Professional Documents
Culture Documents
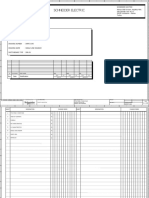
One Line Diagram
Uploaded by
netsavy71Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
One Line Diagram
Uploaded by
netsavy71Copyright:
Available Formats
ONE-LINE DIAGRAMS
The one-line diagram is the blueprint for electrical system analysis. It is the first step in preparing a critical response plan, allowing you to become thoroughly familiar with the electrical distribution system layout and design in your facility.
Whether you have a new or existing facility, the one-line diagram is the vital roadmap for all future testing, service and maintenance actions. As such, the one-line diagram is like a balance sheet for your facility and provides a snapshot of your facility at a moment in time. It needs to be modified as your facility changes to ensure that your systems are adequately protected. An effective one-line diagram will clearly show how the main components of the electrical system are connected, including redundant equipment and available spares. It shows a correct power distribution path from the incoming power source to each downstream load including the ratings and sizes of each piece of electrical equipment, their circuit conductors, and their protective devices. In many process facilities, loads are continually added or removed in small increments. The net effect is not always seen until some part of the system becomes overloaded or exhibits other problems. Many times circuits are added without appropriate modifications of the standard settings on the associated upstream circuit breakers. Regardless of which protective devices you use, they must be coordinated with regard to their time/current curves and with each other. The one-line diagram provides the roadmap to enable proper design of equipment, redundancy, and protection. NFPA-70E requirements mandate accurate, up-to-date one-line diagrams. To meet these needs, Arc Flash Advisors can conduct a comprehensive site survey to develop one-line diagrams for your facility or to update existing diagrams. Including: Verify process is in place that ensures the as-built drawings are maintained in a current condition Confirm loads connected to emergency / standby feeders Inventory of equipment Evaluate design redundancy of critical systems (N, N+1, N+2...) and whether all critical equipment can be maintained without a shutdown Verify existence of as-built drawings and that they are adequately available Verify potential single points of failure Report that outlines the findings by site along with recommended actions Update customer-provided one-line drawings down to the 480V Distribution Switchboards Provide a copy of one-line electrical diagram in AutoCAD format Post as-built drawings at each facility An up-to-date one line diagram is vital for a variety of service activities including: Short circuit calculations
Coordination studies Load flow studies Safety evaluation studies All other engineering studies Electrical safety procedures Efficient maintenance Features & Benefits Helps identify fault locations and simplifies troubleshooting Ensure safety of personnel Stay compliant with NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 requirements Ensure safe, reliable operation of facility Scope of a one line diagram One line diagram information normally includes: Incoming lines (voltage and size capacity and rating) Incoming main fuses, potheads, cut-outs, switches and main and tie breakers Power transformers (rating, winding connection and grounding means) Feeder breakers and fused switches Relays (function, use and type) Current/potential transformers (size, type and ratio) Control transformers All main cable and wire runs with their associated isolating switches and potheads (size and length of run) All substations, including integral relays and main panels and the exact nature of the load in each feeder and on each substation Critical equipment voltage and size (UPS, battery, generator, power distribution, transfer switch, computer room air conditioning)
Work Instructions for preparation of Single line Diagram
