50% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views9 pagesWind Load Calculation
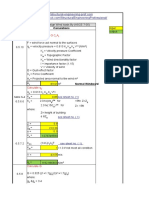
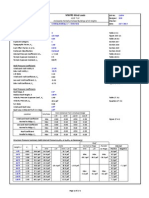
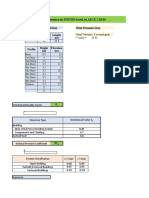
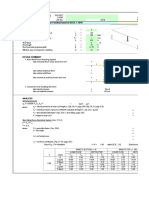
This document provides information and calculations for determining wind pressure (qz) according to the American code ASCE 7-05 Method 2. It lists inputs such as velocity pressure exposure coefficient Kz for exposure category B, topographic factor Kzt, hill shape, directionality factor Kd, basic wind speed, and importance factor I. It then shows the calculated wind pressure qz of 35.41603488 psf.
Uploaded by
Manoj ManoharanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views9 pagesWind Load Calculation
This document provides information and calculations for determining wind pressure (qz) according to the American code ASCE 7-05 Method 2. It lists inputs such as velocity pressure exposure coefficient Kz for exposure category B, topographic factor Kzt, hill shape, directionality factor Kd, basic wind speed, and importance factor I. It then shows the calculated wind pressure qz of 35.41603488 psf.
Uploaded by
Manoj ManoharanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd