Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prospective Memory-Memory of Future Events Such (Remembering To Take Medications) Tends To Decrease As We Age
Uploaded by
esuliman1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prospective Memory-Memory of Future Events Such (Remembering To Take Medications) Tends To Decrease As We Age
Uploaded by
esuliman1Copyright:
Available Formats
Cognition (Memory, Thinking and Language) 7-9% MODELS OF MEMORY Three box/information processing model information is sensed, then
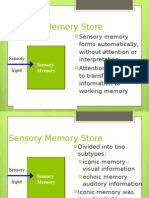
n encoded to STM, then encoded to LTM. Information is retrieved from LTM to the STM (Working memory) Sensory memory Sensory Memory a split second holding tank for incoming sensory information Iconic Memory- split second photograph of a scene. Ex. flashing a series of letters Echoic memory- split second memory of sounds. Ex. Parents ask you to recall what you just said when they think you arent listening. Short-term (working) memory-limited to about 7 items. Chunking- mnemonic device, divide items or numbers into chunks. Mnemonic device- memory aids. Long-term memory (LTM) limitless Explicit Memories with conscious recall a.Episodic memory- specific sequence of events b.Semantic memory memory of facts, meanings, words Implicit Memories without conscious recall c.Procedural memory- remembering how to drive stick shift after not driving stick in awhile
Prospective Memory- memory of future events such (remembering to take medications) tends to decrease as we age.
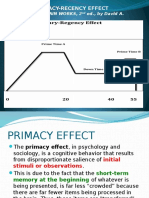
Levels of processing Model - the more deeply processed the more likely to recall it later RETRIEVAL Recall vs. recognition fill in the blank tests vs. multiple-choice tests Priming- (Example- retrieval cues- by giving the class the category of the word to be retrieved.) Primacy effect- tendency to recall the first item of a list. Recency effect- tendency to recall the last item of a list. Serial Position effect- recall is affected by the order of items on a list Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon- trying to remember a persons name (already in LTM) by listing things about their appearance/personality or going through the alphabet. Flashbulb memory- split second memory of an emotionally significant event. Mood-congruent memory- increases the likelihood of recall when you are in the same mood as memory. State-dependent memory- increases the likelihood of recall when you are in the same state of consciousness (example: losing keys while intoxicated will not remember where they are until intoxicated again ). Mnemonics- memory aids such as acronyms and Method of Loci picturing items or words at certain locations in a familiar place. Peg word system one bun, two shoe, three tree..visualize things on a bun when memorizing a list of words Smell- sense that is strongest/most associated with memory, olfactory nerves are connected to the hippocampus Constructive Memory- ability of humans to report false details/recollections of events (not intentionally). Many witnesses recall can be distorted. (misinformation effect) Elizabeth Loftus showed how leading questions can change peoples memories of events by describing car accident as smashed or hit. FORGETTING
Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve At first we forget a lot of information rapidly but the amount remember levels off over time.
Proactive Interference- trying to recall new information (old interferes) Retroactive Interference- trying to recall old information (new interferes) TIP: Focus on what is trying to be recall (retroactive is older) Retrograde amnesia- unable to recall old information Anterograde amnesia- unable to encode new information. MEMORIES AND THE BRAIN Hippocampus is responsible for storing new memories in the brain.
Long Term Potentiation (LTP) neurons can strengthen connections between each other through repeated firing. This is associated with the formation of memories. Language Phonemes- smallest unit of sound language. Ex- sounding out C-A-T. Morpheme- smallest unit of language with meaning (Ex. Pre- is not a word but carries meaning) Syntax- rules of grammar ACQUISITION OF LANGUAGE Babbling Stage- googoogaagaa Telegraphic Speech (about 2 years old) - (EX. - No book, movie). Like a telegraph they are missing several words to the sentence but you understand. Chomsky- born with language acquisition device (nature) children learn some grammar without instruction from parents. A critical period for developing this exists. Overgeneralization (aka overregularization)- misapplication of grammar rules. EX I holded the ball. Chomsky said this was proof that children dont simply model language Skinner- language is learned, modeled (nurture) through reinforcement. Whorfs Linguistic Relativity Hypothesis- language controls/limits our thinking. (EX. The Department of War was changed to the Dept. of Defense and the approval rating of this dept. immediately improved.