The One line Diagram Indicates the flow of electrical system from the source to the loads. Different type of one lines are prepared for different applications This work instruction details the requirements for the preparation of Single line diagram for continuous process industry. Documents required for preparation of SINGLE LINE DIAGRAM 1. Load List This document contains the various loads present in the plant and indicates the capacity of the load with the voltage level. 2. Design Basis This document details the type of electrical connection to be used for the various loads and the protection requirements as per the relevant standards. 3. The ratings of the various components like the transformer, breakers, cables, busbars, Current transformers, motors, Package electrical systems like the UPS, DC system, are indicated in the Single line diagram. DETAILS OF COMPONENTS 1) Transmission line: TL connecting to the switchyard/substation at the plant end from the grid shall be shown. Rating of the same shall be mentioned in kV and and length of the line. 2) Grid : Grid data like MVAsc and X/R ratio shall be shown. 3) Transformer MVA rating, transformer voltage ratio, Impedance, winding type, frequency shall be indicated. 4) Breaker Ampere frame/Ampere trip rating, voltage rating, 3 or 3P+N or 4 P type, with/without releases, Local/remote operability, will need to be indicated. 5) Current transformers and potential transformers: They shall be used as per the protection and measuring requirements. 6) Busbars : Bus bar is the common point at which the incomer and outgoing feeders are connected. Rating of the bus bars mentioned based on the continuous ampere rating of the total connected load (MD) and short circuit value. Usually two bus bars are used in series and are connected with bus coupler. It is required to ensure loads on both the buses should be balanced. 7) MV switchgear: MV switchgear shall shown in block with starter / feeder type for the loads check for the design basis for the loads to
consider in MV rating switchgear and ensure for proper spare feeders 8) LV switchgear: LV switchgear / MCC/PMCC/PCC shall be shown in block with starter / feeder type for the loads. Check for the design basis for the loads to consider in LV switchgear and ensure for proper spare feeders. 9) Capacitor bank: capacitor banks are used in order to compensate for the lagging power factor. Ratings are mentioned in kVAr. 10) Cables: There may be HV/LV cable shall be used as per the feeder rating of rating of the load and short circuit value. Cables shall be sized based on the design criteria. 11) Motor: Motors are the major part of the load in any industrial plant. Motor ratings are mentioned as per their kW and Voltage rating. 12) DG set: DG sets are connected to the essential loads/critical loads and ratings are mentioned in MVA, Volts, pf and % X (impedance) value. 13) DC system: DC systems used shall be shown as per the requirement. DC sizing shall be done as per the plant requirement. Ratings of the DC battery is Vdc and Ah. Redundancy shall be provided as per the design basis. 14) UPS: UPS system required shall be shown in SLD.
15) Lighting DB: feeders for lighting DB shall be shown in terms of Amps 16) Welding receptacle DB: Feeder for welding receptacle board shall be shown in terms of Amps. 17) Scopes for the vendor package and customer/clients shall be clearly shown. 18) Legends and symbols shall be properly followed as per the international standards (IEC). And shall be shown in SLD. 19) All the measuring and protection functions and their interlocks shall be shown in protection SLD as per the standard protection required as per the international standards. 20) Auto/manual transfer scheme for the tie buses shall be verified for proper logic.
You might also like
- Electrical Single Line Diagram GuidanceDocument3 pagesElectrical Single Line Diagram Guidancen73686861No ratings yet
- FR3 LV Insulation CoordinationDocument43 pagesFR3 LV Insulation CoordinationRihlesh ParlNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Lighting System Design (HKU)Document2 pagesElectrical and Lighting System Design (HKU)李梓誠No ratings yet
- Arcflash PDFDocument57 pagesArcflash PDFEma Robertho NaniNo ratings yet
