Professional Documents
Culture Documents
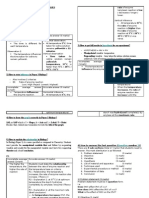
Alkenes Mind Map MARCH 2009
Uploaded by
adam_baylinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkenes Mind Map MARCH 2009
Uploaded by
adam_baylinCopyright:
Available Formats
H C H
CH3 C + H2 H
H
Ni, 150C
CH3 C H
propene
H H propane
A functional group: A functional group: provides a basis for naming compounds provides a basis for naming compounds is the reason why compounds undergo is the reason why compounds undergo similar chemical reactions similar chemical reactions influences physical properties influences physical properties
Hy d
Mar
H C H C
H
120
H C C H
H CH2CH3 but-1-ene
ethene
structural isomers
A positively-charged electrophile A positively-charged electrophile will add on to the carbon atom in an will add on to the carbon atom in an unsymmetrical >C=C< bond that unsymmetrical >C=C< bond that results in the formation of the most results in the formation of the most stable carbocation. (3 >> 2 > 1). stable carbocation. (3 2 > 1).
Functional groups
ro g
en a
tio n
kov ni Rul kovs e
n m mi ris Na me
nd ga
cis geometric isomers trans
H3C
CH3
i so
C C H H cis but-2-ene
Alkenes, CnH2n
CH3 C+ H3C CH3 H3C CH3 C+ H H CH3 C+ H
Tests for unsaturation
po Addi lym tio eri n sat ion
H3C n C H
Tertiary (3)
Secondary (2) Primary (1)
El ec ad trop di hi tio li n c
c Carbo
ations
Bromine water orange/brown colourless Alkaline potassium manganate(VII) purple colourless
H C (g) H
H C H heterolytic fission H+ BrC
CH3 H H electrophilic attack
H C H + C
CH3 H H
H C H
CH3 C H Br
CH3 H C C H H poly(propene)
(s) n
propene
Br intermediate carbocation (2)
2-bromopropane product
Low density poly(ethene) High density poly(ethene) Poly(chloro- Poly(proIncludes ethane) pene) poly(tetrafluoroethene)
Original ideas Dr John Fincham Original ideas Dr John Fincham
You might also like
- 11.3 Relative Stability of Element Group 14Document13 pages11.3 Relative Stability of Element Group 14吴绍轩No ratings yet
- Chemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Document3 pagesChemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Viknish Arumugam50% (2)
- MPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3Document4 pagesMPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3STPMBAHARUNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 3 CHM3011Document8 pagesLab Report Experiment 3 CHM3011Nurin Batrisyia100% (1)
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme TerengganuDocument17 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme Terengganusherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry (Assignment) - Nur Dania Binti Mohd Yusoff MS2117119795 B3t14Document10 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry (Assignment) - Nur Dania Binti Mohd Yusoff MS2117119795 B3t14NUR DANIA MOHD YUSOFFNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements Transition ElementsDocument51 pagesTransition Elements Transition Elements陈凯雯50% (2)
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument20 pagesChemistry AssignmentNurul SarahanisNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Biology Answering TechniquesDocument3 pagesPaper 3 Biology Answering Techniquesriyashree100% (1)
- Laboratory Report AnalysisDocument13 pagesLaboratory Report AnalysisdharwinNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsDocument32 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsYuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Brine Produces Chlorine, Hydrogen and Sodium HydroxideDocument3 pagesElectrolysis of Brine Produces Chlorine, Hydrogen and Sodium Hydroxideshirley_ling_15No ratings yet
- A) Discuss How Student Can Plan For A Successful Laboratory Assignment SubmissionDocument2 pagesA) Discuss How Student Can Plan For A Successful Laboratory Assignment SubmissionNazhan HakeemNo ratings yet
- Bio150 Lab Report - Nurul Alya Binti MokhidinDocument4 pagesBio150 Lab Report - Nurul Alya Binti MokhidinAlya MokhidinNo ratings yet
- GasDocument12 pagesGasJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Discussion (Benzene)Document46 pagesContent-Based Discussion (Benzene)nang kubaiNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur Sem 1 2023Document11 pagesGerak Gempur Sem 1 2023Siva RajaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chapter 9 (Form 5) Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument49 pagesChemistry - Chapter 9 (Form 5) Manufactured Substances in IndustrySamyugta VijayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraDocument63 pagesJawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- CHM Lab Report, 3c.fathiahDocument17 pagesCHM Lab Report, 3c.fathiahFathiah NhNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Study of Matter: A Guide to ChemistryDocument15 pagesThe Scientific Study of Matter: A Guide to ChemistryLavarn PillaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Kapkim3400Document1 pageAssignment Kapkim3400Teow JeffNo ratings yet
- Free Radical Substitution Questions (Chemguide)Document2 pagesFree Radical Substitution Questions (Chemguide)bookdoudah0% (1)
- Chemistry Report 1Document6 pagesChemistry Report 1Athirah BidinNo ratings yet
