Professional Documents
Culture Documents
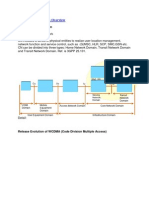
GSM Network Architecture, Mobility Management, SMS Delivery
Uploaded by
杜明訓Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM Network Architecture, Mobility Management, SMS Delivery
Uploaded by
杜明訓Copyright:
Available Formats
2010 Midterm Mobility Management 1. Describe the GSM network architecture. 2.
(i) Describe the following mobile identities: MSISDN, IMSI, TMSI, IMEI (ii) Which of the identities above are known to the GSM users? (iii) What are the advantages of TMSI over IMSI? 3. Can two VLRs generate the same TMSI? 4. How does an MS perform the very first registration? 5. Can you have more than one MSISDN numbers associated with one SIM card? Can two SIM cards have the same MSISDN number? Why? Chapter 1 1. Describe the procedure of SMS delivery from an MS to the other MS. (i) If the acknowledgment request is specified in the short message, which component will send an acknowledgement back to the original MS? (ii) If the short message receiver is not attached to the network (e.g., the MS is turned off), which component will resend the message until success or the message is expired? 2. Describe the NCTU-SMS architecture. What is the NCTU-SMS delivery state tree? 3. Describe the SMS architecture. Does delivery of SMS affects voice call setup? Does it affect voice conversation? 4. Compare the two SMS-IP integration approaches: NCTU-SMS (an approach involving SM-SC) and iSMS (an approach that does not involve SM-SC). Which approach will experience longer transmission delay for end-to-end short message delivery? 5. Describe the three service types defined in iSMS. Can you define a new service type for iSMS? Chapter 2 1. Draw the GSM/GRPS/UMTS networks architectures. 2. Why is RA introduced in GPRS and UMTS? Can we eliminate the concept of RA so that both SGSN and VLR track LA? 3. Consider the RRC state machine in Figure 2.4. In the Cell
4. 5. 6. 7.
Connected Mode, how does the machine know when to move to Idle Mode, and when to move to URA Connected Mode? What is the purpose of periodic location update? How do you set the periodic RA update timer? Draw the message flows for intra-SGSN RA update and interSGSN RA update. Draw the message flow for inter-SGSN SRNC relocation. Draw the message flow for combined hard handoff with SRNC relocation.
Chapter 4 1. Describe the meta-functions performed in the GGSN. 2. What is APN? In UMTS, which network nodes maintain the APN information? 3. In the PDP context activation procedure, how is the IP address of the GGSN derived? 4. Describe and compare the three tunneling techniques used between UMTS and external PDN Chapter 5 1. What is SRNC? What is DRNC? Draw a figure to illustrate which is the SRNC and which is the DRNC. 2. Describe SRNC duplication (SD), core network bi-casting (CNB), and fast SRNC relocation (FSR).
You might also like
- GPRS Wireless Project OverviewDocument12 pagesGPRS Wireless Project OverviewVinayakNo ratings yet
- Interview - QST Ans TelecomDocument19 pagesInterview - QST Ans TelecomSwarna Sekhar Dhar100% (1)
- Interview Preparation - GSM Network Components & FunctionsDocument15 pagesInterview Preparation - GSM Network Components & FunctionsAashish VigNo ratings yet
- BSNL 3G NETWORK AND SERVICESDocument11 pagesBSNL 3G NETWORK AND SERVICESVIKAS NIGAMNo ratings yet
- Ussd Gateways Esme AND GSM ServicesDocument103 pagesUssd Gateways Esme AND GSM Services15octNo ratings yet
- MK Kapita Selekta Sistem Instrumentasi GPRSDocument7 pagesMK Kapita Selekta Sistem Instrumentasi GPRSHandy MoseyNo ratings yet
- GPRS PDFDocument6 pagesGPRS PDFHandy MoseyNo ratings yet
- IMS Service Centralization and Continuity Guidelines 9 May 2012Document14 pagesIMS Service Centralization and Continuity Guidelines 9 May 2012eru5No ratings yet
- GSM Idle Mode BehaviourDocument2 pagesGSM Idle Mode BehaviourBipin JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Common Control Channel (CCCH) Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH)Document3 pagesUnit-Iii: Common Control Channel (CCCH) Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH)Mustafa Troy TroyNo ratings yet
- 2G & 3G Network Planning OptimizationDocument3 pages2G & 3G Network Planning Optimizationdungnt84No ratings yet
- Research Paper On GSM ArchitectureDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On GSM Architecturenodahydomut2100% (1)
- GSM - GPRS CP - 02 GSM and GPRS System DescriptionDocument36 pagesGSM - GPRS CP - 02 GSM and GPRS System Descriptionadelhamadi007No ratings yet