- Generator Grounding SystemDocument4 pagesGenerator Grounding Systemaanas36624100% (1)
- Overview of Grid Code and Operational Requirements of Grid-Connected Solar PV Power Plants-NOTA TECNICADocument7 pagesOverview of Grid Code and Operational Requirements of Grid-Connected Solar PV Power Plants-NOTA TECNICAEdgardo Kat ReyesNo ratings yet
- Absolyte Engineering PDFDocument110 pagesAbsolyte Engineering PDFwizlishNo ratings yet
- 15-Chapter 4 Short Circuit Analysis-Objectives and MethodologyDocument4 pages15-Chapter 4 Short Circuit Analysis-Objectives and MethodologyRyan Anthony UmaliNo ratings yet
- Calculation Short Circuit LengkapDocument80 pagesCalculation Short Circuit LengkapInsan AzizNo ratings yet
- Skip To Main Content Catalog Electrical Solutions Xchange™ NFCSS™Document18 pagesSkip To Main Content Catalog Electrical Solutions Xchange™ NFCSS™mujib100% (1)
- Battery EeeDocument27 pagesBattery EeeNaisarg ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Trainer Guide PDFDocument99 pagesTrainer Guide PDFPhil ChawiraNo ratings yet
- Busway PDFDocument148 pagesBusway PDFJavier OmarNo ratings yet
- Iecen 62040 1 2Document11 pagesIecen 62040 1 2pravinuntooNo ratings yet
- UPS With BypassDocument4 pagesUPS With BypassfaizalpsNo ratings yet
- Sub-Station SpecificationDocument6 pagesSub-Station SpecificationsbpathiNo ratings yet
- How To Size DG Set - CumminsDocument4 pagesHow To Size DG Set - CumminsNalin KumarNo ratings yet
- Grounding Considerations For Large kVA Pad-Mount TransformersDocument4 pagesGrounding Considerations For Large kVA Pad-Mount TransformersRuwan DeegayuNo ratings yet
- Indelec Lightning Conductors Surge Protection PDFDocument107 pagesIndelec Lightning Conductors Surge Protection PDFDennis S.0% (1)
- ERS REPORT OF Com Site 3Document20 pagesERS REPORT OF Com Site 3Areeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Single Line DiagramDocument6 pagesSingle Line DiagramMuhammad Hammad Sabir PansotaNo ratings yet
- Overview of IEEE Color BooksDocument9 pagesOverview of IEEE Color Bookssalsa222100% (1)
- Gabinete Eléctrico Schneider SMFR71348 A DM1DDocument8 pagesGabinete Eléctrico Schneider SMFR71348 A DM1DEduardo Antonio Juarez CarreonNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument30 pagesMajor ProjectRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- 9 Recommended Practices For GroundingDocument6 pages9 Recommended Practices For Groundingsikander843562No ratings yet
- Installation Practices FOR Cable Raceway Systems: The Okonite CompanyDocument56 pagesInstallation Practices FOR Cable Raceway Systems: The Okonite CompanyharlyganNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and DesignDocument13 pagesPower System Analysis and DesignMian Junaid MuzamilNo ratings yet
- NGR Brochure 2009Document7 pagesNGR Brochure 2009Amit sahaNo ratings yet
- Discrimination CurveDocument6 pagesDiscrimination Curvemilekitic2005No ratings yet
- Equipment Ring Main Unit Sno Spec Clause No. Query / Clarification Required Bidder's Response Resolution Technical Resolution Project: Name of ManufacturerDocument4 pagesEquipment Ring Main Unit Sno Spec Clause No. Query / Clarification Required Bidder's Response Resolution Technical Resolution Project: Name of Manufacturersyedabuthahir_mNo ratings yet
- Safety Compl - SS Earthing DesignDocument5 pagesSafety Compl - SS Earthing DesignRahul SinganiaNo ratings yet
- SLDDocument8 pagesSLDHARIS AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- 1 Tutorial Handouts 150Document80 pages1 Tutorial Handouts 150GokulGopiNo ratings yet
- Seeds-I: Revision No. 00Document22 pagesSeeds-I: Revision No. 00ArnieNo ratings yet
- HV Electrical Calculation NoteDocument15 pagesHV Electrical Calculation NoteJohan BLANDIGNERESNo ratings yet
- Study of Different Components and Their Functions of An Air Circuit Braker (ACB)Document5 pagesStudy of Different Components and Their Functions of An Air Circuit Braker (ACB)Zahid Hasan KhokaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Power CablesDocument4 pagesSelection of Power Cablesa.wNo ratings yet
- Digital Switchgear Concepts For MV Applications 61850 and IoT Advantages PDFDocument69 pagesDigital Switchgear Concepts For MV Applications 61850 and IoT Advantages PDFAdamNo ratings yet