Thinking
Metacognition thinking about thinking
Prototype best example of a category (ex. Rose in the category of flower) PROBLEM SOLVING Algorithm- logical step by step rule that guarantees solving a problem (Ex. Searching every aisle in the grocery store ) Heuristic- a rule of thumb strategy used to solve a problem or make a judgement, a mental shortcut. (Ex- anytime you do a search on the internet.) Availability Heuristic- judging the likelihood of a situation based similar situations that are available in the immediate memory. (Ex. Fear of flying after seeing a plane crash in the news.) Representative Heuristic- judging the likelihood of a situation based on stereotypes or prototypes (Ex. Truck drivers who read poetry or Ivy League professors who like poetry.) Belief Bias make illogical conclusions to confirm preexisting beliefs. (EX. I believe blondes are dumb and I hear a blonde make a stupid statement so I say to myself, theres the proof that blondes are dumb Belief Perseverance- tendency not to change our preexisting beliefs even in the face of contradicting evidence. (EX. I tell you that research says blondes are of equal intelligence to brunettes yet you continue to believe blondes are dumber. IMPEDIMENTS TO PROBLEM SOLVING, Ethnocentrism- tendency for people to believe that ones culture is superior to others. Mental Set (rigidity) tendency for people to fall into established thought patterns or ways of solving problems. Using methods that worked in the past. Older people may drive to the library and spend 45 mins. to look up information that could have been googled on the internet) Functional Fixedness- inability to see a new use for an object. (EX- butter knife as screwdriver) Confirmation Bias- tendency for people to seek out information that confirms their beliefs. False Consensus Effect- tendency for people to overestimate the number of people who share their beliefs and values. Framing- the way a problem is presented (EX. Meat that is 80% lean vs. 20% fat) Divergent Thinking- thinking that searches for multiple answers.
You might also like
- Two Storage Mechanisms in Free Recall (Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966)Document10 pagesTwo Storage Mechanisms in Free Recall (Glanzer & Cunitz, 1966)Jenny Vargas SantosNo ratings yet
- PSY 101 Sample Exam QuestionsDocument15 pagesPSY 101 Sample Exam Questionsveledimaraz80% (5)
- Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument48 pagesCognitive Psychology NotesSoman100% (1)
- History of Cognitive PsychologyDocument7 pagesHistory of Cognitive PsychologyRanjan Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Sales InfluenceDocument178 pagesSales InfluenceEnrique Rf50% (4)
- What is Memory? Understanding the Brain's Information Processing and StorageDocument11 pagesWhat is Memory? Understanding the Brain's Information Processing and StorageMadona BadoevNo ratings yet
- Ap PsychDocument41 pagesAp PsychSherelle HiggsNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument3 pagesMemoryMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- PSYC1001 Lecture Memory AGBDocument30 pagesPSYC1001 Lecture Memory AGBOdaine BennettNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Chapter Three Memory and ForgetingDocument65 pagesLearning Outcomes: Chapter Three Memory and ForgetingDiego Abdi NasiibNo ratings yet
- Experimental Psychology: Remembering and ForgettingDocument50 pagesExperimental Psychology: Remembering and ForgettingHanzala BilalNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psych Chap 6 7Document8 pagesCognitive Psych Chap 6 7kjgitalioNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv-Memory and ForgettingDocument20 pagesUnit-Iv-Memory and ForgettingGaurav RajNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology (How Neutrons Worked) : Top Down Processes Use Past Experience/knowledge To Come To ADocument7 pagesBiopsychology (How Neutrons Worked) : Top Down Processes Use Past Experience/knowledge To Come To ABenjamin TanNo ratings yet
- 355 FinalDocument16 pages355 Finalapi-283327301No ratings yet
