Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nassereldeen Ahmed Kabashi Department of Biotechnology Engineering, Tel: Ext. 4524 Sem I, 2011-2012 BTE 4415 Bioprocess Control
Uploaded by
Hana HamidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nassereldeen Ahmed Kabashi Department of Biotechnology Engineering, Tel: Ext. 4524 Sem I, 2011-2012 BTE 4415 Bioprocess Control
Uploaded by
Hana HamidCopyright:
Available Formats
NASSERELDEEN AHMED KABASHI
DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
ENGINEERING
nasreldin@iium.edu.my, Tel : Ext. 4524
Sem I, 2011-2012
BTE 4415 Bioprocess Control
Week 11:
Dynamic Response
Part E: Rouths Stability Criterion
Sem I, 2011-2012
Introduction
Goal: Determining whether the system
is stable or unstable from a
characteristic equation in polynomial
form without actually solving for the
roots.
Rouths stability criterion is useful for
determining the ranges of coefficients of
polynomials for stability, especially when
the coefficients are in symbolic
(nonnumerical) form
Sem I, 2011-2012
A necessary condition for
Routh Stability
A necessary condition for stability of the
system is that all of the roots of its
characteristic equation have negative
real parts, which in turn requires that all
the coefficients be positive.
A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for stability
is that all the coefficients of the polynomial
characteristic equation be positive.
Sem I, 2011-2012
A necessary and sufficient
condition for Stability
Rouths formulation requires the
computation of a triangular array that
is a function of the coefficients of the
polynomial characteristic equation.
A system is stable if and only if all the elements of
the first column of the Routh array are positive
Sem I, 2011-2012
Characteristic Equation
Consider an nth-order system whose the
characteristic equation (which is also the
denominator of the transfer function) is:
0
0
1
1
2
2
1
1
) ( s a s a s a s a s s a
n
n n n
+ + + + + =
Sem I, 2011-2012
Method for determining the
Routh array
Consider the characteristic equation:
First arrange the coefficients of the
characteristic equation in two rows,
beginning with the first and second
coefficients and followed by the even-
numbered and odd-numbered coefficients:
0
0
1
1
3
3
2
2
1
1
1 s a s a s a s a s a s ) s ( a
n
n n n n
+ + + + + + =
5 3 1
1
4 2
:
1 :
a a a s
a a s
n
n
Sem I, 2011-2012
Routh array: method (contd)
Then add
subsequent rows
to complete the
Routh array:
* :
* :
* * :
:
:
:
1 :
0
1
2
3 2 1
3
3 2 1
2
5 3 1
1
4 2
s
s
s
c c c s
b b b s
a a a s
a a s
n
n
n
n
?!
Sem I, 2011-2012
Routh array: method (contd)
Compute elements
for the 3
rd
row:
* :
* :
* * :
:
:
:
1 :
0
1
2
3 2 1
3
3 2 1
2
5 3 1
1
4 2
s
s
s
c c c s
b b b s
a a a s
a a s
n
n
n
n
1
1 6 7
3
1
1 4 5
2
1
1 2 3
1
1
,
1
,
1
a
a a a
b
a
a a a
b
a
a a a
b
=
=
=
Sem I, 2011-2012
Routh array: method (contd)
Compute elements
for the 4
th
row:
* :
* :
* * :
:
:
:
1 :
0
1
2
3 2 1
3
3 2 1
2
5 3 1
1
4 2
s
s
s
c c c s
b b b s
a a a s
a a s
n
n
n
n
1
1 7 4 1
3
1
1 5 3 1
2
1
1 3 2 1
1
,
,
b
b a b a
c
b
b a b a
c
b
b a b a
c
=
=
=
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 1:
Given the characteristic equation,
is the system described by this characteristic
equation stable?
Answer:
One coefficient (-2) is negative.
Therefore, the system does not satisfy the
necessary condition for stability.
4 s 4 s s 2 s 3 s 4 s ) s ( a
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + =
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 2:
Given the characteristic equation,
is the system described by this characteristic
equation stable?
Answer:
All the coefficients are positive and nonzero.
Therefore, the system satisfies the necessary
condition for stability.
We should determine whether any of the
coefficients of the first column of the Routh array
are negative.