- Ieee 1584 and Nfpa 70eDocument5 pagesIeee 1584 and Nfpa 70ejesusbarajasNo ratings yet
- In S Coords Ample CalcDocument36 pagesIn S Coords Ample CalcPankaj ThataiNo ratings yet
- Lightning ProtectionDocument9 pagesLightning Protectioncharitha RanwalaNo ratings yet
- Basic Line ProtectionDocument30 pagesBasic Line ProtectionMaduike Obinna HenryNo ratings yet
- 2012Ch1 Supple NotesDocument12 pages2012Ch1 Supple Noteskhaldoun samiNo ratings yet
- Ibusway For Data Center An Innovative Rack Power Distribution Ready For It Room EvolutionsDocument25 pagesIbusway For Data Center An Innovative Rack Power Distribution Ready For It Room EvolutionsSargurusivaNo ratings yet
- Busbar Arrangement (BUSBAR SCHEME) PDFDocument7 pagesBusbar Arrangement (BUSBAR SCHEME) PDFRaditya Ghani100% (1)
- Emergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting AnalysisDocument6 pagesEmergency Generator Sizing and Motor Starting AnalysisK.RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Selection of Surge Protective Device (SPD) - (Part 3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument8 pagesSelection of Surge Protective Device (SPD) - (Part 3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesRahul ItaliyaNo ratings yet
- Ibusway AECOMDocument25 pagesIbusway AECOMSargurusivaNo ratings yet
- Spec Motor Control CentersDocument12 pagesSpec Motor Control CentersDolyNo ratings yet
- Heatloss in Industrial Plants Part 1 PDFDocument10 pagesHeatloss in Industrial Plants Part 1 PDFMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Busduct Catalogue PDFDocument184 pagesBusduct Catalogue PDFJulian RiañoNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protective Device Coordination StudyDocument3 pagesOvercurrent Protective Device Coordination StudySankalp TiwariNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design GuideDocument222 pagesElectrical Design GuideMeCebu Philippinetonan100% (1)
- Project PowerdistributionDocument10 pagesProject Powerdistributionchilamkurti_sivasankararaoNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationDocument46 pagesSingle Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationWelday100% (1)
- PTW Dapper ADocument4 pagesPTW Dapper Aoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- Design Guide 2015 LV Power Factor Correction Cubicles Panel Builder GuideDocument72 pagesDesign Guide 2015 LV Power Factor Correction Cubicles Panel Builder Guidehizbi7100% (2)
- General Rules of Electrical Installation Design: Chapter ADocument20 pagesGeneral Rules of Electrical Installation Design: Chapter Agenial72No ratings yet
- Single-Line Diagrams: Ensuring ComplianceDocument2 pagesSingle-Line Diagrams: Ensuring ComplianceAhmed MagdyNo ratings yet
- EIG A Electrical DesignDocument20 pagesEIG A Electrical DesignMahmoud FakhereddinNo ratings yet
- The Age of Analytics - Competing in A Data-Driven World - McKinsey & CompanyDocument6 pagesThe Age of Analytics - Competing in A Data-Driven World - McKinsey & Companynetsavy71No ratings yet
- Isolator 1pdfDocument326 pagesIsolator 1pdfnetsavy71No ratings yet
- Symbols Used: Multiplication: X or : (Specific Gravity of Material)Document3 pagesSymbols Used: Multiplication: X or : (Specific Gravity of Material)netsavy71No ratings yet
- Power & Control Cables: Document Title: Document No.: PMCDocument6 pagesPower & Control Cables: Document Title: Document No.: PMCnetsavy71No ratings yet
- Short Circuit and Arc FlashDocument20 pagesShort Circuit and Arc FlashRene GonzalezNo ratings yet
- SPI User GuideDocument1,812 pagesSPI User GuideSatish Sohani67% (3)
- Daleel CTRDocument5 pagesDaleel CTRnetsavy71No ratings yet
- Health Insurance in IndiaDocument7 pagesHealth Insurance in Indianetsavy71No ratings yet
- Training Manual For Local ConsultantsDocument24 pagesTraining Manual For Local Consultantsnetsavy71No ratings yet
- (India) PVT LTD: FJ5705 1/6 - SS 75 6008/I 140597101Document22 pages(India) PVT LTD: FJ5705 1/6 - SS 75 6008/I 140597101netsavy71No ratings yet
- Investment Trends 2013Document14 pagesInvestment Trends 2013netsavy71No ratings yet
- DCS PLCDocument21 pagesDCS PLCnetsavy71No ratings yet
