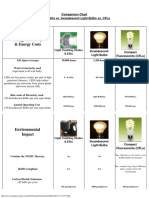
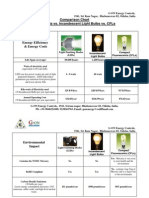
Energy Efficiency & Energy Costs Life Span (average) Watts of electricity used (equivalent to 60 watt bulb). LEDs use less power (watts) per unit of light generated (lumens). LEDs help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from power plants and lower electric bills Kilo-watts of Electricity used (30 Incandescent Bulbs per year equivalent) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) 50,000 hours Incandescent Light Bulbs 1,200 hours Compact Fluorescents (CFLs) 8,000 hours
6 - 8 watts
60 watts
13-15 watts
329 KWh/yr.
3285 KWh/yr.
767 KWh/yr.
Environmental Impact
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
No
Incandescent Light Bulbs
No
Compact Fluorescents (CFLs)
Contains the TOXIC Mercury
Yes - Mercury is very toxic to your health and the environment
RoHS Compliant Carbon Dioxide Emissions (30 bulbs per year) Lower energy consumption decreases: CO2 emissions, sulfuroxide, and high-level nuclear waste.
Yes
Yes
No - contains 1mg-5mg of Mercury and is a major risk to the environment
451 pounds/year
4500 pounds/year
1051 pounds/year
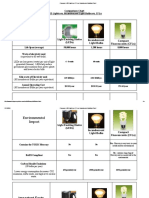
Important Facts
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
None
Incandescent Light Bulbs
Some
Compact Fluorescents (CFLs)
Yes - may not work under negative 10 degrees Fahrenheit or over 120 degrees Fahrenheit Yes
Sensitivity to low temperatures
Sensitive to humidity On/off Cycling Switching a CFL on/off quickly, in a closet for instance, may decrease the lifespan of the bulb. Turns on instantly
No
Some
No Effect
Some
Yes - can reduce lifespan drastically
Yes Very Durable - LEDs can handle jarring and bumping 3.4 btu's/hour
Yes Not Very Durable - glass or filament can break easily 85 btu's/hour
No - takes time to warm up Not Very Durable - glass can break easily 30 btu's/hour Yes - may catch on fire, smoke, or omit an odor
Durability
Heat Emitted
Failure Modes
Not typical
Some
You might also like
- LED Lighting for Your Home & Business: LED Lights Save Money and Make Your Home Lighting SpectacularFrom EverandLED Lighting for Your Home & Business: LED Lights Save Money and Make Your Home Lighting SpectacularNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart LED CFL ILDocument5 pagesComparison Chart LED CFL ILVer BautistaNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency & Energy Costs: Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. CflsDocument2 pagesEnergy Efficiency & Energy Costs: Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. Cflspditzel8599No ratings yet
- WWW Designrecycleinc Com Led Comp ChartDocument2 pagesWWW Designrecycleinc Com Led Comp Chartrsiva98No ratings yet
- Catagories Led Incadescent: 50,000 Hours 1,200 Hours 6 - 8 Watts 60 Watts 329 Kwh/Yr. 3285 Kwh/Yr. 1645 16425Document2 pagesCatagories Led Incadescent: 50,000 Hours 1,200 Hours 6 - 8 Watts 60 Watts 329 Kwh/Yr. 3285 Kwh/Yr. 1645 16425Sayantan RoyNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. CflsDocument6 pagesComparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. CflsPankaj ShidurkarNo ratings yet
- Led PresentationDocument28 pagesLed PresentationhemadribabuNo ratings yet
- CFL vs. Led: A Few More Facts: CflsDocument5 pagesCFL vs. Led: A Few More Facts: CflsAira VeniceNo ratings yet
- Compare LED Lights Vs CFL Vs IncandescenDocument4 pagesCompare LED Lights Vs CFL Vs Incandescenمعاذ محزريNo ratings yet
- SL DesignDocument3 pagesSL DesignJer A' MealNo ratings yet
- Lighting Comparison Chart PDFDocument2 pagesLighting Comparison Chart PDFpaul_aldNo ratings yet
- 02 - Izvori SvjetlaDocument23 pages02 - Izvori SvjetlaRanko SkansiNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of Magnetic Induction LampsDocument7 pagesThe Advantages of Magnetic Induction LampsnntoolNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Benefits of LED LightingDocument8 pagesTop 10 Benefits of LED LightingVIKAS BHANDARENo ratings yet
- Seminar OnDocument25 pagesSeminar OnJayant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Lighting SystemsDocument27 pagesLighting SystemsSri Ch.V.Krishna Reddy Assistant Professor (Sr,)No ratings yet
- Comparison Chart LED CFL ILDocument5 pagesComparison Chart LED CFL ILver_at_workNo ratings yet
- Light Output Leds Cfls Incandescents 450 750 - 900 1100 - 1300 1600 - 1800 2600 - 2800Document2 pagesLight Output Leds Cfls Incandescents 450 750 - 900 1100 - 1300 1600 - 1800 2600 - 2800TeJas PaTelNo ratings yet
- "Energy Saved Is Equivalent To Energy Produced": Chapter 1-IntroductionDocument33 pages"Energy Saved Is Equivalent To Energy Produced": Chapter 1-IntroductionRamyata MahajanNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart LED CFL ILDocument5 pagesComparison Chart LED CFL ILver_at_workNo ratings yet