- Colorful Portfolio XLDocument20 pagesColorful Portfolio XLUmi ZulaihahNo ratings yet
- Information Processing TheoryDocument43 pagesInformation Processing TheoryALISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Why We Remember: The Science of MemoryDocument4 pagesWhy We Remember: The Science of MemoryDiamond BroNo ratings yet
- Memory Processes and ModelsDocument3 pagesMemory Processes and ModelsSophie ZacharekNo ratings yet
- Memoryrvpart 3Document55 pagesMemoryrvpart 3api-296712028No ratings yet
- Memory: Group Name: U - Turn-MDocument57 pagesMemory: Group Name: U - Turn-Mshoaib rasheed100% (1)
- Midterms 1-SENSORY MEMORYDocument42 pagesMidterms 1-SENSORY MEMORYAristoteles MacaraigNo ratings yet
- 2 Edition For AP: Myers' PsychologyDocument19 pages2 Edition For AP: Myers' PsychologyGabrielitoNo ratings yet
- Memory: Definitions, Processes, and TypesDocument24 pagesMemory: Definitions, Processes, and TypesPrerana Das MSCP ClinicalNo ratings yet
- I. The Key QuestionsDocument6 pagesI. The Key Questionsharriet virtudazoNo ratings yet
- The Most Powerful Learning Takes Place in Multiple Memory Lanes.Document3 pagesThe Most Powerful Learning Takes Place in Multiple Memory Lanes.MarviNo ratings yet
- Psychology: Memory IDocument3 pagesPsychology: Memory Iarkangel97No ratings yet
- MODULE 12 - 13 Memory Systems, Cognition, and LanguageDocument12 pagesMODULE 12 - 13 Memory Systems, Cognition, and Languageartadiel28No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourAdvait MadanalNo ratings yet
- 06Document42 pages06Zack ZawaniNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument43 pagesMemoryTanveer KhanNo ratings yet
- Assimilative Memory or, How to Attend and Never ForgetFrom EverandAssimilative Memory or, How to Attend and Never ForgetNo ratings yet
- PY1101 Lecture 4 NotesDocument11 pagesPY1101 Lecture 4 NotesSeah Fu MeiNo ratings yet
- CognitiveDocument44 pagesCognitiveRizwan ImranNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Short Term MemoryDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Short Term Memoryluwahudujos3100% (1)
- What Is The Nature of Memory?Document8 pagesWhat Is The Nature of Memory?Prithvi RajNo ratings yet
- Memory PDFDocument65 pagesMemory PDFArijit GuhaNo ratings yet
- 11 MemoryDocument34 pages11 Memoryyummywords1254100% (1)
- 11 Memorization TechniquesDocument5 pages11 Memorization TechniquesLuciano DutraNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument6 pagesMemoryMohamed EldessoukiNo ratings yet
- 1650chapter 6 Notes2023Document3 pages1650chapter 6 Notes2023Camille Kelley (Dani)No ratings yet
- Cognitive Level of AnalysisDocument46 pagesCognitive Level of AnalysisDavin Do100% (1)
- MODULE 3 CogpsychDocument26 pagesMODULE 3 CogpsychMadyNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit TermsDocument1 pageMemory Unit Termsapi-320166476No ratings yet
- Human Memory: Course Instructress: Mahshameen MunawarDocument24 pagesHuman Memory: Course Instructress: Mahshameen MunawarZarar ANo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Memory and Forgetting: Learning OutcomesDocument34 pagesChapter Four Memory and Forgetting: Learning OutcomesNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- Psychology Chapter 9Document3 pagesPsychology Chapter 9cardenass100% (2)
- Memory Definition of Memory: George SperlingDocument9 pagesMemory Definition of Memory: George SperlingNeha MalikNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument33 pagesMemoryapi-202268486100% (1)
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 pagesExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworNo ratings yet
- Psy 1 Notes CH 7 Memory S23Document13 pagesPsy 1 Notes CH 7 Memory S23travelingchristina123No ratings yet
- Memory Types and Stages ExplainedDocument8 pagesMemory Types and Stages ExplainedShariq Ghouri100% (1)
- Memory Encoding, Storage and RetrievalDocument18 pagesMemory Encoding, Storage and RetrievalHà BeNo ratings yet
