Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormones & Regulation
Hormones & Regulation
Uploaded by
Farahh ArshadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hormones & Regulation
Hormones & Regulation
Uploaded by
Farahh ArshadCopyright:
Available Formats
HORMONES 1.
Growth Hormone
REGULATIONS 1-Hypothalamic control 2-Feedback control 3.Stimuli increase secretion : - hypoglycemia & starvation - increase blood level certain amino acid (Arginine) -decrease FFA concentration in blood - deep sleep - exercise & trauma 1-Hypothalamic regulation (PRH & PIH) 2-Negative feedback regulation 3-Sleep 4-Other factors : -exercise, stress, trauma -stimulation of nipple 1- Osmotic stimuli 2- Volume depletion 3- Angiotensin II 4- Drugs -increase : nicotine, morphine, transquilizers, anesthetics -decrease : alcohol 5- stress 1- Suckling reflex 2- Stretching of uterine cervix 3- Genital stimulation 4- (inhibition) fear, pain, anxiety, alcohol 1- Hypothalamic regulation (TRH.TSH) 2- Pituitary regulation 3- feedback regulation 4-Blood iodine level
HYPOFUNCTION Dwarfism (childhood) Partial hypopituitarism Panhypopituitarism
HYPERFUNCTION Gigantism (childhood) Acromegaly (Adult)
2.Prolactin
Galactorrhea Amenorrhea Impotence in male
3.ADH/Vasopressin
Diabetes insipidus : -polyuria -polydepsia
4.Oxytocin
5.Thyroid hormone(T3,T4)
Hypothyroidism : 1. Myxedema (adult) 2. Cretinism
Hyperthyroidism (toxicgoiter, thyrotoxicosis, Graves disease)
5- Prolonged emotional reaction 6- Excitement & anxiety 7- Effect of cold 6.Parathyroid hormone 1-Calcium concentration in blood 2- Phosphate concentration 1- ^ plasma Ca concentration >10% 2- (stimulate) dopamine & estrogen 3- (stimulate) gastrin, CCK, glucagon, secretin 1-Effect of plasma calcium level 2- Effect of plasma PO4 level -markedly increase during emergencies (diffuse sympathetic discharge) 1- K ion concentration in ECF 2- Renin-angiotensin sys. 3- Quantity body Na 4- effect of ACTH 1-Hypothalamic regulations (CRF) 2- Pituitary regulation (ACTH) 3- Negative feedback 4- Physiological stress 5- Cicardian rhythm Controlled by ACTH (pituitary regulation)
(childhood)
Hypoparathyroidism hypocalcemia tatany: -manifest tetany -latent tetany
Hyperparathyroidism ostitisfibrosacystica
7.Calcitonin
8.Vitamin D3
9.Catecholamines
Non-essential
Pheochromocytoma
10.Aldosterone
-Na & water lost in urine - hyperkalemia - mild acidosis
Hyperaldosteronism primary : Conns syndrome
11.Cortisol
-Primary hypoadrenalism (Addisons disease) -Secondary adrenocortical insufficiency -
Hyperadrenalism Cushings syndrome
12. Adrenal androgens
Adrenal virilism (Adrenogenital syndrome) Hyperinsulinism
13.Insulin
1-Stimulation by blood glucose 2- (stimulation) Amino
Diabetes mellitus
acid : arginine, lysine 3- increase intracellular K decrease secretion 4- GIT hormones : gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, gastric inhibitory peptide 5- other hormones : GH, glucagon, cortisol, progesterone & testosterone 6-Autonomic nervous system 14.Glucagon 1-Blood glucose concentration 2-(stimulate) high concentration amino acid : arginine & phenylalanine 3-(stimulate) CCK & gastrin (inhibit) secretin 4-Exercise 5-sympathetic stimulation of pancreas All factors related ingestion of food stimulate SS : - ^ blood glucose - ^ amino acid - ^ fatty acid - ^ GIT hormones in response to food intake
15.Somatostatin
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Physiology CVS MCQ (Dr. Nassar)Document23 pagesPhysiology CVS MCQ (Dr. Nassar)زياد سعيدNo ratings yet
- C. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesC. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsMarynette MapaNo ratings yet
- Icd 11 (2018)Document2,440 pagesIcd 11 (2018)Dr VJ George100% (2)
- Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureDocument36 pagesPhysiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureFrancesNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy Questions and Answers 2Document16 pagesPhlebotomy Questions and Answers 2emeki20029700100% (2)
- L5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmDocument45 pagesL5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmatefmoussaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Digestive System: ExerciseDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive System: ExerciseJ NepoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology BacteriaDocument4 pagesMicrobiology BacteriaFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Meningocele Case Study (Emergency Nursing) - Theory BasedDocument47 pagesMeningocele Case Study (Emergency Nursing) - Theory BasedKyssel Seyer100% (2)