- Complex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Document4 pagesComplex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Skema Test 1 Phy150 Apr 2019Document2 pagesSkema Test 1 Phy150 Apr 2019muhammad illyasNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument37 pagesPlant NutritionWen Shan ChuaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pressure, Mixing and Temperature on Acetic Acid-Baking Soda ReactionDocument11 pagesEffect of Pressure, Mixing and Temperature on Acetic Acid-Baking Soda ReactionElaine PuiNo ratings yet
- Latihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaDocument6 pagesLatihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Bio STPM 2018 2019Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Bio STPM 2018 2019Mohamad Sahimi Bin MahatNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials ExamDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials ExamViknaraj Subramaniam100% (1)
- Chemical Energetics QuestionsDocument34 pagesChemical Energetics QuestionsGeorge Choo100% (1)
- Taklimat Kerja KursusDocument33 pagesTaklimat Kerja KursusUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Hydrocarbonmeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- MOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Document19 pagesMOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Ung Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 3 CHM3201Document7 pagesLab Report Exp 3 CHM3201ARMAN AKRAM BIN OMAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document8 pagesExp 3ValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Determination of A Mixture of Xylene Isomers Using Infrared (Ir) SpectrometerDocument8 pagesExperiment 2: Determination of A Mixture of Xylene Isomers Using Infrared (Ir) SpectrometerNur Atiqah Mohd RedzuanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument39 pagesPhysicsRosdy DyingdemonNo ratings yet
- CALORIMETRY HESS’S LAW EXPERIMENTDocument7 pagesCALORIMETRY HESS’S LAW EXPERIMENTaqielah shaifulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Algebra dbm10133Document54 pagesChapter 1-Algebra dbm10133Nisa ArNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaDocument16 pagesTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- TU PTPTN Booklet Guidelines and Procedures 2019 PDFDocument18 pagesTU PTPTN Booklet Guidelines and Procedures 2019 PDFSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam Treatment Lowers Pollutants in Textile WastewaterDocument22 pagesElectron Beam Treatment Lowers Pollutants in Textile WastewaterFatimah Mohd JamilNo ratings yet
- STPM Trial Negeri Sembilan 2007 Chemistry Paper 2Document21 pagesSTPM Trial Negeri Sembilan 2007 Chemistry Paper 2stuart5051No ratings yet
- Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument13 pagesManufactured Substances in IndustryNorsuriani AwangNo ratings yet
- PHY 210-Chapter 4 StudentsDocument87 pagesPHY 210-Chapter 4 StudentsFatimah AzzahrahNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu - QDocument9 pagesTrial Terengganu - Qshinichi_kesian6117No ratings yet
- SECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionDocument15 pagesSECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionFazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Document39 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Yuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Direct Potentiometric Titration of Fluoride IonDocument3 pagesDirect Potentiometric Titration of Fluoride IonDozdiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Document12 pagesCHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (2)
- STPM2023 S1 PhysicsDocument18 pagesSTPM2023 S1 PhysicsNatasha TasaNo ratings yet
- 3-ethyl-2-methylhexaneThe longest continuous carbon chain is 6 carbons (hexane)The side chains are an ethyl group (CH2CH3) at carbon #3 and a methyl (CH3) at carbon #2Document55 pages3-ethyl-2-methylhexaneThe longest continuous carbon chain is 6 carbons (hexane)The side chains are an ethyl group (CH2CH3) at carbon #3 and a methyl (CH3) at carbon #2Karel BrionesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter on Structure and Properties of Carbon CompoundsDocument122 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter on Structure and Properties of Carbon Compoundssaxman011No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For USTH Students Lecture 2: Electrophilic Addition To C CDocument107 pagesOrganic Chemistry For USTH Students Lecture 2: Electrophilic Addition To C CminhminhNo ratings yet
- 3rd and 4 TH - Alkenes& AlkynesDocument45 pages3rd and 4 TH - Alkenes& AlkynesMontazer WorkNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7 & 8Document66 pagesChapters 7 & 8Amirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- c2 AlkenesDocument4 pagesc2 Alkenesapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Xylem: Transporting Water and Minerals in PlantsDocument2 pagesXylem: Transporting Water and Minerals in Plantsadam_baylinNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Mind Map MARCH 2009 PDFDocument1 pageAlkanes Mind Map MARCH 2009 PDFadam_baylinNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Assignment Front Cover ReportDocument1 pageBIOLOGY Assignment Front Cover Reportadam_baylinNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Mind Map MARCH 2009 PDFDocument1 pageAlkanes Mind Map MARCH 2009 PDFadam_baylinNo ratings yet