4 4 2 3 4 ) (
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + + = s s s s s s s a
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 2 (contd): Routh array
4 4 2 3 4 ) (
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + + = s s s s s s s a
? : s
? ? : s
? ? : s
? ? ? : s
? ? ? : s
0 4 2 4 : s
4 1 3 1 : s
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 2 (contd): Routh array
? :
? ? :
? ? :
? ? ? :
4 0 2 5 :
0 4 2 4 :
4 1 3 1 :
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
4 4 2 3 4 ) (
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + + = s s s s s s s a
2
5
4
10
4
4 3 2 1
=
0
4
0
4
4 1 4 1
= =
4
4
16
4
4 4 0 1
=
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 2 (contd): Routh array
? :
? ? :
? ? :
0 5 12 2 :
4 0 2 5 :
0 4 2 4 :
4 1 3 1 :
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
4 4 2 3 4 ) (
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + + = s s s s s s s a
2 ) 2 (
2 5
2 5 2 0 4
= =
5
12
5
20 32
2 5
2 5 4 4 4
=
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 2 (contd): Routh array
4 :
0 15 76 :
4 3 :
0 5 12 2 :
4 0 2 5 :
0 4 2 4 :
4 1 3 1 :
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
4 4 2 3 4 ) (
2 3 4 5 6
+ + + + + + = s s s s s s s a
The elements of
the 1
st
column
are not all positive:
the system is unstable
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 3: Stability versus
Parameter Range
Consider a feedback system such as:
The stability properties of this system are a
function of the proportional feedback gain K.
Determine the range of K over which the
system is stable.
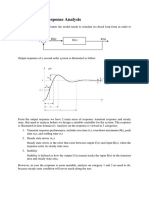
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 3 (contd)
The characteristic equation for the system is
given by:
0
) 6 )( 1 (
1
1 =
+
+
+
s s s
s
K
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 3 (contd)
Expressing the characteristic equation in
polynomial form, we obtain:
0 ) 6 ( 5
2 3
= + + + K s K s s
0
) 6 )( 1 (
1
1 =
+
+
+
s s s
s
K
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 3 (contd)
The corresponding
Routh array is:
Therefore, the
system is stable
if and only if
K s K s s s a + + + = ) 6 ( 5 ) (
2 3
K s
K s
K s
K s
:
5 ) 30 4 ( :
5 :
6 1 :
0
1
2
3
5 . 7 K
0 K and 5 . 7 K
0 K and 0
5
30 K 4
>
> >
> >
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 3 (contd)
Solving for the roots using MATLAB gives:
-5 and 1.22j for K=7.5
The system is unstable (or critically stable) for
K=7.5
-4.06 and 0.47 1.7j for K=13
-1.90 and 1.54 3.27j for K=25
=> The system is stable for both K=13 and K=25
K s K s s s a + + + = ) 6 ( 5 ) (
2 3
Sem I, 2011-2012
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
Time (sec)
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
Step-Response Versus K parameter
K=6.5
7
7.5
8
10
12.5
Sem I, 2011-2012
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4: Stability versus
Two Parameter Range
Consider a Proportional-Integral (PI) control
such as:
Find the range of the controller gains
so that the PI feedback system is stable.
) K , K (
1
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4 (contd)
The characteristic equation for the system is
given by:
0
2 1
1
1
1
=
+ +
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
) s )( s ( s
K
K
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4 (contd)
Expressing the characteristic equation in
polynomial form, we obtain:
0 2 3
1
2 3
= + + + + K s ) K ( s s
0
2 1
1
1
1
=
+ +
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
) s )( s ( s
K
K
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4 (contd)
The corresponding
Routh array is:
For stability, we
must have:
K s K s s s a + + + = ) 6 ( 5 ) (
2 3
1
0
1
1
1
2
3
3 3 6
3
2 1
K : s
) K K ( : s
K : s
K : s
+
+
2
3
0
1
1
> >
K
K and K
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4: Allowable region
for Stability
Sem I, 2011-2012
Example 4: Transient
Response for the System
Sem I, 2011-2012
You might also like
- Multiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsFrom EverandMultiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsNo ratings yet
- Clas 9Document28 pagesClas 9asimnaqvi2003No ratings yet
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementFrom EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument8 pagesStabilityGianco VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Material 5 - Time Domain Response Analysis-1Document6 pagesMaterial 5 - Time Domain Response Analysis-1Ninggar TitanNo ratings yet
- Stability CriterionDocument34 pagesStability CriterionNina ButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 - Stability AnalysisDocument27 pagesChapter4 - Stability AnalysisKedar BikkNo ratings yet