- 1.12 Location UpdateDocument3 pages1.12 Location Updateyaser.ahmedNo ratings yet
- What Is IUBDocument17 pagesWhat Is IUBtuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- 1.16 Call Re-EstablishmentDocument3 pages1.16 Call Re-Establishmentrathore_123No ratings yet
- Call Setup in A GSM NetworkDocument6 pagesCall Setup in A GSM NetworkluvdembadNo ratings yet
- System Introduction: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSystem Introduction: ObjectivesSudhakar BsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- GSM Full InitialDocument22 pagesGSM Full Initialvishwajeet1986100% (1)
- IT-702 WMC Assignment Unit 1: Q.N o Questions MarksDocument3 pagesIT-702 WMC Assignment Unit 1: Q.N o Questions MarksamaniNo ratings yet
- The Market Forecast of HLR (English Version)Document26 pagesThe Market Forecast of HLR (English Version)Ian YeonNo ratings yet
- CM CFA EB Quick Ref MaterialDocument20 pagesCM CFA EB Quick Ref MaterialJayaNo ratings yet
- Procedures: UMTS System OverviewDocument45 pagesProcedures: UMTS System OverviewRock DolphinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Machindra GaikarNo ratings yet
- GPRS Networks Location Management FactorsDocument20 pagesGPRS Networks Location Management FactorsNicky NiranjanNo ratings yet
- IT351 - Mobile & Wireless Computing Tutorial - 5Document3 pagesIT351 - Mobile & Wireless Computing Tutorial - 5Blaise TembongNo ratings yet
- It1402 Mobile Computing 2Document24 pagesIt1402 Mobile Computing 2bhrathikNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SystemsDocument136 pagesMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Sri Vidya College Mobile Computing Course Material QuestionsDocument3 pagesSri Vidya College Mobile Computing Course Material QuestionsMustafa Troy TroyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication ProblemsDocument4 pagesMobile Communication ProblemsIshan DixitNo ratings yet
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pages2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555No ratings yet
- Scavenger Hunt QuestionsDocument4 pagesScavenger Hunt QuestionsKA de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Relative Resource Manager 2Document18 pagesRelative Resource Manager 2Jack WilshireNo ratings yet
- GSM Short Message ServiceDocument13 pagesGSM Short Message ServiceihabgamilNo ratings yet
- Cs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Document20 pagesCs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Rama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- GSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioDocument5 pagesGSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioImen DjebliNo ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersNivithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-gsm, Umts, LteDocument23 pagesChapter 6-gsm, Umts, LteNurlign YitbarekNo ratings yet
- What Is MSRN? in Which Type of Call ItDocument2 pagesWhat Is MSRN? in Which Type of Call Itlushanga100% (3)
- Sig TranDocument6 pagesSig TranRao UmairNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oDocument34 pagesBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithNo ratings yet
- Core NetworkDocument13 pagesCore Networksamba5113100% (1)
- QB3Document14 pagesQB3prakash_oxfordNo ratings yet
- E5-E6 - Text - Chapter 3. Overview of Mobile CommunicationDocument46 pagesE5-E6 - Text - Chapter 3. Overview of Mobile Communicationsumit15sksNo ratings yet
- The history and overview of the GSM mobile systemDocument18 pagesThe history and overview of the GSM mobile systemhieuvnp3No ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersValar MathiNo ratings yet
- Program: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thDocument17 pagesProgram: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thNidhi ChavanNo ratings yet
- GMSC Routes Calls Outside Mobile NetworkDocument5 pagesGMSC Routes Calls Outside Mobile NetworkUtkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sms Transmission Using Pdu Mode and Bit Coding SchemeDocument6 pagesSms Transmission Using Pdu Mode and Bit Coding Schemeclementlambert891No ratings yet
- GSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsDocument11 pagesGSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsalonindNo ratings yet
- Question Bank SUBJECT: GSM (06EC844) Part-A: Unit 1 (GSM Architecture and Interfaces)Document6 pagesQuestion Bank SUBJECT: GSM (06EC844) Part-A: Unit 1 (GSM Architecture and Interfaces)Santhosh VisweswarappaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocument25 pagesLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- MD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01Document17 pagesMD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01MD HasanNo ratings yet
