0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views3 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis and Calculations
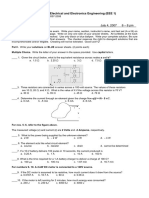
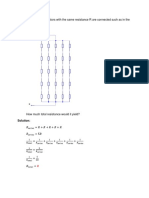
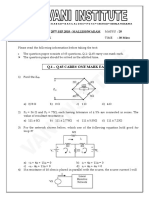
The document contains 9 problems related to electric circuits involving concepts like power calculations, nodal analysis, source transformations, Thevenin's theorem, and maximum power transfer. The problems have numerical answers provided in parentheses after each problem statement.
Uploaded by
iamcrazy1729Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views3 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis and Calculations
The document contains 9 problems related to electric circuits involving concepts like power calculations, nodal analysis, source transformations, Thevenin's theorem, and maximum power transfer. The problems have numerical answers provided in parentheses after each problem statement.
Uploaded by
iamcrazy1729Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd