Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Basic Components of Employee Compensation and Benefits
Uploaded by
Aneeka MelwaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Basic Components of Employee Compensation and Benefits
Uploaded by
Aneeka MelwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
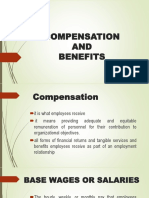
Compensation is comprised of four core elements: Fixed pay Also known as "base pay," fixed pay is nondiscretionary compensation
that does not vary according to performance or results achieved. It usually is determined by the organization's pay philosophy and structure. Short-term incentive pay A form of variable pay, short-term incentive pay is designed to focus and reward performance over a period of one-year or less. Variable pay Also known as "pay at risk," variable pay changes directly with the level of performance or results achieved. It is a one-time payment that must be re-established and re-earned each performance period.
Long-term incentive pay A form of variable pay, long-term incentive pay is designed to focus and reward performance over a period longer than one year. Typical forms include stock options, restricted stock, performance shares, performance units and cash.
Types of Compensation
Base Wages Salary Pay Hourly Pay Piece Rate Pay Premium Pay Shift Differential Pay Weekend/Holiday Pay On-call Pay Call-In Pay Hazard Pay Bi-Lingual Pay Skill-Based Pay
Variable Pay Commissions Team-Based Pay Bonus Programs Incentive Pay - Short-term - Profit Sharing - Individual Performance Based Incentives - Performance-Sharing Incentives - Long-term - Restricted Stock - Performance Shares
Compensation and benefits (abbreviated C&B) is a sub-discipline of human resources, focused on employee compensation and benefits policy-making. It is also known in the UK as total reward and as remuneration in Australia and New Zealand.
The basic components of employee compensation and benefits
Employee compensation and benefits are basically divided into four categories: 1. Guaranteed pay monetary (cash) reward paid by an employer to an employee based on employee/employer relations. The most common form of guaranteed pay is the basic salary. 2. Variable pay monetary (cash) reward paid by an employer to an employee that is contingent on discretion, performance or results achieved. The most common forms are bonuses and sales incentives.
3. Benefits programs an employer uses to supplement employees compensation, such as paid time off, medical insurance, company car, and more. 4. Equity-based compensation a plan using the employers share as compensation. The most common examples are stock options.
Compensation of employees (CE) is a statistical term used in national accounts, balance of payments statistics and sometimes in corporate accounts as well. It refers basically to the total gross (pre-tax) wages paid by employers to employees for work done in an accounting period, such as a quarter or a year. However, in reality, the aggregate includes more than just gross wages, at least in national accounts and balance of payments statistics. The reason is that in these accounts, CE is defined as "the total remuneration, in cash or in kind, payable by an enterprise to an employee in return for work done by the latter during the accounting period". It represents effectively a total labour cost to an employer, paid from the gross revenues or the capital of an enterprise. Compensation of employees is accounted for on an accrual basis; i.e., it is measured by the value of the remuneration in cash or in kind which an employee becomes entitled to receive from an employer in respect of work done, during the relevant accounting period - whether paid in advance, simultaneously, or in arrears of the work itself. This contrasts with other inputs to production, which are to be valued at the point when they are actually used. For statistical purposes, the relationship of employer to employee exists, when there is an agreement, formal or informal, between an enterprise and a person, normally entered into voluntarily by both parties, whereby the person works for the enterprise, in return for remuneration in cash or in kind. The remuneration is normally based on either the time spent at work, or some other objective indicator of the amount of work done.
You might also like
- Compensation AdministrationDocument16 pagesCompensation AdministrationAtul Chanodkar100% (1)
- Compensation & Benefits of Airline IndustryDocument20 pagesCompensation & Benefits of Airline Industryjason_bourne_900No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document7 pagesChapter 9Veronica SangalangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)From EverandUnderstanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Compensation and BenefitsDocument50 pagesCompensation and BenefitsDhearly NaluisNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Compensation ManagementDocument37 pagesProject Report On Compensation Managementgmp_0755% (11)
- Compensation & BenefitDocument29 pagesCompensation & BenefitAaryaAust100% (2)
- Compensation HRMDocument6 pagesCompensation HRMFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF COMPENSATIONDocument6 pagesESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF COMPENSATIONabubakarNo ratings yet
- Income Tax - Chapter 7 Notes PDFDocument6 pagesIncome Tax - Chapter 7 Notes PDFJovelyn Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Bba 404Document46 pagesUnit 3 Bba 404King KingNo ratings yet
- Employee CompensationDocument75 pagesEmployee CompensationGitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Compensation: Compensation Refers To A Reward Paid To An Employee For The Work They Do For AnDocument6 pagesCompensation: Compensation Refers To A Reward Paid To An Employee For The Work They Do For AnbonyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Compensation ManagementDocument38 pagesProject Report On Compensation Managementmohit87% (15)
- Compensation management: Effective systems and employee behaviorDocument52 pagesCompensation management: Effective systems and employee behaviorShalaka MohiteNo ratings yet
- Components of Compensation SystemDocument9 pagesComponents of Compensation SystemShalini MatheswaranNo ratings yet
- Compensation #Hasan - FarDocument5 pagesCompensation #Hasan - FarHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Compensation Is The Results or Rewards That The EmployeesDocument8 pagesCompensation Is The Results or Rewards That The EmployeeskomalNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationDocument43 pagesHuman Resource Management 14 Edition Chapter 9 & 10 CompensationTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Compensation Management: Examples of Financial & Non-Financial CompensationDocument21 pagesUnit 4 Compensation Management: Examples of Financial & Non-Financial CompensationRehan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Compensation ManagementDocument37 pagesProject Report On Compensation ManagementMadhu SunkapakaNo ratings yet
- Projrct Report Compensation BenchmarkingDocument37 pagesProjrct Report Compensation BenchmarkingPoornima GargNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pay SystemDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Pay SystemSubhashNo ratings yet
- Introduction to CompensationDocument105 pagesIntroduction to CompensationgedorjeramNo ratings yet
- BAHR 222 Final SummaryDocument9 pagesBAHR 222 Final SummaryMAILYN BRIGOLENo ratings yet
- COMPENSATIONDocument12 pagesCOMPENSATIONAbinash MNo ratings yet
- Understanding fixed and variable pay components in employee compensationDocument3 pagesUnderstanding fixed and variable pay components in employee compensationSabarish .SNo ratings yet
- Components of CompensationDocument9 pagesComponents of Compensationshruti.shindeNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management Strategies for Attracting and Retaining TalentDocument4 pagesCompensation Management Strategies for Attracting and Retaining TalentVikas JhaNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Compensation and Benefits ExplainedDocument4 pages3 Types of Compensation and Benefits ExplainedLoren Manda100% (1)
- Compensation ManagementDocument5 pagesCompensation ManagementmibshNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Notes:: Monetary Compensation Package of Employees Generally Consists of The FollowingDocument4 pagesSession 1 Notes:: Monetary Compensation Package of Employees Generally Consists of The FollowingShivali MNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Reward ManagementDocument8 pagesCompensation and Reward ManagementVerinderKBhagatNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management: Performance and Reward Management Kmbnhr04Document19 pagesCompensation Management: Performance and Reward Management Kmbnhr04Haris AnsariNo ratings yet
- CM-Module 1Document15 pagesCM-Module 1Prabhat Kumar SwainNo ratings yet
- Salary vs Wages vs Stipend: Key DifferencesDocument3 pagesSalary vs Wages vs Stipend: Key Differencesvraj mishraNo ratings yet
- Appraising and Rewarding PerformanceDocument31 pagesAppraising and Rewarding PerformanceCharles Amiel DionisioNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument4 pagesCompensationalyssa.reazo.gsbmNo ratings yet
- Enteria Joemil HRM Finals Assignment Activity 3Document2 pagesEnteria Joemil HRM Finals Assignment Activity 3JM EnteriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-4 CONTEMPORARY WORLDDocument19 pagesLesson-4 CONTEMPORARY WORLDMicaella JanNo ratings yet
- Compensation Chapter 1Document32 pagesCompensation Chapter 1Dejene DayNo ratings yet
- Pay Systems Currently in VogueDocument96 pagesPay Systems Currently in VoguePoonam KaushalNo ratings yet
- CompensastionDocument11 pagesCompensastionAnkush At Shiv ShaktiNo ratings yet
- Module 9. CompensationDocument8 pagesModule 9. Compensationriyanshi.natani398No ratings yet
- Salay and Om ModuleDocument33 pagesSalay and Om ModuleRabeka NazimNo ratings yet
- CPM Unit - IDocument11 pagesCPM Unit - Imba departmentNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7. Compensation and BenefitsDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 7. Compensation and BenefitsArriana JutajeroNo ratings yet
- Components of a-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesComponents of a-WPS OfficeCentienne June BalboaNo ratings yet
- Compensation & BenefitsDocument11 pagesCompensation & BenefitsStatistical DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management: Meaning of The Word Compensation Is To Compete I.E., To Pay ForDocument102 pagesCompensation Management: Meaning of The Word Compensation Is To Compete I.E., To Pay ForPraveenNo ratings yet
- Employees Benefit ProgramsDocument2 pagesEmployees Benefit ProgramsAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Defined benefit pension plan explainedDocument8 pagesDefined benefit pension plan explainedhenok AbebeNo ratings yet
- Wage and SalaryDocument20 pagesWage and SalaryPrachi AjitNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management NoteDocument57 pagesCompensation Management NoteAishwaryaSantoshNo ratings yet
- CH 17 Compensation ManagementDocument7 pagesCH 17 Compensation ManagementMD. AL HossainNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter Eight Employee CompensationDocument46 pages8 Chapter Eight Employee CompensationEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- bch513 CompensationDocument45 pagesbch513 CompensationDr.Shaifali GargNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Benefits Administration Module-7Document30 pagesCompensation and Benefits Administration Module-7Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefit and Pension SchemesDocument35 pagesEmployee Benefit and Pension SchemesPayal Harshil Shah100% (2)
- Maximizing Your Wealth: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Gross and Net SalaryFrom EverandMaximizing Your Wealth: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Gross and Net SalaryNo ratings yet
- 5 Trends Transforming CompensationDocument8 pages5 Trends Transforming CompensationAneeka MelwaniNo ratings yet
- Compensation TrendsDocument2 pagesCompensation TrendsAneeka Melwani100% (1)
- Chinese Culture Is One of The World's Oldest CulturesDocument9 pagesChinese Culture Is One of The World's Oldest CulturesAneeka MelwaniNo ratings yet
- IHRM And: MulticulturalismDocument18 pagesIHRM And: MulticulturalismAneeka MelwaniNo ratings yet
- ELP Intro To Human ResourceDocument217 pagesELP Intro To Human Resourcejothi subraNo ratings yet
- Compensation and RetentionDocument12 pagesCompensation and RetentionAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Sitxhrm002 0003002652Document11 pagesSitxhrm002 0003002652Jasmeet LotaNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947: Scope and ObjectivesDocument14 pagesThe Industrial Disputes Act, 1947: Scope and ObjectivesPreethi RaviNo ratings yet
- HRM: Collective Bargaining, Negotiation SkillsDocument4 pagesHRM: Collective Bargaining, Negotiation SkillsDeepika DeepuNo ratings yet
- Grievance MachineryDocument19 pagesGrievance MachineryDlos ProNo ratings yet
- Session 9 Salaries and Wages OkDocument30 pagesSession 9 Salaries and Wages OkYamTooth50% (2)
- University of Immaculate Concepcion v. NLRC, January 26, 2011 (Termination Dispute) XXXDocument2 pagesUniversity of Immaculate Concepcion v. NLRC, January 26, 2011 (Termination Dispute) XXXHeart NuqueNo ratings yet
- Qatar World Cup Activities 1Document1 pageQatar World Cup Activities 1Jimena AbdoNo ratings yet
- Fixed Term Employment in India:An Analysis of Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Central (Amendment) Rules, 2018Document4 pagesFixed Term Employment in India:An Analysis of Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Central (Amendment) Rules, 2018Ollivia xNo ratings yet
- Strategic CompensationDocument45 pagesStrategic CompensationAnjum ShakeelaNo ratings yet
- Bona Fide Suspension of OperationsDocument8 pagesBona Fide Suspension of OperationsGab NaparatoNo ratings yet
- Types of UnemploymentDocument5 pagesTypes of UnemploymentsotawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Managing Human ResourceDocument28 pagesChapter 10 Managing Human ResourceMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- 13thmonth Pay QuestionnaireDocument1 page13thmonth Pay QuestionnaireIshNo ratings yet
- Child Labour Project PDFDocument10 pagesChild Labour Project PDFfkkfoxNo ratings yet
- Self Employed Women AssociationDocument7 pagesSelf Employed Women AssociationDibya Jyoti MajhiNo ratings yet
- DLSU ACYCST1 ONLINE LABOR COST EXERCISESDocument3 pagesDLSU ACYCST1 ONLINE LABOR COST EXERCISESCharles TuazonNo ratings yet
- HR Salary Overview SwitzerlandDocument2 pagesHR Salary Overview Switzerlandravig1986No ratings yet
- GSWU-NAFLU-KMU v. NLRC, October 17, 2006Document15 pagesGSWU-NAFLU-KMU v. NLRC, October 17, 2006Felix TumbaliNo ratings yet
- Agha Steel Human Resources 2017 PDFDocument12 pagesAgha Steel Human Resources 2017 PDFDarlene HarrisNo ratings yet
- 1 Updated Personnel Action MovementDocument89 pages1 Updated Personnel Action MovementBilly JardinNo ratings yet
- Actors in Industrial Relations Practice: Unit 1 SectionDocument6 pagesActors in Industrial Relations Practice: Unit 1 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- SMC Corp v Laguesma: Supervisors and Exempt Employees Can UnionizeDocument3 pagesSMC Corp v Laguesma: Supervisors and Exempt Employees Can UnionizeKornessa ParasNo ratings yet
- Work Words British English StudentDocument7 pagesWork Words British English StudentLuminita Mocanu 150No ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Professionals: Mirpur Cantonment, DhakaDocument3 pagesBangladesh University of Professionals: Mirpur Cantonment, DhakaSinhaj NoorNo ratings yet
- Coverage + Sap MK + Sbs MK w37Document136 pagesCoverage + Sap MK + Sbs MK w37Eva LaveniaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University 2017-18Document12 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University 2017-18Shalini SonkarNo ratings yet
- Ilgl MCQ: by Cs Tushar PahadeDocument143 pagesIlgl MCQ: by Cs Tushar PahadeSyed BukhariNo ratings yet
- Assignment and Lecture DistributionDocument6 pagesAssignment and Lecture DistributionNasrul Abu BakarNo ratings yet