- How To Determine The Location of A Mobile Subscriber: Sergey PuzankovDocument3 pagesHow To Determine The Location of A Mobile Subscriber: Sergey PuzankovMisterAto MaisonNo ratings yet
- 16MC5T023Document2 pages16MC5T0233201313No ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Intruder alarm control panel manualDocument40 pagesIntruder alarm control panel manualJohnny WalkerNo ratings yet
- Farmpacker 200FPX Manual-CDocument177 pagesFarmpacker 200FPX Manual-CElvio Alvitez TandaypanNo ratings yet
- Ds Datalog8 040416 UkDocument2 pagesDs Datalog8 040416 UkMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Installation and Use Instructions 7 Day Electronic Timer (TE103)Document2 pagesInstallation and Use Instructions 7 Day Electronic Timer (TE103)eeindustrialNo ratings yet
- Manual Crossover Focal Utopia Be CrossblockDocument31 pagesManual Crossover Focal Utopia Be CrossblockJason B.L. ReyesNo ratings yet
- 5G Tech Express 2019 HuaweiDocument75 pages5G Tech Express 2019 HuaweiUmar Mir100% (2)
- Handheld Scanner Series BCS 3600: User ManualDocument110 pagesHandheld Scanner Series BCS 3600: User ManualAhmad IbrahimNo ratings yet
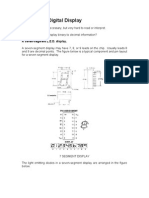
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument6 pages7 Segment DisplayTwesigomwe Gilbert GabrielNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 RTLDocument46 pagesChapter7 RTLNamrata ChughNo ratings yet
- Introducing Samsung DVD Recorder (DVD-R128 - R129)Document74 pagesIntroducing Samsung DVD Recorder (DVD-R128 - R129)tomverstratenNo ratings yet
- HCC/HCF4000B-4001B HCC/HCF4002B-4025B: Nor GateDocument13 pagesHCC/HCF4000B-4001B HCC/HCF4002B-4025B: Nor Gatedhiya auliaNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument43 pagesTransformersDavid LeviNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning MIKEHOLTDocument1 pageAir Conditioning MIKEHOLTWilliamNo ratings yet
- Action Replay CodesDocument5 pagesAction Replay CodesSunghoon Yook0% (1)
- OJT Certificates Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegeDocument5 pagesOJT Certificates Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegeChristian Albert HuertoNo ratings yet
- Operating System For WSN: - OS For Data Centric & Resource Constraint WSN - Category of Sensor NodeDocument20 pagesOperating System For WSN: - OS For Data Centric & Resource Constraint WSN - Category of Sensor NodechristopherNo ratings yet
- 3 Operation Instructions, PLC SystemDocument25 pages3 Operation Instructions, PLC SystemheemaNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Broadband Design Methodology For Linearized High-Efficiency Continuous Class-F Power AmplifiersDocument12 pagesA Simplified Broadband Design Methodology For Linearized High-Efficiency Continuous Class-F Power AmplifiersG H Raisoni College of Engineering NagpurNo ratings yet
- Pic 01 INTRO PDFDocument29 pagesPic 01 INTRO PDFChintan Shah100% (1)
- CCIE Data Center Cheat Sheet TitleDocument4 pagesCCIE Data Center Cheat Sheet TitleNapster KingNo ratings yet
- Minibreakers s280Document46 pagesMinibreakers s280Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Mini-Spectrometer Kacc9003eDocument34 pagesMini-Spectrometer Kacc9003eTalhaNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxides Semiconductor CeramicsDocument14 pagesMetal Oxides Semiconductor Ceramicsumarasad1100% (1)
- Partial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodsDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge Measurement Coupling MethodskashifNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault Location MethodsDocument10 pagesCable Fault Location MethodsPaulo Cardoso0% (1)
- 4730 0013 04bDocument966 pages4730 0013 04bDoron ForshtatNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Computers: 5 Generations from Abacus to AIDocument7 pagesEvolution of Computers: 5 Generations from Abacus to AIOscarLopezHernandez100% (1)
- A Study On Market Segmentation of Samsung Electronics Ltd. With Special References To Mobile PhonesDocument6 pagesA Study On Market Segmentation of Samsung Electronics Ltd. With Special References To Mobile PhonesAgus Ari SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 40-91025-2 en 120V 60HzDocument4 pagesDatasheet 40-91025-2 en 120V 60HzVulpe FlorianNo ratings yet
- Procedure For SCC & OCC TestDocument3 pagesProcedure For SCC & OCC TestAyan MajiNo ratings yet