- Stability of Linear Systems: DR K P Mohandas, Professor, NIT CalicutDocument7 pagesStability of Linear Systems: DR K P Mohandas, Professor, NIT Calicutsuresh1virdiNo ratings yet
- Paper 6Document9 pagesPaper 6RakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam For Luminita Stevens Intermediate MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesSample Exam For Luminita Stevens Intermediate MacroeconomicsKevin ShaughnessyNo ratings yet
- FP6 SI0: A Numerical Approximation Method For Stochastic Differential Equations of It6 Type KanekoDocument2 pagesFP6 SI0: A Numerical Approximation Method For Stochastic Differential Equations of It6 Type KanekoAlexei HannaNo ratings yet
- Lect9 - Sys Char & RouthDocument15 pagesLect9 - Sys Char & RouthDominiqe LeVonta HodgeNo ratings yet
- Report 1 - Week 1 - Group 5Document10 pagesReport 1 - Week 1 - Group 5Bảo ThiênNo ratings yet
- EEE350 Control Systems: Assignment 2Document15 pagesEEE350 Control Systems: Assignment 2Nur AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Bivariate AnalysisDocument46 pagesBivariate AnalysisChef G KrishanaNo ratings yet
- Root-Locus Analysis of Delayed First and Second Order SystemsDocument8 pagesRoot-Locus Analysis of Delayed First and Second Order SystemsSanika TalathiNo ratings yet
- Three-Step Implicit Block Method For Second Order Odes: E.O. Adeyefa, F.L. Joseph and O.D. OgwumuDocument5 pagesThree-Step Implicit Block Method For Second Order Odes: E.O. Adeyefa, F.L. Joseph and O.D. OgwumuinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Co-Simulation Control of Robot Arm Dynamics in ADAMS and MATLABDocument6 pagesCo-Simulation Control of Robot Arm Dynamics in ADAMS and MATLABMarlon Andres Cajamarca VegaNo ratings yet
- Routh Hurwitz Stability Criteria - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 pagesRouth Hurwitz Stability Criteria - GATE Study Material in PDFPraveen AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ExamMSE 170122 TEORIEDocument9 pagesExamMSE 170122 TEORIEWolf Andrew 73No ratings yet
- Shainin Variable SearchDocument30 pagesShainin Variable Searchshivaprasadmvit100% (1)
- Revision PDFDocument11 pagesRevision PDFsdsds-54No ratings yet
- ECE-S513 Fundamentals of Systems III (Moshe Kam) : Final ExamDocument3 pagesECE-S513 Fundamentals of Systems III (Moshe Kam) : Final Exammurat FatihNo ratings yet
- Exam1 s16 SolDocument10 pagesExam1 s16 SolVũ Quốc NgọcNo ratings yet
- State Space Representation Part-1Document47 pagesState Space Representation Part-1SingappuliNo ratings yet
- Aashikpelokhai and MomoduDocument7 pagesAashikpelokhai and MomoduSandaMohdNo ratings yet
- UJ - Control - Semester Test#1 - 13 Sep - 2022Document6 pagesUJ - Control - Semester Test#1 - 13 Sep - 2022Dimakatso NgobeniNo ratings yet
- Delay-Dependent Robust H Control of Time-Delay Systems: M. Sun Y. JiaDocument9 pagesDelay-Dependent Robust H Control of Time-Delay Systems: M. Sun Y. JiainfodotzNo ratings yet
- Test 2: ENGI 5821: Control Systems I March 15, 2010Document6 pagesTest 2: ENGI 5821: Control Systems I March 15, 2010Abdul Basit ZaideeNo ratings yet
- RME Repeated Part - BDocument11 pagesRME Repeated Part - BsaravananNo ratings yet
- Kuo-Zuo-koon K Out NDocument50 pagesKuo-Zuo-koon K Out NKenshin HimuraNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document11 pagesProject 1Ahmed AbdelhalimNo ratings yet
- Lab TasksDocument53 pagesLab TasksAhmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Control Systems U3 (TEL306)Document84 pagesControl Systems U3 (TEL306)Ruvenderan SuburamaniamNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Isoperametric PDFDocument16 pagesFinite Element Method Isoperametric PDFasd123456789asdcomNo ratings yet
- Exam With SolutionsDocument7 pagesExam With SolutionsCarlos Andres Pinzon LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reactor With Side InjectionsDocument17 pagesTubular Reactor With Side InjectionsMohamad Abou DaherNo ratings yet
- A Matrix Pencil Approach To The Row by Row DecouplDocument22 pagesA Matrix Pencil Approach To The Row by Row DecouplfatihaNo ratings yet
- End Sem 21 22 SpringDocument2 pagesEnd Sem 21 22 Springkshitibhusan bhoiNo ratings yet
- Ijer 2014 205Document4 pagesIjer 2014 205Innovative Research Publications0% (1)
- SISO Feedback LinearizationDocument24 pagesSISO Feedback LinearizationTarek BmrNo ratings yet
- Exam2 Final Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesExam2 Final Differential EquationshellooceanNo ratings yet
- Control Lecture 8 Poles Performance and StabilityDocument20 pagesControl Lecture 8 Poles Performance and StabilitySabine Brosch100% (1)
- MECN5015A - Chapter 5 - Lecture SLidesDocument36 pagesMECN5015A - Chapter 5 - Lecture SLidesGulain MayomboNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Initial Value ProblemsDocument17 pagesNumerical Solution of Initial Value ProblemslambdaStudent_eplNo ratings yet