- Anatomy of KidneyDocument19 pagesAnatomy of KidneydrsooryasridharNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone DR DeepakDocument107 pagesAlveolar Bone DR DeepakDeepak Kumar100% (2)
- Ent MCQ A.pfdDocument61 pagesEnt MCQ A.pfdSuresh Kumar Bansal90% (10)
- Periodontal Flap Surgery Auto Saved)Document93 pagesPeriodontal Flap Surgery Auto Saved)Raghavendra NaikNo ratings yet
- Professional English in Use - MedicineDocument244 pagesProfessional English in Use - MedicineAlbeliz CordobaNo ratings yet
- Semen Practical BiochemDocument51 pagesSemen Practical BiochemFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Male Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Document83 pagesMale Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Cervical Polyp and Carcinoma - Pathology (Lect22-11)Document29 pagesCervical Polyp and Carcinoma - Pathology (Lect22-11)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Ovary (Lect 19-11)Document28 pagesOvary (Lect 19-11)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- PERINEUM and Urogenital Triangle (Lect 18-11)Document29 pagesPERINEUM and Urogenital Triangle (Lect 18-11)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S9Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S9Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S8Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S8Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- SectionDocument1 pageSectionFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S1Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S1Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- 2nd Week (IUMP)Document2 pages2nd Week (IUMP)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Price List (Unit Economy ACE 2012)Document2 pagesPrice List (Unit Economy ACE 2012)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S7Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S7Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S2Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S2Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Hormones & MetabolismDocument3 pagesHormones & MetabolismFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- 1st Week (IUMP)Document2 pages1st Week (IUMP)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
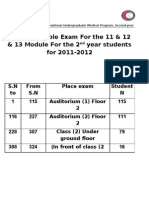
- Jadual ExamDocument1 pageJadual ExamFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Adrenal GlandDocument20 pagesDiseases of Adrenal GlandFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Module 11. 12 - 13 ExamDocument1 pageModule 11. 12 - 13 ExamFarahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System-1Document77 pagesMale Reproductive System-1Je Lan NieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CVSDocument22 pagesAnatomy of CVSAreej TariqNo ratings yet
- Module 1: The Endocrine System: Learning ObjectivesDocument1 pageModule 1: The Endocrine System: Learning ObjectivesZeina SharkasNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentDocument6 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentnehaNo ratings yet
- CH 05 Active Lecture QuestionsDocument33 pagesCH 05 Active Lecture QuestionsunixkNo ratings yet
- Fcps SurgeryDocument75 pagesFcps SurgeryLANKAPATRUDU6772No ratings yet
- Urinary Dysfunction - Traditional Chinese MedicineDocument5 pagesUrinary Dysfunction - Traditional Chinese Medicinepar_avionNo ratings yet
- Act Medical Certificate FormatDocument2 pagesAct Medical Certificate Formats anithaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument31 pagesIntegumentary Systemjcali06No ratings yet
- Plan of The Course Anatomy and Clinical Anatomy: Academic Year 2013/2014Document7 pagesPlan of The Course Anatomy and Clinical Anatomy: Academic Year 2013/2014Rinor MujajNo ratings yet
- Function of The Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesFunction of The Urinary SystemMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Dog & Cat Dentistry Anatomy SummaryDocument4 pagesDog & Cat Dentistry Anatomy SummaryBrbr LndsyNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Science 5 3rd QuarterDocument38 pages1st Summative Test Science 5 3rd QuarterEdna ZaraspeNo ratings yet
- Sas 06Document4 pagesSas 06Keziah Kish Torres GilNo ratings yet
- Scientific Thought and Clinical Practice - Edit. Dejan MarkovicDocument251 pagesScientific Thought and Clinical Practice - Edit. Dejan MarkovicskychiNo ratings yet
- Blood Biochemistry 2 (2021)Document29 pagesBlood Biochemistry 2 (2021)anis izzatiNo ratings yet