- Memory Encoding: Structures ProcessesDocument3 pagesMemory Encoding: Structures ProcessesCrizzy Jhem Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Memory and LearningDocument9 pagesMemory and LearningTrữ LưuNo ratings yet
- Psychology AQA A MemoryDocument19 pagesPsychology AQA A MemorySquigglyBeep100% (2)
- SLA NotesDocument9 pagesSLA NotesArwenNo ratings yet
- Human Memory: Encoding, Storage and RetrievalDocument4 pagesHuman Memory: Encoding, Storage and RetrievalRitu DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Memory Pt. 2Document61 pagesChapter 9 Memory Pt. 2Maricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Memory Essay PlansDocument6 pagesMemory Essay Planswalae rihamNo ratings yet
- Memory: Ayesha Shahid SheikhDocument29 pagesMemory: Ayesha Shahid SheikhAyza HamidNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument4 pagesMemorykomal janNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document19 pagesLecture 11Nael Nasir ChiraghNo ratings yet
- Understanding Memory in Four StepsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Memory in Four StepsGeorgeta TufisNo ratings yet
- Cogniiii Chap 6Document5 pagesCogniiii Chap 6Khayla AcramanNo ratings yet
- Cognitive BiasesDocument19 pagesCognitive Biasesrkdas_sust5091No ratings yet
- ECLUE Journal Vol 3 No. 2 SeptemberDocument154 pagesECLUE Journal Vol 3 No. 2 SeptemberM Gidion MaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MemoryDocument22 pagesChapter 6 - Memorycammcbean100% (1)
- Key People Review Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesKey People Review Cheat SheetAnonymous 3V86sdNo ratings yet
- AP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETDocument6 pagesAP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETNathan HudsonNo ratings yet
- Block-1979 Time and ConsciousnessDocument20 pagesBlock-1979 Time and ConsciousnessLeone2008No ratings yet
- Bjork Seven Study TechniquesDocument78 pagesBjork Seven Study TechniquesFrancesco GentileNo ratings yet
- 06Document42 pages06Zack ZawaniNo ratings yet
- The Little Black Book For Managers by John Cross, Rafael Gomez and Kevin MoneyDocument35 pagesThe Little Black Book For Managers by John Cross, Rafael Gomez and Kevin MoneyCapstone PublishingNo ratings yet
- Primacy Recency Theory1aDocument17 pagesPrimacy Recency Theory1aapi-340631738No ratings yet
- FGHFGHDocument103 pagesFGHFGHWilliam FalguiNo ratings yet
- The Principals of Adult LearningDocument26 pagesThe Principals of Adult Learningapi-312305061No ratings yet
- (Elizabeth F Loftus) Memory, Surprising New InsightsDocument147 pages(Elizabeth F Loftus) Memory, Surprising New Insightsinfantf100% (1)
- CONSUMER MEMORY AND COGNITIVE LEARNINGDocument60 pagesCONSUMER MEMORY AND COGNITIVE LEARNINGSehrish AnsariNo ratings yet
- Master Memory, Reading & Focus in 40 MinutesDocument86 pagesMaster Memory, Reading & Focus in 40 Minutestengkujoy0% (1)
- Writing Persuasive Articles Is A SkillDocument7 pagesWriting Persuasive Articles Is A SkillAini WanNo ratings yet
- Reliability of MemoryDocument5 pagesReliability of MemoryAyse KerimNo ratings yet
- But Not Negative, Emotion Words in Immediate Serial RecallDocument20 pagesBut Not Negative, Emotion Words in Immediate Serial Recallrodney_jr__3No ratings yet
- Memory: A Five-Day Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersDocument64 pagesMemory: A Five-Day Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersBeary7No ratings yet
- Culture and MemoryDocument20 pagesCulture and MemoryHoa NguyenNo ratings yet
- English Corpus Linguistics An Introduction: Charlesf - MeyerDocument23 pagesEnglish Corpus Linguistics An Introduction: Charlesf - MeyerBajro MuricNo ratings yet
- Communication and PersuationDocument27 pagesCommunication and PersuationAkanksha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Recency/Primary Effect Memory ExperimentDocument3 pagesRecency/Primary Effect Memory ExperimentCaner YıldırmNo ratings yet
- Masterfile Let ReviewerDocument644 pagesMasterfile Let ReviewerApril Claire Pineda Manlangit50% (4)
- Learning - IVDocument8 pagesLearning - IVChunauti DuggalNo ratings yet