- Fault Tolerance ExamDocument14 pagesFault Tolerance Examahmadhassan306No ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document19 pagesLecture 7Derrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsNikhil V NainoorNo ratings yet
- Solutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edDocument496 pagesSolutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edRicardo Vega100% (6)
- Lecture 14, 15 StabilityDocument45 pagesLecture 14, 15 StabilityHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- MTH 1112Document11 pagesMTH 1112Nurfarina HusseinNo ratings yet
- Control Systems: Inst Ruct Ions T O Cand Idat EsDocument2 pagesControl Systems: Inst Ruct Ions T O Cand Idat Eseuforia hubNo ratings yet
- Exercise Prod Design PracticingDocument9 pagesExercise Prod Design PracticingLaura AlósNo ratings yet
- Simulation Exercise CS II - 2024Document2 pagesSimulation Exercise CS II - 2024alokb210846eeNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document3 pagesLab 6Vu LeNo ratings yet
- 6.01 Midterm 1 Spring 2011: Name: SectionDocument21 pages6.01 Midterm 1 Spring 2011: Name: Sectionapi-127299018No ratings yet
- Confidential: Final Examination Semester Ii SESSION 2012/2013Document13 pagesConfidential: Final Examination Semester Ii SESSION 2012/2013marwanNo ratings yet
- 2014 MBRC Simulation RT ControlDocument10 pages2014 MBRC Simulation RT ControlMinhaj NaimNo ratings yet
- Mm326 System Dynamics - SolutionDocument10 pagesMm326 System Dynamics - SolutionOğulcan Aytaç50% (2)
- M16 Tier1Document184 pagesM16 Tier1ShahrizatSmailKassimNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument5 pagesCourse OutlineHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemDocument28 pages8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemHana HamidNo ratings yet
- ECOC1Document16 pagesECOC1Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics For Class Presentation: International Islamic University General Studies DepartmentDocument1 pageSelected Topics For Class Presentation: International Islamic University General Studies DepartmentHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Document33 pages8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Fed Batch Reactors 8.3.1 Variable Volume Fermentation (VARVOL and Varvold)Document34 pages8.3 Fed Batch Reactors 8.3.1 Variable Volume Fermentation (VARVOL and Varvold)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics For Class Presentation: International Islamic University General Studies DepartmentDocument1 pageSelected Topics For Class Presentation: International Islamic University General Studies DepartmentHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 10 Alphabetical List of ExamplesDocument1 page10 Alphabetical List of ExamplesHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Part II Dynamic Bioprocess Simulation Examples and The Berkeley Madonna Simulation LanguageDocument33 pagesPart II Dynamic Bioprocess Simulation Examples and The Berkeley Madonna Simulation LanguageHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Document33 pages8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemDocument28 pages8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemDocument28 pages8.4.8 Two Stage Culture With Product Inhibition (Staged) : SystemHana HamidNo ratings yet
- References: References Cited in Part IDocument10 pagesReferences: References Cited in Part IHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Fed Batch Reactors 8.3.1 Variable Volume Fermentation (VARVOL and Varvold)Document34 pages8.3 Fed Batch Reactors 8.3.1 Variable Volume Fermentation (VARVOL and Varvold)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Pages9 53Document45 pagesPages9 53Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Part I Principles of Bioreactor ModellingDocument6 pagesPart I Principles of Bioreactor ModellingHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Mass Transfer in Biological ReactorsDocument27 pages5.1 Mass Transfer in Biological ReactorsHana HamidNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Mass Transfer in Biological ReactorsDocument27 pages5.1 Mass Transfer in Biological ReactorsHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Biological Reaction in Immobilized Biocatalyst SystemsDocument16 pagesDiffusion and Biological Reaction in Immobilized Biocatalyst SystemsHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Pages55 66Document12 pagesPages55 66Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- BTE 4225 Computer Simulation in Biological System: International Islamic University Malaysia Kulliyyah of EngineeringDocument12 pagesBTE 4225 Computer Simulation in Biological System: International Islamic University Malaysia Kulliyyah of EngineeringHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Biological Reaction Engineering: I. J. Dunn, E. Heinzle, J. Ingham, J. E. PfenosilDocument16 pagesBiological Reaction Engineering: I. J. Dunn, E. Heinzle, J. Ingham, J. E. PfenosilHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Report 1 and Assignment 1 - 0611866Document14 pagesReport 1 and Assignment 1 - 0611866Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Simulink IntroDocument44 pagesSimulink IntroHana HamidNo ratings yet