- Leadership Essentials For Process ProfessionalsDocument30 pagesLeadership Essentials For Process ProfessionalsSteven BonacorsiNo ratings yet
- Space Requirements For Electrical RoomsDocument2 pagesSpace Requirements For Electrical Roomsnetsavy71100% (1)
- Drill Site Audit ChecklistDocument5 pagesDrill Site Audit ChecklistKristian BohorqzNo ratings yet
- Summary Scholten's GroupsDocument8 pagesSummary Scholten's GroupsLily Samardzic-Rafik100% (4)
- 13 Lombe Mumba Ramson 2017 Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Breast Self Examination For Early Detectoin of Breast Cancer Among Women in Roan Constituency in Luanshya Copperbelt Province ZambiaDocument9 pages13 Lombe Mumba Ramson 2017 Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Breast Self Examination For Early Detectoin of Breast Cancer Among Women in Roan Constituency in Luanshya Copperbelt Province ZambiaArick Frendi AndriyanNo ratings yet
- 2023 VGP Checklist Rev 0 - 23 - 1 - 2023 - 9 - 36 - 20Document10 pages2023 VGP Checklist Rev 0 - 23 - 1 - 2023 - 9 - 36 - 20mgalphamrn100% (1)
- Mbs KatalogDocument68 pagesMbs KatalogDobroslav SoskicNo ratings yet
- PD 984Document38 pagesPD 984mav3riick100% (2)
- DSM-5 Personality Disorders PDFDocument2 pagesDSM-5 Personality Disorders PDFIqbal Baryar0% (1)
- Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulator (C.E.S.) Earlobe Stimulator, Pocket-Transportable, 9VDocument1 pageCranial Electrotherapy Stimulator (C.E.S.) Earlobe Stimulator, Pocket-Transportable, 9VemiroNo ratings yet
- Fomula Spreadsheet (WACC and NPV)Document7 pagesFomula Spreadsheet (WACC and NPV)vaishusonu90No ratings yet
- Effect of Moisture Content On The Extraction Rate of Coffee Oil From Spent Coffee Grounds Using Norflurane As SolventDocument8 pagesEffect of Moisture Content On The Extraction Rate of Coffee Oil From Spent Coffee Grounds Using Norflurane As SolventMega MustikaningrumNo ratings yet
- Pet 402Document1 pagePet 402quoctuanNo ratings yet
- Aircaft Avionics SystemDocument21 pagesAircaft Avionics SystemPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- FNCP Improper Waste DisposalDocument2 pagesFNCP Improper Waste DisposalKathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Synthesis ConverterDocument26 pagesAmmonia Synthesis ConverterKvspavan Kumar100% (1)
- Data Management For Human Resource Information SystemDocument14 pagesData Management For Human Resource Information SystemRajeshsharmapurangNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document9 pagesMini Project 2gunjan_pattnayak2007No ratings yet
- Poisoned NeedleDocument147 pagesPoisoned NeedleMark Cooper100% (3)
- Senographe Crystal: The Choice Is Crystal ClearDocument7 pagesSenographe Crystal: The Choice Is Crystal ClearmuhammadyassirNo ratings yet
- E3sconf 2F20187307002Document4 pagesE3sconf 2F20187307002Nguyễn Thành VinhNo ratings yet
- EngineCleaningAndVolcanicAsh InternDocument69 pagesEngineCleaningAndVolcanicAsh InternLucio Portuguez AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Brain Slides SEMINAR 1 - 220606 - 142811 - 220606 - 223805Document32 pagesBrain Slides SEMINAR 1 - 220606 - 142811 - 220606 - 223805pang pangNo ratings yet
- Rotary Screw Gas: CompressorsDocument2 pagesRotary Screw Gas: CompressorsLucas SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Ground-Fault Protection - All You Need To KnowDocument9 pagesGround-Fault Protection - All You Need To KnowCamila RubioNo ratings yet
- Photoperiodism Powerpoint EduDocument12 pagesPhotoperiodism Powerpoint EduAlabi FauziatBulalaNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: Explosion-Proof Motor Mf07, Mf10, Mf13Document18 pagesOwner'S Manual: Explosion-Proof Motor Mf07, Mf10, Mf13mediacampaigncc24No ratings yet
- Wago PCB Terminal Blocks and Connectors Catalog 7Document105 pagesWago PCB Terminal Blocks and Connectors Catalog 7alinupNo ratings yet
- High CarbonDocument2 pagesHigh CarbonKarisoNo ratings yet
- Ifm Product Innovations PDFDocument109 pagesIfm Product Innovations PDFJC InquillayNo ratings yet
- Studovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)Document8 pagesStudovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Test Questions For Oncologic DisordersDocument6 pagesTest Questions For Oncologic Disorderspatzie100% (1)