- Our PartnerDocument18 pagesOur PartnerEvelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Utilization - Leds: Guide: Dr. S.S. BhattDocument44 pagesElectrical Power Utilization - Leds: Guide: Dr. S.S. BhattAbhilash MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. CflsDocument4 pagesComparison Chart Led Lights vs. Incandescent Light Bulbs vs. CflsK Vijay Bhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving Tube LightDocument18 pagesEnergy Saving Tube LightJude Rahul Mathew67% (6)
- Low Pressure SodiumDocument10 pagesLow Pressure SodiumCyrus JainNo ratings yet
- Induction LightingDocument2 pagesInduction Lightingnosyparker619No ratings yet
- What Is Useful Life For White Light Leds? Lighting Research CenterDocument12 pagesWhat Is Useful Life For White Light Leds? Lighting Research CenterAbigail RamosNo ratings yet
- Assigment Basic Electric 1Document9 pagesAssigment Basic Electric 1zhareef yazitNo ratings yet
- Cost Comparison Between LEDsDocument5 pagesCost Comparison Between LEDsnaleengtNo ratings yet
- Comparisan LED Vs PLC Vs IncandescentDocument2 pagesComparisan LED Vs PLC Vs IncandescentRizal IdrisNo ratings yet
- No Formulas and Numericals: Step 1Document11 pagesNo Formulas and Numericals: Step 1Ashdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Greening My Home: How Do I Reduce My Energy Footprint?: Hy We Must Think of Energy Efficient Life Style?Document15 pagesGreening My Home: How Do I Reduce My Energy Footprint?: Hy We Must Think of Energy Efficient Life Style?EngArab FqNo ratings yet
- EXXSN ProfileDocument10 pagesEXXSN ProfileHamza TariqNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Week 2021Document12 pagesEnergy Conservation Week 2021santosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Architecture BLD NOTES 2Document12 pagesArchitecture BLD NOTES 2Mwaniki WilNo ratings yet
- Green Building With RefDocument11 pagesGreen Building With RefRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources and Energy ConservationDocument100 pagesRenewable Energy Sources and Energy ConservationSreejith KailasNo ratings yet
- Artificial LightingDocument37 pagesArtificial LightingRanu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- LED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)Document63 pagesLED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)AV Shrinivas100% (3)
- Types of Lamps and LightingDocument52 pagesTypes of Lamps and LightingKevin Ndeti100% (1)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractsowmya_vmNo ratings yet
- Led Lighting Is ThornDocument88 pagesLed Lighting Is ThornhansdubarryNo ratings yet
- Efficient Energy Solutions For Street Lighting at OGDCLDocument11 pagesEfficient Energy Solutions For Street Lighting at OGDCLZain NadeemNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy EfficiencyDocument5 pagesSustainable Energy EfficiencyAEEENo ratings yet
- Cab ch7Document53 pagesCab ch7dmurenNo ratings yet
- Led There Be Light PDFDocument3 pagesLed There Be Light PDFAlessandro LeonaNo ratings yet
- Ecostar LED: A Sustainable Lighting SolutionDocument3 pagesEcostar LED: A Sustainable Lighting SolutionMaetin67No ratings yet
- Primamax PVT LTDDocument30 pagesPrimamax PVT LTDSalman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Led Fundamentals: Luminous EfficacyDocument10 pagesLed Fundamentals: Luminous EfficacyKalp KartikNo ratings yet
- About LVDDocument19 pagesAbout LVDAmit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency: For More Details On This Topic, SeeDocument2 pagesEnergy Efficiency: For More Details On This Topic, SeeVer BautistaNo ratings yet
- Energy EfficiencyDocument2 pagesEnergy EfficiencyVer BautistaNo ratings yet
- Various Sources of White Light and Their WokringDocument5 pagesVarious Sources of White Light and Their WokringAditi KanjoliaNo ratings yet
- Lighting Materials and FixturesDocument11 pagesLighting Materials and FixturesMichael Root100% (1)
- Ar. Leslie Dias School of Architecture S.I.T - MangaloreDocument20 pagesAr. Leslie Dias School of Architecture S.I.T - MangaloreBmssa 2017BNo ratings yet
- LED Vs Fluorescent Tubes - Comparison in Energy Consumption, Lighting Performance & EfficiencyDocument4 pagesLED Vs Fluorescent Tubes - Comparison in Energy Consumption, Lighting Performance & EfficiencydikshaNo ratings yet
- CFL & LED Bulbs: A ComparisonDocument4 pagesCFL & LED Bulbs: A Comparisonjoel_goh_3No ratings yet
- ImmaculateLED CatalogueDocument2 pagesImmaculateLED CatalogueRajbir Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- OSRAM LED LCA Summary November 2009Document26 pagesOSRAM LED LCA Summary November 2009bustiboyNo ratings yet
- Title: M EthodologyDocument7 pagesTitle: M EthodologyCharles BayangNo ratings yet