- BTE 4225 Computer Simulation in Biological System: International Islamic University Malaysia Kulliyyah of EngineeringDocument9 pagesBTE 4225 Computer Simulation in Biological System: International Islamic University Malaysia Kulliyyah of EngineeringHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Example of A Proposal - Exam Question3Document4 pagesExample of A Proposal - Exam Question3Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Report 1 and Assignment 1 - 0611866Document14 pagesReport 1 and Assignment 1 - 0611866Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Matlab CmdsDocument7 pagesMatlab CmdsHana HamidNo ratings yet
- Midterm Bte 4225Document3 pagesMidterm Bte 4225Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Digital Sat Math Test 2Document11 pagesDigital Sat Math Test 2nakrit thankanapongNo ratings yet
- 271 - AI Lect Notes PDFDocument128 pages271 - AI Lect Notes PDFkiransangeetaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 PROGRAMMINGDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 PROGRAMMINGGeorges karamNo ratings yet
- Generalized Linear ModelsDocument109 pagesGeneralized Linear ModelsaufernugasNo ratings yet
- TSNotes 2Document28 pagesTSNotes 2YANGYUXINNo ratings yet
- Problem Handouts 1Document1 pageProblem Handouts 1Ron MendozaNo ratings yet
- VTU ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesVTU ThermodynamicsVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.4 AVL Search Trees, B, B Trees, Heap, Heap Sort.Document47 pagesLecture 3.1.4 AVL Search Trees, B, B Trees, Heap, Heap Sort.borab25865No ratings yet
- Linear Programming (LP) : Deterministic Operations ResearchDocument27 pagesLinear Programming (LP) : Deterministic Operations ResearchAbenetNo ratings yet
- Tesis Damian TDocument359 pagesTesis Damian TpalfrancaNo ratings yet
- TextbooksDocument4 pagesTextbooksMaria DoanNo ratings yet
- BCA2021Document78 pagesBCA2021CBSE-Bhavana SureshNo ratings yet
- Basic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10th Edition Washington Solutions ManualDocument39 pagesBasic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10th Edition Washington Solutions Manualpatentlymoietypuhae100% (14)
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicszap_123No ratings yet
- ReMaDDer Software Tutorial (v2.0) - Fuzzy Match Record Linkage and Data DeduplicationDocument59 pagesReMaDDer Software Tutorial (v2.0) - Fuzzy Match Record Linkage and Data DeduplicationmatalabNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Calculation Course 24jan08Document91 pagesNitrogen Calculation Course 24jan08jujuroyale100% (2)
- Seminar 5, 6,7,8Document28 pagesSeminar 5, 6,7,8Євгеній БондаренкоNo ratings yet
- 6300 Course Introduction Lecture NotesDocument26 pages6300 Course Introduction Lecture NotesFatima Al-Doski100% (1)
- Completing The Square (Technique Only) Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCompleting The Square (Technique Only) Cheat SheetebxrvvtmdxfthezwhlNo ratings yet
- 205 Notes 2008Document53 pages205 Notes 2008sam00786No ratings yet
- Class - 10 Maths Pre-Board PaperDocument7 pagesClass - 10 Maths Pre-Board PaperBhavik DhakaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8 Junior - HighschoolDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 8 Junior - HighschoolKarlstein Foñollera DiaoNo ratings yet
- PAA Dynamic ProgrammingDocument14 pagesPAA Dynamic ProgrammingRichmafia21No ratings yet
- 4) XOR Prac 4Document7 pages4) XOR Prac 4Anb BajwaNo ratings yet
- LCA BI - Financial Report UsageDocument13 pagesLCA BI - Financial Report UsageJackNo ratings yet
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument28 pagesStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths SankaraDocument40 pagesMaths SankaraA Vinod KaruvarakundNo ratings yet
- Maths CET SampleDocument6 pagesMaths CET SampleJS ManishNo ratings yet
- Learn Python and IPython Note Book in A Day!Document3 pagesLearn Python and IPython Note Book in A Day!Srinivas LNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 For SPM 2019 2020 - AnswerDocument35 pagesPhysics Paper 3 For SPM 2019 2020 - AnswerAzman SelamatNo ratings yet